Feng Gao, MD
- Professor of Medicine
- Member of the Duke Human Vaccine Institute

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/feng-gao-md
The spleen may be congenitally absent (asplenia) or have the pancreatic tail usually inserts into the splenic hilum many unfused components (polysplenia) virus zapadnog nila purchase zyvox 600mg mastercard. Inflammatory or neoplastic splenic anomalies and are associated with cardiovascular conditions affecting the pancreatic tail can easily invade the anomalies virus map buy zyvox discount, situs inversus virus 2014 adults buy zyvox 600 mg cheap, and other anomalies antibiotic resistance facts generic zyvox 600 mg without prescription, often with splenic parenchyma bacteria water test kit discount zyvox online american express, resulting in intrasplenic pseudocyst zeomic antimicrobial buy zyvox online, for serious and even life-threatening consequences. Conversely, splenic tumors or an accessory spleen may mimic a pancreatic tail mass. The spleen is rarely on a long mesentery and may be found in any abdominal or pelvic location ("wandering spleen"), placing Splenic infarction is a relatively common cause of acute left it at risk for trauma and torsion with infarction. It appears as a sharply defined, often wedge-shaped zone of minimal enhancement abutting the the spleen is the largest lymphatic organ, the size of which splenic capsule. Patients at risk for infarction include those varies among individuals and even in the same person by with sickle cell disease and those with cardiovascular blood volume, state of nutrition and hydration. A ventricular assist devices are especially prone to embolic calculated splenic index (length x width x breadth) over 480 infarction of the spleen. The average length is up to 12 cm, with a width and breadth of 7 and 4 cm, respectively. The white pulp is the lymphoid tissue and the red is Splenosis is the peritoneal implantation of splenic tissue that composed of the vascular tissue and splenic cords (plates of may follow traumatic rupture of the spleen. Because of its vascularity, the red pulp mistaken for polysplenia or peritoneal implants of tumor enhances rapidly, giving the spleen a very heterogeneous (carcinomatosis). This may be mistaken for splenic pathology but is a usually allow accurate diagnosis. This could be mistaken for a primary pancreatic mass, such as a neuroendocrine tumor. The spleen is of variable shape and size, even within the same individual, varying with states of nutrition and hydration. The medial surface is often quite lobulated as it is interposed between the stomach and the kidney. The tail of the pancreas also inserts into the splenic hilum through the splenorenal ligament. The gastrosplenic ligament carries the short gastric and left gastroepiploic vessels to the stomach and upper portion of the spleen. Splenomegaly is a common abnormality and can be caused by congestion, hematologic disorders, inflammatory/infectious conditions, tumors, or infiltrative processes. Note the foci of calcification from histoplasmosis in the main and accessory spleen. A heat-damaged red blood cell scan (not shown) proved this to be an accessory spleen. Masses in the splenic hilum may arise from or involve the tail of the pancreas or spleen. The majority of the small bowel is on one side of the abdomen, in keeping with malrotation. Such large abscesses are unusual in the spleen, especially in the absence of prior splenic infarction. The patient deteriorated rapidly, and multiple tuberculous abscesses were identified at autopsy. This patient had a prior rupture of a hepatic hydatid cyst with diffuse spread throughout the abdomen. Tonolini M et al: Nontraumatic splenic emergencies: cross-sectional imaging pancreatitis findings and triage. Blood cultures identified Staphylococcus and the patient recovered with antibiotics. An echocardiogram showed multiple vegetations in both the aortic and mitral valves, suggesting that this abscess is due to underlying endocarditis. The patient underwent an echocardiogram, which additionally revealed aortic valve vegetations from endocarditis (not shown). The most common causes of massive splenomegaly are cirrhosis/portal hypertension, lymphoma, chronic myelogenous leukemia, extramedullary hematopoiesis, myelofibrosis, and Gaucher disease. In most patients with splenomegaly, there are clues as to the underlying cause on the imaging study, as in this case. Manenti A et al: Splenomegaly Secondary to Myeloproliferative Neoplasms and Portal Hypertension. The patient was later found to have thoracic lymphadenopathy, and biopsy showed the spleen to be a manifestation of sarcoidosis. This normal variant is often more prominent in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. While sickle cell patients can develop a small, calcified autoinfarcted spleen, the spleen may be enlarged in the early stages of the disease. Embolic disease is likely the most common cause of splenic infarcts in older patients. Gaetke-Udager K et al: Multimodality imaging of splenic lesions and the role of non-vascular, image-guided intervention. This mass was found at surgery to represent torsion and infarction of a "wandering" spleen. The spleen in such cases is found in ectopic locations due to laxity or absence of the splenic ligaments. This was found at surgery to represent a massively infarcted spleen with contained rupture, resulting in the fluid collection. Massive acute infarction is often not desired in splenic embolotherapy, as patients can develop infections of infarcted tissue. Splenosis is most commonly seen within the peritoneal cavity, with extraperitoneal splenosis more rare. The patient had a distant history of traumatic splenic injury with diaphragmatic rupture, the most common reason for thoracic splenosis. Note the absence of any enhancing or soft tissue components within this splenic cyst. The patient was symptomatic with pain and early satiety and consequently underwent surgical cyst deroofing. While the typical nodular, centripetal enhancement seen with hepatic hemangiomas is less common in the spleen, splenic hemangiomas often demonstrate avid enhancement. Thipphavong S et al: Nonneoplastic, benign, and malignant splenic diseases: Multiloculated cystic appearance internal echoes cross-sectional imaging findings and rare disease entities. Although they resemble hemangiomas with nodular enhancement, these were