Valerie L. Katz, MD, FACS
- Assistant Professor of Clinical Surgery
- Weill Medical College of Cornell University
- Section Chief, Department of General Surgery
- Lincoln Medical and Mental Health Center
- Bronx, New York
The vascular plexus within the papillary body of the dermis may be supplied by two routes (Fig prehypertension systolic normal diastolic adalat 30mg without a prescription. These arteries usually run over muscles blood pressure numbers mean generic adalat 20mg with amex, parallel to the surface of the skin blood pressure 0 0 generic adalat 20mg without a prescription, and give o vertical vessels (in addition to the vessels from the subdermal plexus) to the skin blood pressure low pulse high generic 20 mg adalat overnight delivery. It is possible to raise skin Áaps on these arteries which are considerably longer than random pattern Áaps blood pressure young male purchase adalat 30 mg visa. Owing to the special a position of the artery along the axis of the Áap’s pedicle arteria rectal superior buy generic adalat pills, these Áaps are known as axial pattern Áaps or arterial Áaps. Typical examples of such arteries are the superÀcial tempo ral artery (“temporal Áap”) and the supratrochlear artery (“(para-)median forehead Áap”, see Fig. On the other hand, the restoration of a structure with the aid of adjacent tissue must not be undertak en at the expense of destroying the aesthetic unit of the donor site. The aesthetic units of the face are the frontal, supraorbital, orbital, infraorbital, nasal, zygomatic, buccal, labial, and mental units (Fig. Incisions on the face should correspond to the direction based on polyglycolic and polylactic acid. These have a half-life (time until re scar formation) or, when creases are present, follow the wrinkle duction of the tensile strength to 50 %) of 10–12 days. The absorption time of a thread is determined by its size, among 4 other factors, so the times stated above are therefore average Rules, Tips, and Tricks values. Skin sutures are placed using monoÀlament, nonabsorbable synthetic strands made out of polyamide. These sutures have a high Instruments tensile strength, skin irritation is minimal, and they have no “wick e ect” (inÀltration of bacteria into deeper skin layers). The instruments must be adapted to the special requirements A suture size of 4/0 or 3/0 is usually chosen for subcutaneous of plastic surgery. Skin suturing for the face should be undertaken with a jaws of needle holders should be suitably small, although the maximum suture size of 5/0, even better 6/0. Needle holders: Instruments with Áat jaw surfaces for hold Cutting needles of various lengths and forms are suitable. Semicircular or even more strongly either pass through the grooves, making it impossible to curved needles are used for deep sutures, especially for sites grasp, or be crushed and thus lose its tensile strength. The various manufacturers use di erent Forceps: Adson or Adson–Brown forceps for plastic surgery terminology for the needle shapes, so there is no universally have Àne tips to allow tissue to be grasped precisely and valid nomenclature. Nevertheless, despite this reduced tissue trauma tization, only the subcutaneous tissue should be grasped, whenever possible. Wound Healing and General Wound Scissors: One rounded and one pointed, curved pair of scis Management sors are usually adequate. Hooks/retractors: Fine single skin hooks are very useful and Wound Healing can be inserted through the skin without leaving scars. This allows the skin to be moved or held without the crushing Wound healing proceeds in several phases. Retractors with more prongs are used is initially covered with a Àbrin net, and after 24 hours the epi for extensive mobilization, but should then only grasp the dermis begins to close over the wound. For mobilization of larger skin areas to cover defects, yet provide the wound with any tensile strength, however. The especially in the area of the neck and chest, a correspond necessary stability is only achieved with the production of col ingly larger curved blade (No. Bipolar coagulation forceps: Targeted bipolar coagulation is an essential guarantee for good hemostasis with minimal Table 5. Given that only the production of collagen results in a vis Wound tension: Skin sutures should never be placed under ible scar, it must be contained within limits by correct wound tension. In certain cases this may not be possible; if so, skin sutures should be left for a corre spondingly longer time and possible cosmetically unfavor able scar formation must be accepted. Suture Techniques 5 Standard Suture Technique If increased collagen production is induced by dehiscence of the wound edges, reduction of the wound surface by contraction Primary wound closure usually involves a subcutaneous suture will occur and the surface will be covered by a thin, functionally and a skin suture (Fig. This form of secondary healing results in such a way that the knot is buried in the depths of the tissue in considerable deformity of the surrounding tissue and should (Fig. General Wound Management Rules, Tips, and