Todd W. B. Gehr, MD
- Department of Medicine
- Division of Nephrology
- Virginia Commonwealth University
- Richmond, VA
As his team begins planning later for their inception job on Fischer sleep aid without antihistamine purchase 25 mg unisom, Cobb suggests that to be e ective the idea they plant should take a positive rather than negative spin insomnia jet lag buy unisom online pills. The apparent outcome of the act of inception perpetrated on Fischer is quite di erent from the unanticipated consequences of its prior success with Mal insomnia robin williams discount unisom online american express. Where Fischer starts out doubting himself sleep aid in advil pm cheap 25 mg unisom with amex, insecure because he had never felt accepted by his father sleep aid noises unisom 25mg fast delivery, he walks away from the dream with renewed self-con dence and an increased capacity to trust in others insomnia film discount unisom online mastercard. Of course what we see of her in the lm is only what Cobb remembered of her from the end before she took her life, a projection he also realizes in the end is no more than a pale imitation of the fascinatingly complex and lovely woman with whom he lived so long in life and in Limbo. As Ariadne emphasizes, Cobb is himself in danger of slipping from the real world and putting the rest of them in jeopardy, as a result of a combination of suspicion and self-doubt inspired by guilt. In the real world, it behaves like a top, spinning for a time until it eventually topples over. That seems precisely to be what happened to Mal, who subconsciously allowed the top to stop, and then hid it away in a safe, thereby undermining any possible future doubts she might have that the dream was not real. The irony is that to overcome self-deception requires that one place trust in others, as Cobb comes to trust Ariadne, who helps him to see that he needs to work through his guilt over Mal. When Miles pleads with Cobb to return to reality, he means to return to the presence of other people, to allow once again the intimacy of trust that he attempts to protect himself from through his incessant use of the totem. While doubt may protect me against the deceptions perpetrated against me by my senses and by others, it also e ectively excludes me from the presence of those others whose perspectives can o er essential correctives to my own. In the context of that choice, he can spin the top and look away and let it fall as it may. Imagine that the last ten years of your life have actually been a dream and when you wake up tomorrow, you will revert back to your reality from ten years ago. How would you be able to reset your mind to begin living again in this old reality that now seems so far away Cobb ended up in a dream state called Limbo with his wife Mal while the two were investigating the multiple levels of shared dreaming. Although Ariadne may not understand why a person would choose to live in a dream, Mal understands perfectly. Inception also shows us a group of twelve nameless people who choose to live in a dream world instead of the real world. Yusuf, a chemist who creates sedatives that allow the user to have stable dreams for multiple dream levels, hosts a den where this group can come to take this concoction and enter into a shared dream state. Unlike Mal, their respective motives for living in the dream world are unspecified. Inception seems to present both sides of this argument, allowing us to decide for ourselves whether a life in shared dreams would be better than living in reality. Choosing a Real Life over a Dream Life In 1974, American philosopher Robert Nozick considers this question in his book Anarchy, State, and Utopia. All the time you would be oating in a tank, with electrodes attached to your brain. While it would be fun to live in a fantasy world where you could imagine any object and have it appear, play out your favorite movie moments, or perform any dangerous act with relative safety (since you wake up when you die in the dream), Nozick argues that we would choose to live a real life over the simulated dream life. If he plugs into the experience machine, he could nally experience this fantasy life. However, when he eventually wakes from the dream, he will realize that he did not actually accomplish his lifelong goal. There are no distinguishing personality characteristics for any of these individuals. While the characters could imagine their own vision of heaven, they would still be limited by the constraints of the human mind. Additionally, the more the dreamer changes things, the quicker the subconscious projections attack the dreamer. This means that trying to dream of heaven would just result in the dreamer being torn apart by the subconscious. It is this last point of maintaining a connection to reality that seems to in uence Cobb to leave limbo with Mal. I must leave Limbo to actually raise my children, and not merely experience raising them 2. I must return to the real world in order to have a truly deep connection with my children. We could argue that since Cobb has the freedom to create anything he wishes while in Limbo, he could always imagine his children to exist in this world and then raise them. However, these projections would be inauthentic simulations instead of the genuine articles. Cobb would only be able to view them as toddlers since his consciousness would only know them as such. All of his advice would be sound and useful because his subconscious drive to be a good father would allow it to be so. Just as Nozick would argue, Cobb would only be able to accomplish this task in the real world and would rightly choose reality over the experience. Making the Dream Real While Cobb rejects the ersatz nature of Limbo, Mal is enticed by it and even begins to view it as her reality. Given that she and Cobb have the same knowledge that they are in a dream world, why would she consciously choose to live in this arti cial experience What could possibly be so important to Mal that would lead her to this conclusion Mal only asks about her children once, in the dream within a dream that opens the movie. Edited by Foxit Reader Our subjective senses are able to conceive a design of the world that surrounds us through signi ed ideas.