found to represent metastatic angiosarcoma. The size of the mass raised concern for malignancy and precipitated splenectomy, where the lesion was found to be sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation. The cystic components within the mass are unusual prior to treatment, as lymphoma usually appears as a solid hypodense mass. Diffuse involvement of spleen (or liver) may be difficult to recognize on imaging, often appearing as nonspecific organomegaly. Melanoma is one of several tumors which can appear cystic, as in this case, and be misinterpreted as a splenic abscess. In most published reports, breast cancer is the most common primary source for splenic metastases. Segmental Anatomy of the Liver Several newer contrast agents have been introduced into the Couinaud system of defining liver segmental anatomy clinical imaging that include a heterogeneous group of divides the liver into 8 segments by vertical planes that extend paramagnetic agents that are taken up in hepatocytes and through the course of the hepatic veins and by a horizontal excreted in bile; these are referred to collectively as plane that extends through the right and left portal veins. This phase, however, is usually not effective in detecting liver with an enlarged caudate and small right lobe indicates focal masses, even those that are hypervascular. Late arterial phase (35-45 sec): this is usually the optimal Hepatic vein occlusion is usually the result of Budd-Chiari phase for depiction of hypervascular hepatic masses, such as syndrome, hypercoagulable state, or tumor encasement. Hepatocellular carcinoma for the same reason, which is focally disordered hepatic. Hepatic pyogenic abscess history of cirrhosis or extrahepatic malignancy, this likely. The falciform ligament plane separates the medial (segment 4) from the lateral (segments 2 and 3) left lobe. This coronal reformation shows both hepatic arteries arising from the proper hepatic artery? Some of the intravenously injected contrast medium is still circulating through the arteries, resulting in enhancement of the aorta. This, along with the presence of a capsule in a young, otherwise healthy woman is essentially diagnostic of hepatic adenoma. While a neoplastic mass could not be excluded by imaging characteristics alone, the appearance is more suggestive of infection. Metastases could have an identical appearance but are rare within a cirrhotic liver. While cholangiocarcinoma could have a similar appearance, the diagnosis of focal confluent fibrosis is much more likely given the clinical and radiographic evidence of alcoholic cirrhosis. The lobular architecture in adjacent parenchyma is well maintained with normal central veins. This patient had biopsy-proven congenital hepatic fibrosis, which results in hepatic failure and accounts for splenomegaly. Vajro P et al: Management of adults with paediatric-onset chronic liver disease: strategic issues for transition care. Venkatanarasimha N et al: Imaging features of ductal plate malformations in Demographics adults. There are innumerable tiny bright cystic lesions in the liver, which are biliary hamartomas. The cysts ranged in size from microscopic to 5 cm in greatest dimension and contained clear fluid. This liver, which weighed 9 kg, was resected due to intractable patient discomfort and pressure on other organs. Benzimra J et al: Hepatic cysts treated with percutaneous ethanol 60%) sclerotherapy: time to extend the indications to haemorrhagic cysts and Women often have larger and more numerous cysts polycystic liver disease. Abu-Wasel B et al: Pathophysiology, epidemiology, classification and treatment options for polycystic liver diseases. Venkatanarasimha N et al: Imaging features of ductal plate malformations in adults. Expert 0 Isolated polycystic liver disease is distinct genetic disease Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. The right kidney was displaced caudally and was hydronephrotic due to compression of the renal pelvis (not shown). Two weeks later, the patient was clinically well and required no further treatment, though a residual liver mass was still present. On needle aspiration, blood-tinged purulent material was found and drained via pigtail catheter. Lymphomatous parenchymal involvement is rarely detected as such small discrete lesions. Larger, less numerous; spleen usually not involved Candida liver abscesses associated with endocarditis. As in this case, most (85%) amebic abscesses are solitary and in the right hepatic lobe. Gunther J et al: Short report: Amebiasis-related mortality among United States residents, 1990-2007. The contents are very heterogeneous and echogenic, with little apparent posterior acoustic enhancement. Most amebic abscesses are single or few in number, while pyogenic abscesses are clustered and multiple. Fungal abscesses are even more numerous and usually appear as innumerable "microabscesses" in the liver &/or spleen. At surgery, the appendix appeared to be thickened and chronically inflamed; an appendectomy was performed. Hydatid disease can affect any abdominal organ, though involvement of retroperitoneal organs is unusual. This woman came from a sheep-raising area of Italy where hydatid disease is endemic. The mass compresses or occludes the inferior vena cava, indicated by an enlarged azygous vein. Note the extraordinarily widened hepatic fissures deeply dividing the segments of the liver along the portal vein branches. This is a characteristic feature of hepatic schistosomiasis; the appearance of the liver has been described as that of a tortoise shell. The predominantly peripheral location and calcification of the fibrotic regions are distinguishing features from viral or alcoholic cirrhosis. Mild hepatocyte swelling and necrosis are often evident, reflecting the resultant hepatocyte injury. Acute hepatitis generally causes more impressive gallbladder wall edema than does acute cholecystitis. There is nothing specific about these findings to indicate the exact etiology of this case of hepatitis. Imaging helps to exclude other causes of acute abdominal pain and liver disfunction, such as biliary obstruction. Patients with these findings plus clinical evidence of hepatic failure are likely to die unless urgent liver transplantation is performed. Lymphadenopathy is seen in at least 2/3 of patients with viral hepatitis and should not be interpreted as a sign of malignancy.