Tricks the prerequisites for correct suturing are as follows. Wounds managed by suturing do not require any special cover the wound edges must be of equal length at skin level. Exceptions are compression dressings required to excision of Burrow’s triangles or by other techniques (Figs. Larger epithelial defects, which Wound edges with di ering depths may be brought to the are to be resurfaced at a later stage, may be managed temporar same level by skin excision and skin advancement (Fig. A compression Entry and exit holes in the skin should lie at the same distance dressing is often inadequate for hematoma prophylaxis of deep from the wound edge (Fig. It is preferable in such cases to insert a soft drain or a the depths of the entry and exit holes of the suture in the area suction drain. The timing depends on two factors: Location of the suture: In skin rich with sebaceous glands, such as the tip of the nose, epithelialization of the puncture a b c a a c c b Fig. To achieve the desired eversion of the wound edges, the a Subcutaneous suture with buried knot. Note: Needle entry and exit holes must be the same distance from c Wound closure completed. Subcuticular Suture the ends of the sutures must be left long enough for their easy removal, but must be cut short enough to prevent them from Surgical Principle interfering with the adjacent sutures. When suturing is completed, the wound edges should be the special advantage of this suture is that usually only one en checked. The epithelium should not be rolled in, but should be try and one exit hole are required. The suture is then passed in a horizontal dermal plane at exactly the same level on al ternating sides of the wound to the far end. The approximation c d of the wound edges is achieved by mild traction on the suture ends, which are then secured with sterile surgical tape to avoid Fig. This technique should only be used for wound surfaces which d Further sutures, each in the middle, distribute the excess skin equally along the whole length of the wound. With longer wounds, bring the suture out once though the skin the suture is inserted perpendicularly approximately 4mm after approximately 3–4 cm. If necessary, repeat after the same from the wound edge, carried down to the subcutis and then distance (removal of the suture is thus considerably facilitated). It is then reinserted as a mattress should be secured by transcutaneous interrupted sutures (the suture 1mm from the wound edge and passed intradermally whole suture line will then not need to be opened up should across to the opposite side, where it is again brought out at the Áuid collection develop). The stitch is pulled just 4 this suture is less suitable for wounds with a signiÀcant curvilin tight enough to evert the wound edges slightly. This technique should therefore only be used in the Surgical Principle facial region when absolutely necessary. As an alternative, a modi Àed half-buried (Allgöwer) mattress suture can be used (Fig. The advantage of the mattress suture is its safer re-approxima tion of wound edges with di erent depths. This suture everts the wound edges and helps avoid “furrowlike” scar formation. Basic Principles 15 Continuous (Running) Suture Rules, Tips, and Tricks 4 Surgical Principle the end of the suture should be held under slight tension by an assistant. On completion, the wound edges should be checked the area of usage of this suture corresponds to that of the inter and, if necessary, everted. Unlike the intracutaneous suture, this suture technique is also Good results can be expected above all in areas of thin and suitable for curvilinear wounds, in which case the stitches should readily mobile skin with few sebaceous glands. In the subcutaneous tissue, entry and exit passage must be the primary management of soft-tissue injuries of the face is made at exactly the same distance from the skin surface. Wounds that are not adequately treat a knot is tied, as with an interrupted suture. Crossing back to the original side, the entry site is at the same intra cutaneous level with a near exit site. Local wound management is the initial scars that lie above skin level but do not extend beyond the treatment for nonurgent bony injuries of the skull; the treat boundaries of the original wound. The tendency to form keloids is often Primary Management of Facial Injuries inherited. Areas of predilection are, among others, the poste Ensure adequate tetanus immunization. Since inconspicuous 5 Check wounds for foreign bodies, consider cleansing and scars, hypertrophic scars, and keloids can coexist in the same irrigation with physiological saline or hydrogen peroxide; patient, the existence of a “normal scar”. Sparingly straighten any jagged wound edges, conservative Standard Operative Techniques for Scar Revision skin excision (no formal wound excision). Re-approximate superÀcially avulsed epithelium with Àbrin Small retracted scars. The operation is per taneous junctions of skin and mucosa (free alar margin, lip, formed under local anesthesia and may be repeated at 4 to eyelid margin). Hypertrophic scars are excised, together with