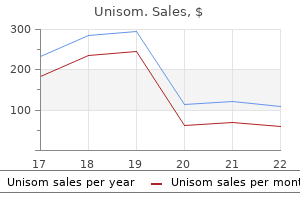
Most patients show no clinical signs insomnia iphone buy generic unisom 25 mg on line, which classically are calf pain insomnia order online purchase unisom with paypal, swelling sleep aid exclusively at walgreens generic 25mg unisom, warmth insomnia 78052 generic unisom 25 mg amex, redness and pyrexia sleep aid 25 mg unisom 25mg discount. B Abdominal operations do not routinely require a nasogastric tube unless the operation has been on the oesophagus or stomach sleep aid zzz buy unisom 25 mg with mastercard. If acute dilatation of the stomach is suspected, a nasogastric tube is inserted to keep the stomach decompressed and prevent aspiration pneumonia. Hence the initial treatment should be a fluid challenge of 250 mL of fluid infused in 1 h. If the patient does not improve, bedside flexible bronchoscopic aspiration by an anaesthetist will be necessary. Following laparoscopic closure, peritoneal lavage might not have been very thorough. Here the patient has come through the immediate postoperative period and has developed late sepsis. Urine and blood are sent for culture, an ultrasound is done to make sure that the patient is emptying his bladder satisfactorily and he is put on an appropriate antibiotic, which might need to be changed after the culture reports are available. This occurs particularly when large resections are undertaken over a prolonged operating time. The patient has hypertension, is confused, restless, has visual disturbances and, in extreme cases, seizures and collapse. He is known to suffer from chronic pancreatitis, the commonest cause of which is alcohol abuse. Advice from the physician should be sought with regard to the best form of treatment. His hyperdynamic circulation (bounding pulse, raised pulse pressure) denotes septic shock. Diminution of chest wall movements, dullness on percussion and lack of air entry are the clinical signs. Postoperative renal failure 1D this patient, who has only one kidney on the right side, has had a right hemicolectomy. The 50 mL of urine passed would have been the urine produced before the right ureter was tied off. Once this mishap is proven, the patient needs urgent exploration by a urologist who would consider some sort of ureteric repair or reimplantation (see Skinner R, Watson D. In multiple trauma, rhabdomyolysis occurs, releasing myoglobin from damaged muscle. In addition, gentamicin levels are measured to ensure there is no drug toxicity and advice is sought from the microbiologist. Liver failure causes systemic vasodilatation, resulting in the secretion of vasoconstrictors, catecholamines and angiotensin-producing intrarenal vasoconstriction. This causes a decrease in the production of intrarenal prostaglandins (which is normally responsible for intrarenal vasodilatation), resulting in poor renal perfusion and causing renal failure. In trauma, which of the following momentarily and is not apparent during statements are true A It is the third most common cause of E A permanent cavity gives an idea of the death overall. B It is the leading cause of death and Blunt injury disability below 40 years of age. Which of the following statements to the potential of non-accidental injury regarding blunt injury are false E the pressure of time shapes trauma C Overt injury should lead the clinician to management. D Proper exposure is essential so as not to Assessment of trauma miss other injuries. A the mechanism of injury and the Covert injury injury produced are the keystones in 5. C Penetrating injuries usually involve the D Positively exclude a critical diagnosis. E Screen patients where clinical signs are D Blunt injuries are the outcome of obvious. C There are likely to be injuries of differing A Low-velocity bullet wounds behave like ages or duration. D There is likely to be aggressive behaviour B High-velocity bullets cause cavitation. C A permanent cavity is one that remains E In multiple fractures, osteogenesis after the initial impact. For example, an obstructed airway, tension pneumothorax, an extradural haematoma or an ischaemic limb can be dealt with by various grades of urgency. E In civilian practice the two commonest groups of mechanisms of injury are blunt and penetrating. Knife injuries over a limb are not always easy to evaluate because penetration of a neighbouring joint may not always be obvious. A, B, C, D High-velocity bullet injury crushes the tissues in its pathway and produces a cavity. Two types of cavity can be produced: a permanent cavity that remains after the initial impact and a temporary cavity that is not apparent and can extend well beyond the site of injury. Therefore, in blunt trauma to the lower chest, liver and splenic injuries are common. In direct blunt trauma, the injury is concentrated at the site of impact and the effects on the soft tissues are at the injured site. For example in fracture of the shaft of the ulna caused by indirect trauma from fall on an outstretched hand (overt injury), there may be a covert injury of a dislocated upper end of head of radius (Monteggia fracture dislocation). A, B, C, D Ideally screening of at-risk patients should be carried out before clinical signs are obvious. This can be done by the deductive approach, such as looking for a flexion spinal injury and damage to the pancreas and duodenum in a child with a lap seatbelt in the back seat of a car involved in a head-on collision. Another example is to look for a posterior cruciate ligament tear and/or posterior dislocation of hip in a dashboard injury. E the carers of an allegedly abused child would usually cite brittle-bone disease (osteogenesis imperfecta) as the cause of multiple fractures. This should not be accepted as the cause and the clinician should admit the patient for further, thorough evaluation and care as a team. This may be due to