Carcinoma in situ confined within the larger mammary ducts vi) Identification of a transmissible retrovirus in early 20th is called intraductal carcinoma bacteria facts for kids order 600 mg zyvox with amex. Clinically antibiotics kills good bacteria buy zyvox with amex, it produces a to the breast-fed daughter-mice prompted researchers to look palpable mass in 30-75% of cases and presence of nipple for similar agent in human breast cancer (Chapter 8) virus ev-d68 buy zyvox once a day. Approximately a quarter no such agent has yet been identified antimicrobial wound dressing order 600 mg zyvox visa, there are reports of presence of reverse transcriptase in breast cancer cells antibiotic resistance usa today discount zyvox online. Infiltrating (invasive) lobular carcinoma the right and is bilateral in about 4% cases disturbed the infection order 600mg zyvox fast delivery. Colloid (mucinous) carcinoma upper outer quadrant is the site of tumour in half the breast 5. Secretory (juvenile) carcinoma Carcinoma of the breast arises from the ductal epithelium 9. Inflammatory carcinoma in 90% cases while the remaining 10% originate from the 10. Patients of in situ lobular carcinoma treated with intraductal carcinoma is far less than that associated with in excisional biopsy alone develop invasive cancer of the situ lobular carcinoma. Grossly, the tumour may incidence of developing a contralateral breast cancer (30%). Grossly, no visible tumour dilated ducts containing cheesy necrotic material (in is identified. In fact, projections of tumour cells which lack a fibrovascular stalk this is the pattern of cancer for which the terms cancer and so as to distinguish it from intraductal papilloma. Clinically, iv) Cribriform pattern is recognised by neat punched out majority of infiltrating duct carcinomas have a hard fenestrations in the intraductal tumour. Cut surface shows a grey white firm tumour extending irregularly into adjacent breast parenchyma. Microscopic features include formation of solid nests, cords, gland-like structures and intraductal growth pattern of anaplastic tumour cells. There is infiltration of densely collagenised stroma by these cells in a haphazard manner. They are found more frequently in the left breast, ii) Infiltration by these patterns of tumour cells into often in the upper outer quadrant. Grossly, the tumour is Infiltrating (Invasive) Lobular Carcinoma irregular, 1-5 cm in diameter, hard cartilage-like mass that cuts with a grating sound. The sectioned surface of the Invasive lobular carcinoma comprises about 5% of all breast tumour is grey-white to yellowish with chalky streaks and cancers. This peculiar morphologic form differs from other often extends irregularly into the surrounding fat invasive cancers in being more frequently bilateral; and (Fig. Grossly, the appearance different from other special types in lacking a regular and varies from a well-defined scirrhous mass to a poorly uniform pattern throughout the lesion. A variety of defined area of induration that may remain undetected histologic features commonly present are as under by inspection as well as palpation. Characteristic histologic features are: one cell wide files of round regular tumour cells (?Indian file arrangement) infiltrating the stroma and arranged circumferentially around ducts in a target-like pattern. Colloid (Mucinous) Carcinoma 763 Infiltrating cells may be arranged concentrically around this is an uncommon pattern of breast cancer occurring more ducts in a target-like pattern. Colloid ii) Tumour cytology?Individual tumour cells resemble carcinoma has better prognosis than the usual infiltrating cells of in situ lobular carcinoma. Some tumours may show signet-ring cells usually a soft and gelatinous mass with well-demarcated distended with cytoplasmic mucin. Histologically, colloid carcinoma contains large amount Medullary Carcinoma of extracellular epithelial mucin and acini filled with Medullary carcinoma is a variant of ductal carcinoma and mucin. Cuboidal to tall columnar tumour cells, some comprises about 1% of all breast cancers. The tumour has a showing mucus vacuolation, are seen floating in large significantly better prognosis than the usual infiltrating duct lakes of mucin (Fig. It is a rare variety of infiltrating hence the alternative name of encephaloid carcinoma. Tubular carcinoma is an Histologically, medullary carcinoma is characterised by uncommon variant of invasive ductal carcinoma which has 2 distinct features (Fig. The ii) Stroma?The loose connective tissue stroma is scanty tubules are quite even and distributed in dense fibrous stroma. Adenoid cystic or invasive cribriform carcinoma is a unique histologic pattern of breast cancer with excellent prognosis. Histologically, there is stromal invasion by islands of cells having characteristic cribriform (fenestrated) appearance. Cut surface of the breast shows a large grey white soft fleshy tumour replacing almost whole of Figure 25. Rarely, invasive ductal carcinomas may have various types of metaplastic alterations such as squamous metaplasia, cartilagenous and osseous metaplasia, or their combinations. Development of squamous cell carcinoma of the breast parenchyma is exceedingly rare and must be separated from lesions of epidermis or nipple region. The nipple bears a crusted, scaly and eczematoid lesion with a palpable subareolar mass in about half the cases. Most of the patients with palpable mass are found to have infiltrating duct carcinoma, while those with no palpable breast lump are usually subsequently found to have intraductal carcinoma. The tumour cells from the underlying ductal carcinoma is found more frequently in children and has a better have migrated up into the lactiferous ducts and invaded the prognosis. Grossly, the skin of the carcinoma of the breast is a clinical entity and does not nipple and areola is crusted, fissured and ulcerated with constitute a histological type. The term has been used for oozing of serosanguineous fluid from the erosions breast cancers in which there is redness, oedema, tenderness (Fig. B, There are clefts in the epidermal layers containing large tumour cells (arrow). In addition, the underlying breast contains invasive or non-invasive duct carcinoma which shows no obvious direct invasion of the skin of nipple. The breast cancers are subdivided into various histologic grades depending upon Figure 25. It is based on Ki-67) or by flow cytometry have a worse prognosis than 3 features: purely diploid tumours. Later, however, distant spread by lymphatic route to on the number and level of lymph nodes involved by internal mammary lymphatics, mediastinal lymph nodes, metastasis. More the number of regional lymph nodes supraclavicular lymph nodes, pleural lymph nodes and involved, worse is the survival rate. Breast is one iii) Fibroadenoma is a long-term risk factor (after over 20 years) of the most suspected source of inapparent primary for invasive breast cancer, the risk being about twice carcinoma in women presenting with metastatic carcinoma. Following factors act as Based on current knowledge gained by breast cancer determinants: screening programmes in the West employing mammo i) Ductal carcinoma in situ (comedo and non-comedo graphy and stereotactic biopsy, various breast