a margin of With dog-bite injuries there are usually full-thickness defects, healthy tissue, if they do not regress spontaneously within commonly in the region of the tip of the nose. Wound tension, which is the cause of the increased pro ing wound, then it may carefully cleaned and primarily closed duction of collagen, must then be reduced. Attempts should be made to reconstruct such defects jacent tissue must be widely undermined to make it possible early (within 24 hours after sterile dressing) with appropriate to approximate the wound edges under minimal tension. Scar contracture after second main tension must be taken up by absorbable subcutaneous su ary healing requires generous excision and undermining of tures (see Figs. Management of Keloids Scar Revision the management of keloids is problematic, given that they are neoplastic growths initiated by injury to the dermis. Any skin Scar revision may be indicated for functional reasons if severe incision made for scar revision will therefore induce the forma contractures and distortions are present. Further measures are taken as prophylaxis against recurrence (see be Questions to Ask in the Preoperative Assessment low). Intralesional injection of the revised wound with a pen, ensuring that the lines of either side interdigi with a steroid crystal suspension, followed by weekly repeat injec tate. In addition, pressure dress the previously marked skin is scored with a pointed scalpel ings should be applied for as long as possible (depending on the blade (No. Should the result the scar is then excised with the scalpel, producing vertical ing defect after excision of the keloid be too large for primary incisional edges down to the subdermis. The triangular skin Áaps are repaired with Àne sutures 5 lar may be treated with a skin graft harvested from the groin. The indication for the revision of keloid scars should be made with extreme caution and the patient should not be encouraged to be too optimistic about the prospects of success. Rules, Tips, and Tricks the triangular skin Áaps should not be cut too small and should W-plasty be raised from unscarred skin. The area of undermining depends upon the resulting defect: it should at least equal the width of the Surgical Principle defect on either side. This undermining of the skin is the simplest method for dealing with skin tension. A few skin sutures for ap Converting a linear scar into a zigzag shape distributes the proximation are helpful before placing the deÀnitive skin suture, tensile forces in the region of the scar so that the scar line is so as not to misjudge each corresponding Áap and be left with a optically “broken up. At the same time retracted scars are corrected by resection and Alternatives undermining. Unlike the regular M or W-shaped scar formation after W plasties, the geometric broken-line technique results rather Indications in a scar that is broken up and rendered less conspicuous. Note the incision along the wound edges where largely congruent surfaces are created. Formation of identical geometric forms on either side of the scar (not mirror images). The mobility of the lateral skin should be taken into consider Surgical Principle ation when planning the operation (remember aesthetic units). Tension between the ends of the scar is relieved (a scar which is “too short” is lengthened). Surgical Principle Indications the technique achieves lengthening of the scar (without trans For any scar revision, it is above all the lengthening and trans position) by linear advancement. The nomenclature comes from the initial V-shaped at the expense of the adjacent lateral tissue (see arrow in Fig. The lateral skin is undermined to create lateral limbs at the end of the wounds and two trian and the opposite end of the wound is placed under tension with gles are elevated by undermining. Rules, Tips, and Tricks Maximal gain in length with reorientation of the scar by 90° is Rules, Tips, and Tricks only achieved if the length of the lateral limbs corresponds to the No new distortions should appear in the lateral regions of the length of the scar and they are at an angle of 60° to the scar (for wound; if necessary, the undermining should be extended. Because of their Adherent Scars thickness, preference should be given to skin Áaps to cover deep-seated defects. The simple excision and primary closure of extensive scars or other skin lesions. The re sulting defect must then be resurfaced either with a Áap or a Management of Soft-Tissue Defects skin graft (see below). This involves removing General Remarks only a part of the area, with dimensions such that a primary wound closure is just about possible. This allows the skin lesion Soft-tissue defects can be managed with either pedicle Áaps or to be excised gradually in several sessions. Pedicle Áaps are attached to the adjacent tissue by a paid here to the site of the resulting scar, any potential distor bridge of tissue, in which the feeding vessels run. Usu directly after excision because of the lack of mobility of the ally other Áap procedures are available to resurface defects of adjacent skin.