exposure, inactivity, hypovolaemia and loss of vasomotor control. The patient has compensatory mechanisms to blood loss to maintain perfusion of vital organs; hypotension in itself is therefore not a problem. In most cases, early management is usually protocol-driven, which allows for easier and quicker decision-making. Moreover, their use protects the patient and the doctor, the latter from litigation. Whilst protocols denote good practice, the team leader may not always decide to adhere slavishly to a protocol in the best interest of the patient. For example, in a bullet injury of the popliteal fossa, deliberations between the vascular and orthopaedic surgeons will tailor the need of that particular individual patient. D Airway management should be A Trauma is the second commonest cause accompanied by cervical spine control. A 25-year-old motorcyclist comes in leads to a 20 per cent rise in case fatality on a spine board with cervical spine risk. He was found at the roadside E Ejection from the vehicle at the time of unconscious following a collision with accident saves a significant number of an oncoming car. His pulse is 110/min and his blood G the Advanced Trauma Life Support pressure is 90/60. He is not H the secondary survey is designed responding to verbal command but to ensure that no new injuries have is muttering incoherently. After the first bolus of fluid, the blood Put the following actions into order of pressure rises to 100/70 mmHg (from priority: 90/0) and the pulse falls to 105/min (from A the child should be moved to the 110). A second bolus produces a further ward and put on hourly neurological improvement, as does a third. No pulses can be felt F the child should be taken straight to the in the foot and there is no capillary refill. A child of 3 years is brought into the B Wait until the blood results are back A&E department having fallen from a and then discuss the situation with the first floor balcony. He is unconscious anaesthetist planning to optimise her for and breathing rapidly (60/min) but surgery on the morning list. Within that group, road traffic accidents are the commonest cause of death with falls running second. As the energy involved in an accident is proportional to the square of the velocity, an increase in speed of as little as 10 per cent leads to a 40 per cent increase in mortality. However, they also cause injuries (a far fewer number), characteristically in the abdomen and thorax. The secondary survey is aimed at checking all other parts of the body and systems once the primary survey has identified immediate life-threatening problems. A, B, C, D When the patient first enters the resuscitation room it is important that the handover is taken from the ambulance (rescue) crew who can give vital information on the energy involved in the accident, the time since the accident occurred and the likely major injuries, all crucial pieces of information. In order to speak coherently, a patient must have a clear airway, be able to breathe and have adequate perfusion of the brain. The cervical spine needs protecting as soon as resuscitation starts, and so control should be started at the same time as the airway is checked. All trauma patients (without fail) should receive 100 per cent oxygen at high rate (15 L/min) via a rebreathing mask. The signs of a tension pneumothorax can be difficult to see and hear in the resuscitation room, but the diagnosis should never be made by X-ray as the condition can progress so quickly that the patient may be dead before the picture is available. The next priority is breathing, so the first action here is to give 100 per cent oxygen. The patient clearly has a sucking wound so a flap valve dressing should be put over this as soon as possible, as this will improve his ventilatory effort. A chest drain will be needed but this is not the next priority, as you have dealt with the critical respiratory crisis. Blood should be sent for cross-match but there is no place for giving blood yet until we see how his pulse and blood pressure respond to the initial fluids. Blood gases will be needed as soon as possible, and then, once the hypovolaemic shock has been stabilised, a chest drain will be needed. His conscious state is also improving, suggesting that he is perfusing oxygenated blood. He needs the standard set of X-rays (cervical spine, chest and pelvis) and these should be performed before the urinary catheter is put in, just in case there is a pelvic fracture which has torn the urethra. The left leg has got some sort of vascular damage so the next priority is defining the level and extent of that damage with an arteriogram. The left tibia is an open fracture and so needs cleaning in theatre once the arteriogram has been performed. B > D > E > F > C > A Children have a higher respiratory rate than adults but this respiratory rate is higher than it should be. In young children the only sign of hypovolaemic shock may be an increase in respiration rate as fall in blood pressure and rise in pulse are very late changes in children (when blood loss exceeds 30 per cent). In the absence of any abnormal findings in the chest, it must be assumed that this child is developing severe hypovolaemic shock. Blood should also be sent immediately for cross-match as it may be needed imminently. This is likely to be a laparotomy as this child is showing the cardinal signs (in this age group) of hypovolaemic shock. B Patients with a fractured neck of femur should be operated on as soon as possible, firstly to relieve their pain and secondly to keep their stay in hospital as short as possible so that they can maintain independence. This planning needs to start immediately, but surgery should only be undertaken when it is complete. It is unlikely that the work-up will be completed before 10pm when all surgery should cease apart from that involving life and limb.