cancer risk subtypes) is diagnosed on the basis of three histologic factors and prognostic factors have been described. These features?nuclear grade, nuclear morphology and necrosis, prognostic factors are divided into following 3 groups: while lobular neoplasia includes full spectrum of changes of 1. Comedo type of in situ carcinoma has higher increased risk than women of the same age. Prognostic and predictive factors A summary combining all these factors is given in for invasive breast cancer have been extensively studied by Table 25. These can be broadly varies localised form of breast cancer without axillary divided into 3 groups: lymph node involvement has a survival rate of 84% while survival rate falls to 56% with nodal metastases. In addition, the skin is concerned with thermoregulation, conservation and excretion of fluid, sensory perception and, of course, has aesthetic role for appearance of the indidivdual. In general, it is composed of 2 layers, the epidermis and the dermis, which are separated by an irregular border. Cone-shaped dermal papillae extend upward into the epidermis forming peg-like rete ridges of the epidermis. The basal cell layer consists of a single layer of keratinocytes that forms by desmosomes. Interspersed in the keratinocytes are the junction between the epidermis and dermis. The nuclei melanocytes, a type of dendritic cells, seen as every tenth cell of these cells are perpendicular to the epidermal basement in the basal layer. These are hyperchromatic and normally contain cytoplasm containing melanin pigment granules that a few mitoses indicating that the superficial epidermal layers determines the appearance of an individual. The other type of ted with each other and with the overlying squamous cells dendritic cells in the basal layer are Langerhans cells which are bone marrow-derived cells of mononuclear-phagocyte system. This layer is composed of several layers of polygonal prickle cells or squamous cells. The layers become flat as they near the surface so that their long axis appears parallel to the skin surface. This layer is present exclusively in palms and soles as a thin homogeneous, eosinophilic, non nucleate zone. Intraepidermal nerve endings are present in the form of and connective tissue components. These are small bundles of the dermis consists of 2 parts?the superficial pars papillaris smooth muscle attached to each hair follicle. When the muscle or papillary dermis, and the deeper pars reticularis or reticular contracts, the hair becomes more erect, the follicle is dragged dermis. The dermis is composed of fibrocollagenic tissue upwards so as to become prominent on the surface of the containing blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves. The specialised nerve endings present at some sites the stratum corneum that develop at specially modified perform specific functions. The nail is composed of Pacinian corpuscles concerned with pressure are present clear horny cells, resembling stratum lucidum but are much in the deep layer of skin. Meissner corpuscles are touch receptors, located in the papillae of skin of palms, soles, tips of fingers and toes. Before describing pathology of common skin diseases, the End-bulbs of Krause are cold receptors found in the external following pathologic terms in common use need to be defined genitalia. These are of 2 types?eccrine and formation of intraepidermal space containing oedema fluid apocrine. They are present all over the skin but are Dyskeratosis: Abnormal development of epidermal cells most numerous on the palms, soles and axillae. They are resulting in rounded cells devoid of their prickles and having coiled tubular glands lying deep in the dermis. Dyskeratosis is a feature of premalignant pass through the epidermis on the surface of the skin as pores and malignant lesions and is rarely seen in benign conditions. Apocrine glands are encountered in progress to vesicle formation in the epidermis. A few common examples of each glands are found everywhere on the skin except on the palms of these groups are described below. They are often found in association with hair but can be seen in a few areas devoid of hair as modified I. Two important forms of ichthyosis are prepuce, and meibomian glands of the eyelids. It Histologically, the characteristic feature is association of has, therefore, an intracutaneous portion present in the hair hyperkeratosis with thin or absent granular layer. The hair follicle consists of epithelial 770 Sex-linked ichthyosis is a sex-(X) linked recessive prone to develop infections, especially of lungs, and disorder. Histologically, the papillary dermis shows numerous Histologically, there is hyperkeratosis with normal or dilated blood vessels. The condition occurs as both autosomal dominant and autosomal A very large number of skin diseases have acute or chronic recessive forms. This is an autosomal the skin from outside or from within the body such as recessive disorder in which sun-exposed skin is more chemicals and drugs, hypersensitivity to various antigens vulnerable to damage. Many idiopathic varieties of skin disorders basal cell carcinoma and melanocarcinoma. In thinning and atrophy of stratum malpighii, chronic general, these conditions are clinically characterised by inflammatory cell infiltrate in the dermis and irregular itching, erythema with oedema, oozing and scaling. Changes However, irrespective of the clinical type of dermatitis, the of skin cancers mentioned above may be present in histopathologic picture is similar. In typical cases, there is extensive spongiosis (intercellular oedema) that may lead to forma papular eruption. The vesicles and bullae as well as the oedematous epidermis are permeated Histologically, the characteristic changes are hyper by acute inflammatory cells. Dyskeratosis congested blood vessels and mononuclear inflammatory results in the formation of corps ronds (present in the cell infiltrate, especially around the small blood vessels. The epidermis shows moderate acanthosis and homogeneous dyskeratotic material) and there is varying degree of parakeratosis in the horny layer with appearance of suprabasal clefts containing acantholytic formation of surface crusts containing degenerated cells. Urticaria pigmentosa may Chronic dermatitis shows hyperkeratosis, parakera occur as congenital form or may appear without any family tosis and acanthosis with elongation of the rete ridges and history in the adolescents. The upper dermis shows perivascular chronic inflammatory infiltrate and fibrosis Histologically, the epidermis is normal except for an (Fig. The most characteristic example of chronic increase in melanin pigmentation in the basal cell layer. Hereditary angioneurotic oedema is an disorder, ataxia appears in infancy, while telangiectasia uncommon variant of urticaria in which there is recurrent appears in childhood. The lesions are located on the oedema not only on the skin but also on the oral, laryngeal conjunctivae, cheeks, ears and neck. The lesions consist of tender red nodules, 1-5 cm in diameter, seen more often on the anterior surface of the lower legs. Erythema nodosum is often found in association with bacterial or fungal infections, drug intake, inflammatory bowel disease and certain malignancies.