Administration of this vaccine in immune individuals may cause severe local induration hypertensive urgency treatment order adalat visa, sterile abscess formation arterial duplex cheap 30 mg adalat free shipping, and even necrosis at the inoculation site heart attack numbness cheap adalat. Antibiotics: Chemoprophylaxis using Tetracycline 500 mg every 6 hours or doxycycline 100 mg every 12 hours for 5–7 days is effective if begun 8-12 days post exposure blood pressure medication history discount generic adalat canada. Chemoprophylaxis is not effective and may only prolong the onset of disease if given immediately (1 to 7 days) after exposure arteria subclavia order cheap adalat online. Typhoidal tularemia presents with fever heart attack right arm purchase adalat 20mg overnight delivery, headache, malaise, substernal discomfort, prostration, weight loss and a non-productive cough. Chest x-ray may reveal a pneumonic process, mediastinal lymphadenopathy or pleural effusion. Treatment: Administration of antibiotics (streptomycin or gentamicin) with early treatment is very effective. A two-week course of tetracycline is effective as prophylaxis when given after exposure. Organisms are relatively easy to render harmless by mild heat (55 degrees Celsius for 10 minutes) and standard disinfectants. Tularemia (also known as rabbit fever and deer fly fever) is a zoonotic disease that humans typically acquire after skin or mucous membrane contact with tissues or body fluids of infected animals, or from bites of infected ticks, deerflies, or mosquitoes. Less commonly, inhalation of contaminated dusts or ingestion of contaminated foods or water may produce clinical disease. Respiratory exposure by aerosol would typically cause typhoidal or pneumonic tularemia. In the early 1900’s, American workers investigating suspected plague epidemics in San Francisco isolated the organism and named it Bacterium tularense after Tulare County, California where the work was performed. This organism could potentially be stabilized for weaponization by an adversary and theoretically produced in either a wet or dried form, for delivery against U. Tularemia typically appears in one of six forms in man depending upon the route of inoculation: typhoidal, ulceroglandular, glandular, oculoglandular, oropharyngeal, and pneumonic tularemia. Typhoidal tularemia (5-15 percent of naturally acquired cases) occurs mainly after inhalation of infectious aerosols, but can occur after intradermal or gastrointestinal challenge. It manifests as fever, prostration, and weight loss, but unlike most other forms of the disease, presents without lymphadenopathy. Pneumonia may be severe and fulminant and can be associated with any form of tularemia (30% of ulceroglandular cases), but it is most common in 45 typhoidal tularemia (80% of cases). Respiratory symptoms, substernal discomfort, and a cough (productive and non-productive) may also be present. Case fatality rates are about 35% in untreated naturally acquired typhoidal cases. Ulceroglandular tularemia (75-85 percent of cases) is most often acquired through inoculation of the skin or mucous membranes with blood or tissue fluids of infected animals. It is characterized by fever, chills, headache, malaise, an ulcerated skin lesion, and painful regional lymphadenopathy. Glandular tularemia (5-10 percent of cases) results in fever and tender lymphadenopathy but no skin ulcer. Oculoglandular tularemia (1-2 percent of cases) occurs after inoculation of the conjunctivae by contaminated hands, splattering of infected tissue fluids, or by aerosols. Chemosis, periorbital edema, and small nodular lesions or ulcerations of the palpebral conjunctiva are noted in some patients. Oropharyngeal tularemia refers to primary ulceroglandular disease confined to the throat. It produces an acute exudative or membranous pharyngotonsillitis with cervical lymphadenopathy. Pneumonic tularemia is a severe atypical pneumonia that may be fulminant and with a high case fatality rate if untreated. It can be primary following inhalation of organisms or secondary following hematogenous / septicemic spread. It is seen in 30 80 percent of the typhoidal cases and in 10-15 percent of the ulceroglandular cases. The case fatality rate without treatment is approximately 5 percent for the ulceroglandular form and 35 percent for the typhoidal form. All ages are susceptible, and recovery is generally followed by permanent immunity. Radiological evidence of pneumonia or mediastinal lymphadenopathy is most common with typhoidal disease. In general, chest radiographs show that approximately 46 50% of patients have pneumonia, and fewer than 1% have hilar adenopathy without parenchymal involvement. Interstitial patterns, cavitary lesions, bronchopleural fistulae, and calcifications have been reported in patients with tularemia pneumonia. Peripheral white blood cell count usually ranges from 5,000 to 22,000 cells per microliter. Differential blood cell counts are normal, with occasional lymphocytosis late in the disease. Mild elevations in lactic dehydrogenase, serum transaminases, and alkaline phosphatase are common. Cerebrospinal fluid is usually normal, although mild abnormalities in protein, glucose, and blood cell count have been reported. Tularemia can be diagnosed by recovery of the organism in culture from blood, ulcers, conjunctival exudates, sputum, gastric washings, and pharyngeal exudates. Recovery may even be possible after the