But over time they also develop movement and other distinctive symptoms that suggest dementia with Lewy bodies insomnia 26 weeks pregnant discount generic unisom canada. For example sleep aid for toddlers 25 mg unisom visa, they know that an accumulation of Lewy bodies is associated with a loss of certain neurons in the brain that produce two important neurotransmitters sleep aid and alcohol 25mg unisom otc, chemicals that act as messengers between brain cells sleep aid quetiapine unisom 25mg mastercard. The other sleep aid games purchase unisom in india, dopamine sleep aid vs melatonin cheap unisom 25mg amex, plays an important role in behavior, cognition, movement, motivation, sleep, and mood. A small percentage of families with dementia with Lewy bodies has a genetic association, but in most cases, the cause is unknown. Troughout the course of the disease, any sudden, major change in functional ability or behavior should be reported to a doctor. The most common symptoms include changes in cognition, movement, sleep, and behavior. Dementia can also include changes in mood and behavior, poor judgment, loss of initiative, confusion about time and place, and difculty with language and numbers. However, if they are frightening or dangerous (for example, if the person attempts to fght a perceived intruder), then a doctor may prescribe medication. At frst, signs of movement problems, such as a change in handwriting, may be very mild and thus overlooked. A sleep specialist can play an important role on a treatment team, helping to diagnose and treat sleep disorders. A person may ask the same questions over and over or be angry or fearful when a loved one is not present. For example, a person may think his or her spouse is having an afair or that relatives long dead are still living. If cognitive symptoms appear within a year of movement problems, the diagnosis is dementia with Lewy bodies. It is executive secretary, important to allow time to adjust to began having trouble managing the the news. Talking about a diagnosis accounting, paper can help shift the focus toward work, and other developing a treatment plan. Visiting a disease A few months later, Janet developed a tremor in her right hand family doctor is often the frst step She was referred to a neurologist, who for people who are experiencing fnally diagnosed Lewy body dementia changes in thinking, movement, or behavior. Geriatric psychiatrists, neuropsychologists, and geriatricians may also be skilled in diagnosing the condition. If a specialist cannot be found in your community, ask the neurology department of the nearest medical school for a referral. A hospital afliated with a medical 14 school may also have a dementia or movement disorders clinic that provides expert evaluation. Tese 15 methods may help diagnose certain features of the disorder, such as dopamine defciencies. Other Helpful Information It is important for the patient and a close family member or friend to tell the doctor about any symptoms involving thinking, movement, sleep, behavior, or mood. Also, discuss other health problems and provide a list of all current medications, including prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and supplements. A comprehensive treatment plan may involve medications, physical and other types of therapy, and counseling. Changes to make the home safer, equipment to make everyday tasks easier, and social support are also very important. If such a specialist cannot be found, a general neurologist should be part of the care team. Sharing experiences and tips with others in the same situation can help people identify practical solutions to day-to-day challenges and get emotional and social support. It is important to work with a knowledgeable health professional because certain medications can make some symptoms worse. Tese drugs, called cholinesterase inhibitors, act on a chemical in the brain that is important for memory and thinking. However, it cannot stop or and many falls prompted physical and occupational therapy, where he reverse the progress of the disease. Because of this risk, which also helped physicians may recommend not treating mild movement symptoms with medication. If prescribed, carbidopa-levodopa usually begins at a low dose and is increased gradually. Clonazepam Lee and his wife get more rest (Klonopin), a drug used to control seizures and relieve panic attacks, is often efective for the disorder at very low dosages. However, it can have side efects such as dizziness, unsteadiness, and problems with thinking. Melatonin, a naturally occurring hormone used to treat insomnia, may also ofer some beneft when taken alone or with clonazepam. If it is severe, a sleep specialist may prescribe a stimulant to help the person stay awake during the day. If trouble sleeping at night (insomnia) persists, a physician may recommend a prescription medication to promote sleep. Increasing daytime exercise or activities and avoiding lengthy or frequent naps can promote better sleep. Some over-the-counter medications can also afect sleep, so review all medications and supplements with a physician. They may also be a result of pain, illness, stress or anxiety, and the inability to express frustration, fear, or feeling overwhelmed. Caregivers must try to be patient and use a variety of strategies to handle such challenging behaviors. Injuries, fever, urinary tract or pulmonary infections, pressure ulcers (bed sores), and constipation can cause behavioral problems to suddenly grow worse. Large crowds or overly stimulating environments can increase confusion and anxiety. Caregivers can help by responding to the fears expressed instead of arguing or responding factually to comments that may not be true. Tese medications may have side efects, such as nausea, and are not always efective. Cholinesterase inhibitors do not afect behavior immediately, so they should be considered part of a long-term strategy. But these types of medications must be used with caution because they can cause severe side efects and can worsen movement symptoms. If antipsychotics