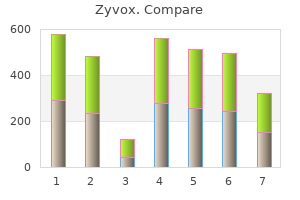
Buy zyvox mastercard. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test- Disc Diffusion Method.
The biceps femoris is isolated by positioning the patient prone with external rotation of the hip and resisted knee flexion treatment for uti breastfeeding generic 600mg zyvox with amex. Hamstring tightness should be differentiated from radicular symptoms caused by the sciatic nerve or lumbar spine infection japanese movie discount zyvox 600 mg amex. However antibiotic resistance mechanisms review cheap zyvox 600mg overnight delivery, when they occur antibiotics on the pill proven zyvox 600 mg, they are usually the result of rapid deceleration from a sprint antibiotics for vre uti order 600 mg zyvox mastercard. The opposite test leg is positioned so that the lower leg hangs off the edge of the table bacteria causing diseases discount 600 mg zyvox with visa. If the test knee rests in less than 90 degrees of flexion, the test is considered positive for tightness of the rectus femoris. A positive result is indicated by the inability to rest the leg flat on the table and an increase in lumbar lordosis when the examiner passively extends the knee by pushing the leg into the table. Information gathered from the Thomas test has not been found to be reflective of dynamic movements of the pelvis during running. The examiner passively flexes the knee and watches for any hip flexion, which indicates a tight rectus femoris. Forceful contraction of the abdominals with the trunk laterally flexed is one mechanism of injury (most common in contact sports). Although trochanteric bursitis occurs most commonly in middle-aged and elderly people, it is also seen in athletes, especially long-distance runners. The first lies between the gluteus maximus and greater trochanter, the second between the gluteus maximus and gluteus medius tendon, and the third between the gluteus medius and greater trochanter. Onset of disease caused by overuse is gradual, and the patient complains of aching over the trochanter and along the lateral thigh. Runners who cross midline have an increased adduction angle, which may increase friction at the greater trochanter. Contact sports such as hockey, football, and soccer may cause bursitis because of direct blows to the lateral hip, which can produce excessive swelling as well as pain. Stretching the gluteus maximus with full hip flexion, adduction, and internal rotation reproduces pain. Resisted testing of abduction, resisted hip extension, and external rotation may be painful. Initial treatment consists of rest, ice, and compression wraps, especially in traumatic cases. Strengthening exercise should correct muscle imbalances across the hip, especially focusing on the gluteals. The patient is positioned in a side-lying position with the tested hip facing upward. The examiner firmly stabilizes the pelvis at the iliac crest to prevent side-bending of the trunk. The iliopectineal bursa lies deep to the iliopsoas tendon anterior to the hip joint. Overuse can occur with sports such as weight lifting, rowing, uphill running, and competitive track and field. Hip joint pathology should be ruled out by checking for a capsular pattern of pain or restriction. Pain occurs at the anterior hip and groin with radiation in an L2 or L3 distribution. The patient may ambulate with a psoatic gait in which the hip is externally rotated, adducted, and flexed during the swing phase. Strength testing of the hip flexors may be painful and external rotation may be weak when tested with the hip flexed. The patient may have a palpable snapping at the anterior hip as the involved hip is passively moved from a flexed position into abduction/ external rotation and then passively returned to neutral. Sanders and Nemeth suggest that ultrasound and interferential current can be beneficial, as is gentle stretching of tightened structures, particularly the iliopsoas. External rotation strengthening has also been proposed, but no studies have verified its efficacy. Hip extension may be reduced in the late stance phase of gait with a shortened stride on the affected side. A positive test shows no increased hip flexion and indicates pathology of the buttock, which may include ischial tuberosity bursitis. Other pathology should be ruled out, including neoplasm, abscess of the buttock, osteomyelitis, fractured sacrum, and septic bursitis. The trunk is flexed forward and toward the side of injury because any side bending or rotation of the trunk is extremely painful. Ice massage is recommended as often as three to four times per day or as pain levels dictate. All exercise should be kept pain free, and pain-relieving modalities such as ultrasound, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, heat, and ice may be used. Radiographs help to rule out iliac crest fracture or displaced epiphyseal fracture in athletes who have not reached skeletal maturity. The patient is unable to flex and extend the knee fully and may not be able to perform an active straight-leg raise or isometric quadriceps contraction. Then weight bearing should progress once the patient has good quadriceps control and 90-degree pain-free range of motion. Ice, pulsed ultrasound, and high-voltage galvanic stimulation help to reduce pain and swelling. Patients should begin with isometric exercise and try to progress to straight-leg raises without a quadriceps lag. As patients progress toward pain-free ambulation, crutch use is discontinued, and strengthening should progress gradually as pain allows. Myositis ossificans may be a complication of quadriceps contusion and involves development of heterotropic bone in nearby muscle. Surgery or paraplegia also can cause myositis ossificans, or it may result from early treatment of a contusion with massage or heat, premature return to aggressive stretching or strengthening, or premature return to sport. About 7 to 10 days after injury, radiographs may show beginning ossification, which can progress to heterotropic bone in 2 to 3 weeks. Initially no strengthening takes place, but once swelling subsides, gentle isometrics can begin. If the defect causes significant loss of function, surgery should be performed 9 to 12 months after injury when a bone scan shows no active calcification. Also known as coxa saltans, snapping hip can be internal, external, or intraarticular. Causesofinternalcoxasaltansincludesnappingoftheiliofemoralligamentsoverthefemoralhead,thesuction phenomenon of the hip joint, and the movement of the iliopsoas tendon over the