institution of appropriate antibiotic therapy. The organism grows poorly on standard media but produces small, smooth, opaque colonies after 24 to 48 hours on media containing cysteine or other sulfhydryl compounds. Titers are usually negative the first week of infection, positive the second week in 50-70 percent of cases and reach a maximum in 4-8 weeks. Strict adherence to the drainage/secretion recommendations of Standard Precautions is required, especially for draining lesions, and for the disinfection of soiled clothing, bedding, equipment, etc. Gentamicin offers the advantage of providing broader coverage for gram-negative bacteria and may be useful when the diagnosis of tularemia is considered but in doubt. In a recent study of treatment in 12 children with ulceroglandular tularemia, ciprofloxacin was satisfactory for outpatient treatment (Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, 2000; 19:449-453). Tetracycline and chloramphenicol are also effective antibiotics; however, they are associated with significant relapse rates. Aerosol challenge tests in laboratory animals and human volunteers have demonstrated significant protection. Vaccine induced protection could be overwhelmed by extremely high doses of the tularemia bacteria. Pre-exposure prophylaxis: Chemoprophylaxis given for anthrax or plague (ciprofloxacin, doxycycline) may confer protection against tularemia, based on in vitro susceptibilities. Viruses are intracellular parasites and lack a system for their own metabolism; therefore, they are dependent on the synthetic machinery of their host cells. This means that viruses, unlike the bacteria, cannot be cultivated in synthetic nutritive solutions, but require living cells in order to multiply. Every virus requires its own special type of host cell for multiplication, because a complicated interaction occurs between the cell and virus. Virus-specific host cells can be cultivated in synthetic nutrient solutions and then infected with the virus in question. Another common way of cultivating viruses is to grow them on chorioallantoic membranes (from fertilized eggs). Diagnosis: Neither electron nor light microscopy are capable of discriminating variola from vaccinia, monkeypox or cowpox. Treatment: At present there is no effective chemotherapy, and treatment of a clinical case remains supportive. Isolation and Decontamination: Droplet and Airborne Precautions for a minimum of 17 days following exposure for all contacts. Patients should be considered infectious until all scabs separate and quarantined during this period. In the civilian setting strict quarantine of asymptomatic contacts may prove to be impractical and impossible to enforce. Despite the global eradication of smallpox and continued availability of a vaccine, the potential weaponization of variola continues to pose a military threat. This threat can be attributed to the aerosol infectivity of the virus, the relative ease of large-scale production, and an increasingly Orthopoxvirus-naive populace. Although the fully developed cutaneous eruption of smallpox is unique, earlier stages of the rash could be mistaken for varicella. Quarantine with respiratory isolation should be applied to secondary contacts for 17 days post-exposure. Vaccinia vaccination and vaccinia immune globulin each possess some efficacy in post-exposure prophylaxis. However, action on this was delayed by the Clinton administration in May 1999 due to concerns over the need for further study of the virus given its potential as a biological warfare agent. The United States stopped vaccinating its military population in 1989 and civilians in the early 1980s. These populations are now susceptible to variola major, although recruits immunized in 1989 may retain some degree of immunity. Variola may have been used by the British Army against native Americans by giving them contaminated blankets from the beds of smallpox victims during the eighteenth century. Clinical manifestations begin acutely with malaise, fever, rigors, vomiting, headache, and backache; 15% of patients developed delirium. Approximately 10% of light-skinned patients exhibited an erythematous rash during this phase. Two to three days later, an enanthem appears concomitantly with a discrete rash about the face, hands and forearms. Lesions quickly progressed from macules to papules, and eventually to pustular vesicles. Lesions were more abundant on the extremities and face, and this centrifugal distribution is an important diagnostic feature. Although variola concentrations in the throat, conjunctiva, and urine diminish with time, virus can be readily recovered from scabs throughout convalescence. However, the prototypical disease variola major caused mortality of 3% and 30% in the vaccinated and unvaccinated, respectively. Other clinical forms associated with variola major, flat-type and hemorrhagic type smallpox were notable for severe mortality. A naturally occurring relative of variola, monkeypox, occurs in Africa, and is clinically indistinguishable from smallpox with the exception of a lower case fatality rate and notable enlargement of cervical and inguinal lymph nodes. Particularly problematic to infection control measures would be the failure to recognize relatively mild cases of smallpox in persons with partial immunity. An additional threat to effective quarantine is the fact that exposed persons may shed virus from the oropharynx without ever manifesting disease. Therefore, quarantine