are prescribed, it is very important to use the newer kind, called atypical antipsychotics. Tese medications should be used at the lowest dose possible and for the shortest time possible to control symptoms. Tese side efects include increased confusion, worsened parkinsonism, extreme sleepiness, and low blood pressure that can result in fainting (orthostatic hypotension). Caregivers should contact the doctor if these side efects continue after a few days. Some antipsychotics, including olanzapine (Zyprexa) and risperidone (Risperdal), should be avoided, if possible, because they are more likely than others to cause serious side efects. In rare cases, a potentially deadly condition called neuroleptic malignant syndrome can occur. Symptoms of this condition include high fever, muscle rigidity, and muscle tissue breakdown that can lead to kidney failure. Doctors, patients, and family members must weigh the risks of antipsychotic use against the risks of physical harm and distress that may occur as a result of untreated behavioral symptoms. Simple measures such as leg elevation, elastic stockings, and, when recommended by a doctor, increasing salt and fuid intake can help. Urinary incontinence (inability to control urinary movements) should be treated cautiously because certain medications may worsen cognition. Constipation can usually be treated by exercise and changes in diet, though laxatives and stool softeners may be necessary. Depending on the procedure, possible alternatives to general anesthesia include a spinal or regional block. Be sure to list prescription and over-the-counter medicines, as well as vitamins and supplements. Getting support from family, friends, and professionals is critical to ensuring the best possible quality of life. Take time to focus on your strengths, enjoy each day, and make the most of your time with family and friends. Getting Help Your family and close friends are likely aware of changes in your thinking, movement, or behavior. For example, you could say that you have been diagnosed with a brain disorder called Lewy body dementia, which can afect thinking, movement, and behavior. You will gradually need more assistance from family members, friends, and perhaps professional caregivers. Although you may be reluctant to get help, try to let others partner with you so you can manage responsibilities together. Tink about home modifcations that may be needed, such as installing grab bars in the bathroom or modifying stairs with ramps. Ask your doctor to refer you to a home health agency for a home safety evaluation. Despite the many challenges and adjustments, you can have moments of humor, tenderness, and gratitude with the people closest to you. For example, listening to music, exercising, or going out for a meal allows you to enjoy time with family and friends. Many sources of help are available, from adult day centers and respite care to online and in-person support groups. A peaceful routine Susan realized that Below are some important her mother, Estelle, actions you can take to adjust could not manage to your new roles, be realistic a lot of stimulation about your situation, and care Estelle easily became agitated and confused, for yourself. Infections, pain, or other medical conditions often cause increased confusion or behavioral problems. You must recognize your strengths and limitations, especially in light of your past relationship with the person. Roles may change between a husband and wife or between a parent and adult children. Adjusting expectations can allow you to approach your new roles realistically and to seek help as needed. Some people want to learn everything possible and be prepared for every scenario, while others manage best by taking one day at a time. On the other hand, you may want to make each day count in personal ways and focus on creating enjoyable and meaningful moments.
These rules are in principle similar to those acting at the global level except that they act locally sleep aid trip purchase 25 mg unisom fast delivery, involving small modulations in tempo (accelerando sleep aid under tongue order unisom 25 mg line, ritardando) sleep aid for dementia patients order unisom 25 mg with amex, pitch (ascent insomnia 2015 line up cheap unisom 25mg line, descent) sleep aid jean coutu purchase unisom 25 mg overnight delivery, volume (crescendo sleep aid non prescription purchase genuine unisom line, diminuendo, sforzando), and length (ritenuto) at the level of the individual element or group of elements. As with global sentic mod ulation, local modulation occurs along a continuous intensity gradient, and this gradient effect is certainly one of the most important charac teristics of speech intonation and musical phrasing. This level of phras ing is one feature that distinguishes one speaker from another or one musician from another. The second local phrasing mechanism involves use of accent or stress as prominence devices to convey emphasis or focus in either speech or musical phrases. A phrase usually has a single point of emphasis, thus making prominence a categorical signal acting at the local level. There are several ways of effecting prominence: a rise in pitch, an increase in amplitude, an increase in duration, or some combination thereof. Local sentic modulation (prosody) and prominence interact in such a way that the part of the phrase that precedes the accent often demonstrates a continuous build-up, whereas the part that follows it shows a continuous fall-off. In both music and speech, prosody is used in the service of prominence by allowing phrases to be elaborated in a smooth rising-and-falling fashion, rather than in a punctuated manner. These four phrasing mechanisms affect the ability of speakers and musicians to convey emphasis, emotional state, and emotional meaning. Summary To summarize this section, I propose an evolutionary progression from a simple system involving a repertoire of unitary lexical-tonal elements (rst musilanguage stage) to a less simple system based on combinator ial arrangements of these lexical-tonal (and