iliopectineal eminence or lesser trochanter. Intraarticular coxa saltans can be caused by the suction phenomenon of the hip joint, subluxation, a torn acetabular labrum, a loose body, synovial chondromatosis, and osteocartilaginous exostosis. The long head of the biceps tendon snapping over the ischial tuberosity can cause snapping bottom. Evaluation of which structure is causing the snap or click is made through palpation and while the causative movement is reproduced. In general, modalities are not required because the condition is usually pain free. It may occur after operations of the prostate or bladder or result from athletic activity such as soccer, race walking, running, fencing, weight lifting, hockey, swimming, and football. Abdominal and adductor muscle spasm may accompany pain, and gait may be antalgic with movement adapted to reduce pain. Radiographs show loss of definition of bony margins with widening of the symphysis pubis. It can occur in a dysplastic hip from changes in the congruence of the joint and abnormal joint stress. Anatomic variations in the proximal femur, such as a reduction in anteversion or head-neck offset, can lead to labral tears. This test has been found to be able to detect incomplete detaching tears of the posterosuperior portion of the acetabular labrum of dysplastic hips, but it does not correlate well with other arthroscopic findings of dysplastic hips. Acetabular tears are treated by reduced weight bearing using crutches and performing range of motion exercises for 4 weeks. If conservative treatment fails, surgery may be an option using open arthrotomy or arthroscopy. Ofthosewhounderwent openarthrotomyorarthroscopicsurgery,outcomeswereimprovedifsurgerywasperformedbeforedamage occurred to the femoral head (which created unfavorable outcomes for approximately 12% of subjects). Cam impingement is a deformity of the femoral head where an abnormally large radius causes abnormal joint contact, especially with hip flexion combined with adduction and internal rotation. Pincer impingement occurs when the acetabulum covers the femoral head and causes persistent contact of the femoral head into the acetabulum. This test has been found to be specific for pain provocation in patients with intraarticular, nonarthritic hip joint pain. Scour test?compression is applied to the hip through the femur, over a hip range of motion. Log roll test?patient is positioned supine and the leg is passively rolled into internal rotation and external rotation. Clicking may be indicative of a labral tear, and increased external rotation range of motion may indicate iliofemoral ligament laxity. Long axis distraction?clinician applies a longitudinal distraction force on 30 degrees flexion, 30 degrees abduction, and 10 to 15 degrees external rotation. Pain is referred in a sciatic distribution because of the close proximity of the piriformis to the sciatic nerve as the two exit the pelvis. Frieberg test?patient is positioned supine with the thigh resting against the table while the examiner applies passive internal rotation of the hip. Pace test?patient is positioned in a sitting position while the examiner resists hip abduction. A variation of this test is performed in the supine position; with the hip and knee maximally flexed, the examiner moves the hip into full adduction. Lee test?patient is positioned in the supine hook-lying position (hip flexed 60 degrees with the foot flat on the table). Fagerson suggests that massage or spray and stretch can help to reduce pain from trigger points in the muscle. Static stretching may be more beneficial than contract-relax if pain is caused by resisted external rotation of the hip. Crossing the legs should be avoided, and wallets should be removed from back pockets. Shock-attenuating insoles may help patients who spend a lot of time on their feet, especially on hard surfaces. Injection of botulinum toxin A in conjunction with physical therapy has also been found to be of benefit. Common causes include tight-fitting garments, such as a hip-pad girdle or a heavy tool belt, obesity, pregnancy, or direct trauma during contact sports. Injection of corticosteroids or surgical nerve release may be required in severe cases. In hamstring syndrome, the sciatic nerve becomes entrapped by adhesions in the proximal hamstrings, which result from repetitive strain. Reduced internal rotation of the hip and anterior innominate rotation may be causative factors. Pain occurs in the gluteal area, and tenderness can be reproduced with palpation just lateral to the greater sciatic notch. Identification of abnormal hip motion associated with acetabular labral pathology. The iliacus test?: New information for the evaluation of hip extension dysfunction. Nonarthritic hip joint pain: Clinical practice guidelines linked to the international classification of functioning, disability and health from the orthopaedic section of the American Physical Therapy Association. Management of common musculoskeletal disorders: Physical therapy principles and disorders (2nd ed. Use of an inclinometer to measure flexibility of the iliotibial band using the Ober test and the modified Ober test: Differences in magnitude and reliability of measurements. Relation of anterior pelvic tilt during running to clinical and kinematic measures of hip extension. A comparison of 2 rehabilitation programs in the treatment of acute hamstring strains. Relationship between the maximum flexion-internal rotation test and the torn acetabular labrum of a dysplastic hip. Internal coxa saltans (snapping hip) as a result of overtraining: A report of 3 cases in professional athletes with a review of causes and the role of ultrasound in early diagnosis and management. Selected hip and pelvis injuries: Managing hip pointers, stress fractures, and more. Patients with preexisting degenerative joint disease may benefit from total hip arthroplasty, although morbidity and mortality are slightly higher. This noncemented prosthesis is used primarily for bedridden and low-demand patients. The superiority of bipolar prostheses has not been proved, although the dislocation rate is lower than with unipolar prostheses. Performing weight-bearing exercises, maintaining adequate calcium intake, maintaining adequate vitamin D intake, decreasing caffeine consumption, cessation of smoking, eliminating household hazards (eg, throw rugs), treating impaired vision, and hormonal implementation can decrease hip fracture risk. The Gamma nail may offer more stability for fractures with subtrochanteric extension.