and initiation of medical countermeasures should be promptly followed by an accurate diagnosis so as to avert panic. The usual method of diagnosis is demonstration of characteristic virions on electron microscopy of vesicular scrapings. Under light microscopy, aggregations of variola virus particles, called Guarnieri bodies are found. None of the above laboratory tests are capable of discriminating variola from vaccinia, monkeypox or cowpox. This differentiation classically required isolation of the virus and characterization of its growth on chorioallantoic membrane. The development of polymerase chain reaction diagnostic techniques promises a more accurate and less cumbersome method of discriminating between variola and other Orthopoxviruses. Any confirmed case of smallpox should be considered an international emergency with immediate report made to public health authorities. Droplet and Airborne Precautions for a minimum of 17 days following exposure for all persons in direct contact with the index case, especially the unvaccinated. A reasonable alternative would be to require contacts to check their temperatures daily. Any fever above 38 C (101 F) during the 17-day period following exposure to a confirmed case would suggest the development of smallpox. Immediate vaccination or revaccination should also be undertaken for all personnel exposed to either weaponized variola virus or a clinical case of smallpox. Smallpox patients were infectious from the time of onset of their eruptive exanthem, most commonly from days 3-6 after onset of fever. Some close contacts harbored virus in their throats without developing disease, and hence might have served as a means of secondary transmission. Cidofovir has been shown to have significant in vitro and in vivo activity in experimental animals. Whether it would offer benefit superior to immediate post-exposure vaccination in humans has not been determined. A vesicle typically appears 54 at the vaccination site 5-7 days post-inoculation, with surrounding erythema and induration. More severe first-time vaccine reactions include secondary inoculation of the virus to other sites such as the face, eyelid, or other persons (~ 6/10,000 vaccinations), and generalized vaccinia, which is a systemic spread of the virus to produce mucocutaneous lesions away from the primary vaccination site (~3/10,000 vaccinations). Despite these caveats, most authorities state that, with the exception of significant impairment of systemic immunity, there are no absolute contraindications to post-exposure vaccination of a person who experiences bona fide exposure to variola. Limited data suggests that vaccinia immune globulin may be of value in post-exposure prophylaxis of smallpox when given within the first week following exposure, and concurrently with vaccination. If greater than one week has elapsed after exposure, administration of both products, if available, is reasonable.
Con Microphthalmos is a common ophthalmic con genital lens luxation from zonular weakness is a 1 genital defect in the foal (Fig blood pressure quotes buy genuine adalat on-line. Anterior early detection and treatment to prevent ulcer Segment Dysgenesis of the Rocky Mountain 1 heart attack 40 discount adalat 30 mg line,4 progression blood pressure chart in pregnancy purchase cheap adalat line. Horse consists of increased corneal curvature blood pressure quiz questions buy adalat 20 mg cheap, iris Iridocyclitis in the foal is generally secondary to hypoplasia blood pressure 200110 purchase adalat 30 mg without prescription, congenital miosis heart attack 85 year old buy adalat online now, uveal cysts, cataracts, septicemia and may be unilateral or bilateral. Homeopathic oint lacrimal system should also be evaluated for damage ments and caustic chemical lotions are effective in 7 when medial canthal injuries are present. Retro followed by Appaloosas and Paints, with the least viruses and papilloma viruses may be involved in prevalence found in Arabians, Thoroughbreds, and the etiology. Descemet’s membrane is the 21 m-thick basement membrane 10,11 of the inner endothelial cell layer. Healing of large diameter, superficial, noninfected corneal ulcers is generally rapid and linear for 5–7 days, and then slows or lags till healing is com 11 plete. Healing time of a 7-mm diameter, midstromal depth, noninfected corneal trephine wound was nearly 12 days in horses (0. These enzymes exist in a bal with local temperatures of 41–50°C, after surgical ance with inhibitory factors to prevent excessive excision. Equine Corneal Microenvironment Horse corneas demonstrate a pronounced fibro the environment of the horse is such that the con 1,4 vascular healing response. The unique corneal junctiva and cornea are constantly exposed to bac healing properties of the horse in regards to exces 1 teria and fungi. Ulcers, uveitis, blepharitis, conjunctivi propriate medical and surgical therapy. Signs of anterior uveitis are prominent eye of the horse may predispose to trau found with every corneal ulcer in the horse and 1,4 matic corneal injury. Corneal ulcers in horses should be aggressively treated no matter how small or su Fluorescein and Rose Bengal Dyes and Other Diagnostics perficial they may be. Fungal involvement should be eyes need to have their corneas stained with both suspected if there is a history of corneal injury with fluorescein dye and rose bengal dye because fungal 304 2002 Vol. Fluorescein and rose bengal