rhythmic) elements (second musilanguage stage). The latter obtains its meaning not just from the jux taposition of the unitary lexical elements but from the use of global phrase-level melodies. It is at the same time a phrasing system based on local and global forms of sentic modulation as well as on prominence effects. One offshoot of this analysis is that phrase melody has three important but distinct sources (gure 16. An important evolutionary point is that combinatorial syntax is seen to precede modality-speci c grammars. This system is, to a rst approximation, a reasonable precursor for the evolution of both music and language out of which both could have emerged while retaining the many important properties they share. Before closing this section, it would be useful to return to the ques tion of generativity and hierarchical organization. I stated at the begin ning of the chapter that generativity is an analogous feature of language and music, not a shared ancestral feature. At the same time, it is not dif cult to imagine hierarchical organization evolv ing out of the musilanguage precursor stage, thereafter becoming exploited by modality-speci c systems. All that is necessary is for some type of either grouping or segregation of elements (or both) to occur to differentiate different elements within the phrase. This could occur at the level of pitch (auditory streaming effects), rhythm (pulse relationships), amplitude (prominence effects), and so on. The point is that the musi language device, based on discreteness, combinatoriality, and intonation, provides all the necessary ingredients for hierarchical organization in what will eventually become two very different grammatical systems. So the actual forms of hierarchical organization in music and language are best thought of as resulting from parallelism rather than from common origins, again with the note that the shared ancestral features of the musi language stage provide fertile ground for evolution of hierarchical organization once the divergence process starts to take off. Acoustically, prominence can be effected by a diversity of mechanisms, including pitch, length, and strength. Precursors Given this analysis of the musilanguage stage as a joint precursor of music and language, two major questions remain: what are the origins of the musilanguage stage Regarding the rst question, one hint comes from a very interesting and well-described class of primate vocalizations, which I call referential emotive vocalizations. The best-described referential emotive system is the alarm call system of the East African vervet monkey, which has a repertoire of at least three acoustically distinguishable calls (Struhsaker 1967). In fact primates and birds have a large number of such functionally referential calling systems that have a similar level of semanticity to that of vervet alarm calls (see table 3. Acoustically, vervet calls are short grunts that are speci c for the predator eliciting the alarm. That vervet monkeys know the meaning of the calls is shown by audioplayback experiments in which the animals engage in appropriate escape behaviors to the different calls, running up into trees on hearing the leopard call, and looking to the sky or running into bushes on hearing the eagle call (Seyfarth, Cheney, and Marler 1980a, b). It is not important that this be an alarm call system per se, but merely a system with its characteristic dual acoustic nature and broad semantic meaning. Although such a system has not been described, the vervet alarm call system holds out as an important model for how it might operate, providing clues as to how the musilanguage stage may have evolved. Divergence the second question was, by what process did the divergence from the musilanguage stage occur to make music and language distinct though related functions This question relates most directly to the origins of language and music as they occur in their current forms. My goal is not to rehash the extensive series of functional theories that have been proposed to account for the origins of human language (reviewed in Wind et al. As stated, music and language sit at opposite ends of a spectrum, with each one emphasizing a particular type of interpretation of communicative sound patterns. The two evolved as reciprocal elaborations of a dual-natured referential emotive system, again suggesting that they differ more in emphasis than in kind. In thinking about the divergence process, it is useful once again to return to the distinction among shared ancestral, analogous, and distinct features of music and language. By de nition, the rst type of feature appeared before the divergence process and the second two after it. Diver gence can therefore be characterized as the process by which the analo gous and distinct features of music and language evolved. Analogous features most likely represent specializations emerging out of the shared ancestral features of the musilanguage stage. Instead they represent modality-speci c (and human-speci c) novelties of these two functions. Because it makes reference to personal experience, this syntax system can be the basis for determinations of truth and falsity. Structurally, it involves not only simple hierarchical organization but recursiveness as well. Looking to music, divergence from the musilanguage stage leads ini tially to the formation of its acoustic mode. The acoustic range and pitch repertoire become greatly expanded over anything seen in the musilan guage precursor or in spoken language, extending to more than eight octaves, each octave being divisible into at least a dozen differentiable pitches. At the level of grammar, music acquires a complex and hierar chical syntax system based on pitch patterning and multipart blending, leading to the creation of diverse motivic types, many forms of polyphony, and complex timbral blends. In addition to this pitch blend ing property, we see the emergence of many categorical formulas for expressing particular emotional states, leading to the various forms of sound emotion that are used in creating