Policies and programs driven by multiple sectors present a chance to address disparities in outcomes antibiotics for clearing acne quality 600mg zyvox, and platforms will be integral to making any progress antibiotics for acne infection order generic zyvox line. However antibiotics xanax purchase 600 mg zyvox with mastercard, creating an evidence base for the use terventions bacteria zapper generic 600mg zyvox with visa, and research are necessary steps to im of technology in pediatric obesity care faces the chal prove reimbursement for long-term antibiotics quinolones order zyvox without prescription, sustainable inter lenge of research funding cycles that move at a much ventions infection from bug bite cheap 600 mg zyvox fast delivery. The use of across several medical specialties and public health web-based interventions, mobile apps, and text mes venues. Although the prevalence of obesity overall saging has led to promising results in adult popula has leveled o? Obesity medicine, a rapidly growing among pediatric populations were not achieved [12]. The use of Wi-Fi scales, blood of dietary interventions, behavioral interventions, and pressure cu? Although patient visits may be cov more than 20 percent of patients experience weight ered if comorbid conditions are present, medications regain with recurrence of comorbidities [16,17]. Approximately 50 percent of employers who rent evidence suggests that starting medication at a provide health insurance opt in for anti-obesity medi weight plateau may be more e? Coverage homeostatic control of body weight by hypothalamic has expanded slightly since this publication [22]. In the disease of obesity, there is a disruption of this Bariatric Surgery homeostasis because of impaired neurohormonal sig Bariatric surgery is the most e? In cases of severe obesity, it is critical to think weight loss and maintenance in patients with severe of reasons beyond diet that may have a? Several commonly pre verse events, use is limited to a small fraction of those scribed medicines can contribute to abnormal weight who are eligible for the procedure. Alternatives to these medi currently the most commonly performed bariatric sur cines should be considered and, if possible, changed gical procedure. There are also limited data on safety to those that are weight neutral or to agents that can and e? Comorbid conditions, as evaluated when patients reach plateaus or regain well as functional impairments associated with moder weight after bariatric surgery. In addition, A novel approach to the treatment of severe obesity the weight loss response to standardized intervention, is incorporating the use of technology. Longer-term risks or complications are to be embraced by the bariatric surgical community. Revisions may be performed on patients gery to patients who meet criteria for such surgery re who have lost less than the desirable weight or expe mains as low as 2 percent or less per year in the United rienced undesirable weight regain. More precise data are needed to identify procedure associated with greater weight loss is one the explanation(s) for this low application of bariatric example of such revision. Problematic recurrent hypoglyce candidates as well as low physician reimbursement mia, although rare, may also require reversal. Alcohol rates, as is the case for Medicaid-covered patients, use disorder has been identi? The frequency and etiology of this surgery, although data clarifying these important phenomenon requires further de? The institution or addition increased personalization of this care, it is reasonable of lifestyle intervention as well as pharmacotherapy to to predict that the application of bariatric surgery will patients desiring additional weight loss beyond that increase. Page 6 Published September 10, 2018 Clinical Perspectives on Obesity Treatment: Challenges, Gaps, and Promising Opportunities Children and Adolescents health status of adolescents with severe obesity who One of the signi? In addition to re severe obesity is limited access to appropriate care and porting the baseline prevalence of numerous obesity resources. This is keenly experienced in low-income related comorbid conditions such as dyslipidemia (74. Furthermore, initially favorable short-term ing delivered by primary care providers and dietitians results and complication pro? In a related mass index between the 85th and the 97th percentile, analysis by Inge et al. In addition to providing robust at the time of surgery predict a higher probability of and uniform data, recent studies have also served to resolution of speci? In addition to the need to address related this analysis also served to highlight post-operative professional education, including the ongoing devel nutritional de? Age less than 18 years and cent), dyslipidemia (38 percent versus 86 percent), speci? Collectively, these reports though it is anticipated that these ongoing studies will not only highlight the ongoing challenges faced by the yield additional long-term data and provide important pediatric population with severe obesity, but highlight insights in the future, a number of related opportuni the need for continuous e? In the past, the success the utilization of metabolic and bariatric surgery in the rate in developing safe and e? Newer medications recently prevalence of weight loss operations among adoles introduced or still in development tend to be more se cents has remained relatively low compared with the lective for known weight control targets and hence are a? Although multiple variables are no doubt cess adiposity involve disturbances in energy intake responsible for the relative paucity of adolescent bar and expenditure. There are 11 rare nonsyndromic Page 8 Published September 10, 2018 Clinical Perspectives on Obesity Treatment: Challenges, Gaps, and Promising Opportunities monogenic forms of human obesity for which the un allow for draining stomach contents before gastroin derlying mutations are known. All of these systems have modest is now available for treating one of these inherited e? Combining two peptides with complementary modes of action is an Challenges other area in development [44]. First, the is if similar event reductions are observed in patients concept of obesity as a disease remains controver with obesity but who do not have type 2 diabetes. Peo Combinations of orally ingested medications using cur ple with obesity are often viewed as lacking willpower rently approved drugs are entering late-stage clinical or self-control and as having psychological problems trials [46]. A prevail Medicines and combination drugs that target hedon ing view is that simply eating less and exercising more ic mechanisms are being evaluated for their weight loss will transform the person with obesity into a healthy e? These misconcep in the arcuate nucleus of the brain showed promising tions, which fail to recognize modern concepts in the e? Bias and fat-shaming Novel approaches, including omics platforms, are create an atmosphere in health care that is not condu also advancing target discovery and identifying safety cive to e? Once the motivated person with obesity seeks care, expert facilities may not be available in their commu Devices nity. The that supports access to and coverage of existing and drugs now available lead to weight losses in the range emerging treatment options for severe obesity. However, to maintain drug-induced weight loss fective care include: at present requires a lifelong commitment to therapy. How, as a dren with obesity; and research community, do we establish when traditional 5. Weight loss has been associated with decreasing Overarching Themes cancer risk [54], but speci? Similar to cancer, accessible to everyone, some have risks, and not all understanding the role of bariatric surgery in inducing treatments are appropriate for all patients. Further diabetes remission is yet another presently under more, patients with severe obesity require multidisci developed sub? The integration of personalized plinary teams that may not be accessible to all patients. Page 10 Published September 10, 2018 Clinical Perspectives on Obesity Treatment: Challenges, Gaps, and Promising Opportunities References Armstrong, D. Eat, play, love: Adolescent and parent American Heart Association Task Force on prac perceptions of the components of a multidisci tice guidelines and the Obesity Society. Teens, social media & technology adolescent overweight and obesity: Summary re overview 2015. Laparo regain or inadequate weight loss: A multi-center scopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment study. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases of obesity: A systematic literature review. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and gastric bypass surgery for obesity. Cardiovascular risk factors in severely obese teristics of children 2 to 5 years of age with severe adolescents: the teen longitudinal assessment of obesity. Weight loss and health status 3 interviewing and dietary counseling for obesity in years after bariatric surgery in adolescents. Flod Page 12 Published September 10, 2018 Clinical Perspectives on Obesity Treatment: Challenges, Gaps, and Promising Opportunities mark, J. Lancet Diabetes Endocri mine for weight management in overweight and nol 5(3):174-183. Journal of trol in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized Contextual Behavioral Science 6(4):398-403. Aronne receives Suggested Citation consulting fees from and serves on advisory boards Heyms? Aronne also receives sity treatment: Challenges, gaps, and promising op research funding from Aspire Bariatrics, Eisai, and portunities. Ihuoma Eneli receives research project Author Information support from Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. Weill Professor of Metabolic Research at his Institution from Rhythm pharmaceuticals. Weill Cornell Medical College and directs the Center for Weight Management and Metabolic Clinical Research. They were developed to assist health care professionals in the management and care for patients with overweight and obesity. The content herein is based on medical literature and the clinical experiences of obesity medicine specialists. In areas regarding inconclusive or insufficient scientific evidence, the authors used their professional judgment. The Obesity Algorithm is a working document that represents the state of obesity medicine at the time of publication. Any decision by practitioners to apply these guidelines must be made in light of local resources and individual patient circumstances. Permissions the Obesity Medicine Association owns the copyright to the Obesity Algorithm but invites you to use the slide set. Access to the Obesity Algorithm content and/or permission for extensive quoting or reproducing excerpts and for the reproduction and use of copyrighted text, images, or entire slides will not be granted until the requestor has signed the copyright consent and permission agreement available at This 2016-2017 version of the Obesity Algorithm incorporates worldwide input, as well as interim scientific and clinical trial data. Purpose To provide clinicians with an overview of principles important to the care of patients with increased and/or dysfunctional body fat, based upon scientific evidence, supported by medical literature, and derived from the clinical experiences of members of the Obesity Medicine Association. Intent of Use the Obesity Algorithm is intended to be a living document updated once a year (as needed). It is intended to be an educational tool used to translate the current medical science and the experiences of obesity specialists to better facilitate and improve the clinical care and management of patients with overweight and obesity. This algorithm is not intended to be interpreted as rules and/or directives regarding the medical care of an individual patient. While the hope is many clinicians may find this algorithm helpful, the final decision regarding the optimal care of the patient with overweight and obesity is dependent upon the individual clinical presentation and the judgment of the clinician who is tasked with directing a treatment plan that is in the best interest of the patient. The Obesity Algorithm is listed by the American Board of Obesity Medicine as a suggested resource and study-aid for the obesity medicine certification exam. Obesity Algorithm Obesity as a Disease Data Collection Evaluation and Assessment Management Decisions Motivational Interviewing Nutritional Physical Behavior Pharmaco Bariatric 10 Intervention Activity Therapy therapy Procedures Reference/s: [1] Obesity Defined as a Disease 11 obesitymedicine. Excessive body fat is caused by genetic or developmental errors, infections, hypothalamic injury, adverse reactions to medications, nutritional imbalance, and/or unfavorable environmental factors. Multiple pathogenic adipocyte and/or adipose tissue endocrine and immune dysfunctions contribute to metabolic disease (adiposopathy or sick fat disease). Multiple pathogenic physical forces from excessive body fat cause stress damage to other body tissues (fat mass disease) the adverse health consequences of increased body fat are not simply co-morbidities or associated risk factors 13 Obesity Algorithm. Reference/s: [1] Obesity Terminology People-first language recognizes the potential hazards of referring to or labeling individuals by their disease. Thus, patient who is overweight or has obesity or patient with overweight or obesity are preferred over obese patient. Reference/s: [2,3] Obesity Health Care Office Environment Clinicians and staff should be trained to avoid hurtful comments, jokes, or being otherwise disrespectful, as patients with obesity may be ashamed or embarrassed about their weight. Large adult blood pressure cuffs or thigh cuffs on waiting rooms patients with an upper-arm circumference greater. Tables/chairs/toilet seats should sustain higher patients who weigh more than 400 pounds body weights. Reading materials in the waiting room that focus on healthy habits rather than physical looks or being thin 15 Obesity Algorithm. Obesity as a Multifactorial Disease Genetics/ Epigenetics Environment Neurobehavioral (Social/Culture) Medical Immune Endocrine 17 Obesity Algorithm. Reference/s: [1] Multifactorial Inheritance Factors Contributing to Obesity Mother Father Familial/cultural/ Genetic Epigenetic societal inheritance inheritance inheritance Obesity and its complications 18 Obesity Algorithm. Reference/s: [6] Genetics: Melanocortin 4 Receptor Deficiency Clinical Presentation Genetic Abnormality. Reference/s: [6,7] Genetics: Prader?Willi Syndrome Clinical Presentation Genetic Abnormality. Reference/s: [6] Genetics: Bardet?Biedl Syndrome Clinical Presentation Genetic Abnormality. Reference/s: [6] Obesity: Epigenetic Etiology/Causes Epigenetics: Alterations in gene expression without alteration in the genetic code Pre-pregnancy. Pre-conception paternal or maternal overweight/obesity may influence epigenetic signaling during subsequent pregnancy:?