dyes are extremely impor painful eye that needs frequent therapy. The clarity of the cornea, the depth and size of the ulcer, the degree of corneal vascularization, the amount of tearing, the pupil size, and intensity of the anterior uveitis should be monitored. Serial ulcers in the earliest stage will be negative to the fluorescein staining of the ulcer is indicated to as fluorescein but positive for the rose bengal. As the cornea heals the stimulus for rescein dye retention is diagnostic of a full-thickness the uveitis will diminish, and the pupil will dilate epithelial defect or corneal ulcer. Vigorous corneal scraping at the edge and base of Antibiotics a corneal ulcer is used to detect bacteria and fungal Bacterial and fungal growth must be halted and the hyphae. Topical atropine has been shown to prolong intes Cefazolin (55 mg/ml), chloramphenicol, bacitracin, tinal transit time and reduce and abolish intestinal and carbenicillin are effective against beta-hemolytic sounds in the small intestine and large colon of Streptococcus. Activation and/or pro duction of proteolytic enzymes by corneal epithelial cells, leucocytes, and microbial organisms are re 1,4 sponsible for stromal collagenolysis or “melting. Autogenous serum administered topi cally can reduce tear film and corneal protease ac tivity in corneal ulcers in horses. Cecal impaction may oc corneal diseases including corneal erosions, neuro 1,4 cur secondary to topical atropine administration. De bacterial and fungal opportunists by interfering bridement to remove abnormal epithelium of refrac with non-specificinflammatory reactions and cellu tory superficial erosions can be accomplished with lar immunity. Corticosteroid therapy by all routes topical anesthesia and a cotton-tipped applicator. Even topical corticosteroid instillation, cial ulcers with a 20-gauge needle can increase the to reduce the size of a corneal scar, may be disas ability of the epithelial cells to migrate and adhere 1,4 trous if organisms remain indolent in the corneal to the ulcer surface in superficial ulcers. Conjunctival Flaps Please Remember the Following Conjunctival grafts or flaps are used frequently in ● Corneal ulcers are frequently not clearly visi equine ophthalmology for the clinical management ble even with proper examination lighting of deep, melting, and large corneal ulcers, desce ● All red or painful eyes must be stained with metoceles, and perforated corneal ulcers with and fluorescein and rose bengal dyes without iris prolapse. The most often proposed pathogenesis of ul cerative fungal keratitis in horses begins with slight to severe corneal trauma resulting in an epithelial defect, colonization of the defect by fungi normally present on the cornea, and subsequent stromal in vasion. Fungi seem to have an affinity for Descemet’s membrane with hyphae frequently found deep in the equine cornea. Diagnostic tests should include fluorescein and rose bengal staining, corneal cytology, corneal cul ture with attempted growth on both fungal and aer obic plates, and biopsy if surgery is performed. Treatment must be directed against the fungi as well as against the iridocyclitis that occurs after fungal replication and fungal death. This can be seen as a herd quite prolonged and scarring of the cornea may be 1,4 problem! Conjunctival flap and penetrating keratoplasty Corneal stromal abscesses can be a vision-threat are used in treating aggressive keratomycosis in ening sequelae to apparently minor corneal ulcer horses. A painful, blinding chronic Viral Keratitis is seen as a superficial punctate iridocyclitis may result. Both superficial and able response to topical antivirals, but topical deep stromal abscesses do not heal until they be 308 2002 Vol. The patterns of corneal vascu ocular problems are present, and the foal’s person larization are often unique suggesting that ality will tolerate aggressive topical medical therapy. General anesthesia Superficial stromal abscesses may initially re with its attendant risks is required for cataract 1,4,6,18 spond positively to medical therapy. The emulsified lens is then high-risk for rejection in infected, vascularized cor aspirated from the eye while intraocular pressure is neal tissue. The rate of cataract progres in reducing anterior uveitis in horses with cataracts. Heritable, traumatic, flurbiprofen, and suprofen must also be used to sup nutritional, and post-inflammatory etiologies have press signs of anterior uveitis. Diseases of the Uveal Tract by focal to generalized peripapillary regions of de pigmentation in the nontapetum can result. Hypersensitivity vision, decrease pain, and prevent or minimize the to infectious agents such as Leptospira interrogans recurrence of attacks of uveitis. Treatment should be where ocular antigens found in the horse eye are aggressive and prompt to maintain the transpar identical to antigens found in Leptospiral and other ency of the ocular structures. The presence of living Lepto be slowly reduced in frequency once clinical signs spira organisms is not necessary for disease produc abate. Seropositive (1: costeroids and nonsteroidal drugs, are used to con 400) Appaloosas (100%) seronegative Appaloosas trol the generally intense intraocular inflammation (72%) seropositive non-Appaloosas (51%) sero that can lead to blindness. Medication can be negative non-Appaloosas (34%) at having blindness administered topically as solutions or ointments, occur in at least one eye within 