coherent and emotively mean ingful musical phrases. Finally, at the rhythmic level, music acquires the distinct feature of isometric time keeping, so much a hallmark in Western culture. This metric-pulse function is based on a human-speci c capacity to both keep time and to entrain oneself rhythmically to an external beat. This permits rhythmical hierarchies in both the horizontal and vertical dimensions of musical structure, including such things as heterometers and polyrhythms. Evolutionary divergence results in signi cant differences between music and language at the highest levels. The last thing to explain is how these two systems came together to create yet newer functions. For this, it is important to distinguish between the shared properties and interac tive functions. Shared properties of music and language are posited by the musilanguage model to be either shared ancestral or analogous func tions. Interactive functions are areas in which music and language come together to create novel functions that strongly involve both systems. It includes principally all those functions that I call the vehicle mode of music operation, not to mention the use of meter in poetry and the many exaggerated uses of intonation to convey information, attitude, and emotion. The major point is that interactive functions develop through a coevolutionary process that re ects the evolutions of both the linguis tic and musical systems. For this reason, we expect interactive functions, such as verbal song, to evolve through a series of stages that re ect the evolution of the two systems contributing to these novel functions. It posits that music and language evolved as two specializations from a common ancestor, such that a series shared ancestral features evolved before either analo gous or distinct features. This model is distinguished from those holding that music evolved from a dedicated linguistic capacity (music outgrowth model) or that language developed from a dedicated musical capacity (language outgrowth model). It argues instead that shared ancestral fea tures of music and language should be thought of as musilinguistic rather than either musical or linguistic. This by itself establishes the functional spectrum that will later de ne music and language as two separate specializations. From this we see the development of the musilanguage stage, which is thought to have occurred in two steps. The rst step was the use of level tones (discrete pitches) and pitch contours for referential communication. The second step was the development of meaningful phrases, generated through combinatorial rules for joining discrete elements into phrases, these phrases being subject to four levels of modulation: local sentic rules for expressive modulation; global sentic rules for the overall level (intensity) of expression; local categorical rules for prominence; and global cate gorical formulas for generating phrase-level contour-meaning associa tions. These devices make independent but related contributions to the overall acoustic properties of the phrase. Semantically, the musilanguage device is a sophisticated referential emotive communication system that generates meaning at two levels: rst, from the relational juxtaposition of unitary elements (local level), and second, from overall contour meaning associations (global level). Next, the musilanguage stage is thought to evolve by a two-step process, beginning rst with a unitary lexical-tonal system, followed by a phrase system involving both combinatorial syntax and expressive phrasing properties. This musilanguage stage provides for the shared ancestral features of music and language. This involves not only different fundamental units at the phono logical level but different interpretations of these units at the meaning level. An important aspect of the divergence process is the formation of different syntax types: propositional syntax in the case of language, and blending syntax in the case of music. The nal step is development of interactive properties by a coevolutionary process. Divergence occurs due to the reciprocal elaboration of either sound as referential meaning or sound as emotive meaning, ultimately making language and music different in emphasis rather than in kind. Finally, simultaneous with the divergence process is the formation of interactive functions, exempli ed by verbal song and all the other vehicle functions of music. In other words, diver gence is accompanied by rebinding of music and language in the form of novel functions that evolve parallel to their separation. The emergence of these interactive functions re ects coevolution of the underlying lin guistic and musical systems. Thus, we can imagine verbal song as evolv ing through a series of stages that parallel biological developments in both systems. I do not think anyone would deny that both music and language are highly multifunctional. However evolutionary models are adaptationist interpretations of how traits evolve, and tend to focus monolithically on a single adaptive func tion and a single selection mechanism for a given trait. So far, the mono lithic approach to language has failed miserably, and I doubt that it will work for music either. But in addition, and more controversially, I sin cerely doubt that functionalist concepts of music origins based exclu sively on individual selection processes will, in the end, bear fruit. There is just too much about music making that reveals an essential role in group function to ignore the issue of multilevel selection (Sober and Wilson 1998). Nobody questions that music is done in groups, but Miller (this volume) seriously questions whether it is done for groups. Half a century of ethnomusicological research suggests that a principal func tion, if not the principal function, of music making is to promote group cooperation, coordination, and cohesion (Merriam 1964; Lomax 1968; Hood 1971). Music making has all the hallmarks of a group adaptation and functions as a device for promoting group identity, coordination, action, cognition, and emotional expression.
It is typical to be stumped by new concepts and problems when we first focus on them insomnia wheesung discount unisom online american express. The Einstellung effect refers to getting stuck in solving a problem or understanding a concept as a result of becoming fixated on a flawed approach sleep aid gadgets order unisom uk. When you are consciously thinking of a problem insomnia in toddlers buy 25mg unisom with amex, which mode is active and which is blocked How were you able to change your thinking to get past the preconceived sleep aid hangover buy unisom 25mg mastercard, but erroneous insomnia 720p yify discount unisom 25mg, notion Explain how the focused and diffuse modes might be equated to an adjustable beam on a flashlight sleep aid luna purchase unisom with paypal. Why is procrastination sometimes a special challenge for those who are studying math and science I studied longer and harder than I ever had before, yet no matter how many problems I did or how long I stayed in the library I was learning nothing. But here are some things that have helped me understand a concept that at first seems complicated or confusing. I understand better when I read the book rather than listen to someone speak, so I always read the book. I skim first so I know basically what the chapter is trying to get at and then I read it in detail. Even as his lab was burning to the ground in a horrific accidental fire, Edison was excitedly sketching up plans for a new lab, even bigger and better than before. Shifting between the Focused and Diffuse Modes For most people, shifting from focused to diffuse mode happens naturally if you distract yourself and then allow a little time to pass. Or you can work on something that occupies other parts of your brain: listening to music, conjugating Spanish verbs, or 1 cleaning your gerbil cage. The key is to do something else until your brain is consciously free of any thought of the problem. One remarkably inventive chemist of the mid-1800s, Alexander Williamson, observed that a solitary walk was worth a week in the laboratory in helping him 3 progress in his work. Once you are distracted from the problem at hand, the diffuse mode has access and can 4 begin pinging about in its big-picture way to settle on a solution. After your break, when you return to the problem at hand, you will often be surprised at how easily the solution pops into place. Brilliant inventor Thomas Edison (above) is thought to have used a clever trick to switch from focused to diffuse mode. This was the same trick used by famed surrealist painter Salvador Dali (below) for his artistic creations. When faced with a difficult problem, instead of focusing intently on it, Edison, according to legend, took a nap. But he did so while sitting in a lounge chair, holding a ball bearing in his hand above a plate on the floor. The clatter woke him so he 5 could grasp the fragments of his diffuse-mode thinking to create new approaches. Creativity Is about Harnessing and Extending Your Abilities There is a deep connection between technical, scientific, and artistic creativity. Wild surrealist painter Salvador Dali, like Thomas Edison, also used a nap and the clatter of an object falling from his hand to tap into his diffuse-mode creative perspectives. For example, there are more than three hundred different known proofs of the Pythagorean theorem. As we will soon learn, technical problems and their solutions may be considered a form of poetry. Creativity, however, is more than simply having a developed set of scientific or artistic capabilities. From Focused to Diffuse Read the following sentence and identify how many errors it contains: Thiss sentence contains threee errors. The third, paradoxical error becomes 8 obvious only when you change perspectives and adopt a more diffuse approach. To work past them, start early on your assignments and, unless you are really enjoying what you are doing, keep your working sessions short. Remember, when you take breaks, your diffuse mode is still working away in the background. Sleep is probably the most effective and important factor in allowing your diffuse mode to tackle a difficult problem. One way to think of the diffuse mode is as a base station when you are mountain climbing. Base stations are essential resting spots in the long journey to difficult mountaintops. But you would never confuse resting at a base station with the hard work of getting to the top of a mountain. Enlisting the focused mode, which is often what you need to do to first get a problem into your brain, requires your full attention. When your energy flags, sometimes you can take a break by jumping to other focused-type tasks, such as switching from studying math to studying French vocabulary. Taking time off between weight sessions helps build strong muscles in the long run. As a result of this uncomfortable and discouraging situation, students end up unnecessarily dropping out of math and science. A lighter load of math and science courses can, for many, be the equivalent of a heavy load of other types of courses. Especially in the early stages of college, avoid the temptation to keep up with your peers. You may be surprised to discover that learning slowly can mean you learn more deeply than your fast-thinking classmates. One of the most important tricks that helped me retool my brain was learning to avoid the temptation to take too many math and science classes at once. Avoid Einstellung (Getting Stuck) Remember, accepting the first idea that comes to mind when you are working on an assignment or test problem can prevent you from finding a better solution. Chess players who experience Einstellung truly believe they are scanning the board for a different solution. But careful study of where their eyes are moving shows that they are keeping their focus on the original solution. According to recent research, blinking is a vital activity that provides another means of reevaluating a situation. Closing our eyes seems to provide a micropause that momentarily deactivates our attention and allows us, for the briefest of moments, to refresh and renew our 16 consciousness and perspective. Now we can begin to understand Magnus Carlsen and his genius for appreciating the importance of seemingly trivial distractions. Turning his eyes and attention elsewhere likely was critical in allowing his diffuse intuition to go to work on his game with Kasparov. His expertise in chess probably played a role, along with his own intuitive practice skills. This is a hint that you, too, may be able to develop ways to quickly toggle between the focused and diffuse modes as you develop your expertise in a subject. Incidentally, Carlsen probably also knew his bouncing from his chair would distract Kasparov. Each interlude in which you are not directly focused on the problem allows your diffuse mode to look at it in a fresh way. When you turn your focused attention back to the problem, you consolidate new ideas and patterns that the diffuse mode has delivered. Learning well means allowing time to pass between focused learning sessions, so the neural patterns have time to solidify properly. The next day when I tried it again, I would be able to play it perfectly, as if by magic. In the car on the way to the Renaissance festival, it came to me and I had to write it on a napkin before I forgot! Usually a few hours is long enough for the diffuse mode to make significant progress but not so long that its insights fade away before being passed on to the focused mode. A good rule of thumb, when you are first learning new concepts, is not to let things go untouched for longer than a day. The diffuse mode not only allows you to look at the material in new ways but also appears to allow you to synthesize and incorporate the new ideas in relation to what you already know.
Discount generic unisom uk. Fall Asleep Fast: Deep Sleep Music Meditation Music Relaxing Music Sleeping Music ★134.