11 yr of the first subconjunctivally, orally, intramuscularly, and/or 21 attack. Cataract formation may occur if horses become refractory to the beneficial effects of the inflammation does not subside quickly. Should gut motility de crease during treatment with topically administered atropine, one can either discontinue the drug or change to the shorter acting tropicamide. An intracameral injection of 50–150 g/eye can be made at the limbus with a 27-gauge needle under Horses with previous or concurrent uveitis, aged general anesthesia. Vitrectomy hibitor dorzolamide (q12h), and the beta-blocker seems more beneficial in European Warmbloods timolol maleate (0. Flunixin meglumine, phenylbuta Horses can adapt amazingly well to blindness, zone, or aspirin are indicated. Topical medication whether unilateral or bilateral, if allowed to adjust does not reach the retina and is only indicated if to their new condition. Aniridia and secondary cataracts There is no therapy for this condition but affected 2. Histomorphometry of the hypoplasia optic nerves of normal horses and horses with glaucoma. Retinal dysplasia associated with retinal de periorbital sarcoid in the horse: 445 cases from 1974 to tachments in some cases 1999. Rose bengal pos itive epithelial microerosions as a manifestation of equine keratomycosis. Uveitis in the horse: a review of the aetiological and immunopathological aspects of the disease. Association of lepto spiral seroreactivity and breed with uveitis and blindness in References horses: 372 cases (1986–1993). So someone who is hoping for a more youthful appearance may be disappointed if they just get their eyelids treated and nothing else—es pecially if their brow is covering their eyelids,” said Evan H. Chemical brow-lifts using ophthalmic, plastic and orbital surgery Botox or Dysport relax these muscles and allow the muscles that pull the brow at the Kresge Eye Institute in Detroit. In fact, the recent financial reces sion has resulted in a boom in chemi can help them hold on to a job, or snag thinking more about what a procedure cal eyebrow lifts. But in addition to being as a means to increase revenue in their brow-lifts, or ‘liquid lifts. But people are assistant professor of surgery at Brown eyenet 35 Oculoplastics University in Providence, R. The possible side Black agreed, “Chemical brow-lifts are common areas for Botox treatments effects from Botox or Dysport can for younger, active patients who really are the glabellar folds, crow’s-feet and include hypersensitivity in some pa don’t want a convalescent period where forehead,” said Dr. Topical anesthetics can be help the most common adverse outcome is Chemical brow-lifts are accomplished ful, however, for larger treatments,” he bruising, according to Dr. Both products relax the amount of time that the lift lasts vitamin E and certain herbals, includ corrugator, procerus and orbicularis doesn’t just correlate with the amount ing flaxseed, fish oil and garlic. If the oculi muscles that pull the eyebrow of Botox or Dysport that is used but patient is an easy bruiser, oral medical down. The muscles that pull the brow also depends on how the individual grade arnica is very helpful and can be up, such as the frontalis, can then patient metabolizes the drugs over started the day before the procedure. Consequently, Also, any trauma to the face can result fects last from three to six months. Choosing among these amount of Botox, they should continue revenue in ophthalmic practices, and and deciding whether they might be it. Or if they’d like to try a little bit less neither expense nor training is a par used together depends on the aesthetic and see if it works, that’s great. But if ticular obstacle for a fully trained oph results the patient wants as well as par you don’t get the correction you want, thalmologist. Errors can oc but training for chemical brow-lifts, pulled down, giving an appearance cur with brow-lifts done with Botox such as those that require Dysport or of frowning, will benefit more from and Dysport. There is a difference, Botox, can be accessed through the Botox or Dysport while those with a for example, between lifting the brow pharmaceutical companies that make deep-set, sunken look to their face who and eliminating the appearance of these drugs. But some patients can ben effect of putting Botox in the forehead for treating both cervical dystonia efit from a combination of chemical is to drop the brow because muscles and glabellar lines, and Botox is also lifts,” he added. For the cosmetic indi procedure, it’s important to let patients with brow ptosis. It can are interested in facial injectables or temporary and can lift the brow by track into the orbit and cause tempo aesthetic procedures. The forming sophisticated procedures on “I tell people ‘This is not going to be a good—and bad—thing about Botox the eye and to working with surgeries super-huge change. Surgical brow-lifts—which include the coronal, 2010-2011 Basic and the endoscopic and the direct brow Clinical Science Course lift procedures—require a significant investment in training and equipment. An essential resource for practicing Physicians who do surgical brow-lifts ophthalmologists and residents must have extensive working knowl edge of facial and forehead anatomy and, if they perform endoscopic brow-lifts, use of an endoscope. And the physician’s cost for performing a chemical brow-lift is much less than for surgical brow-lifts, which require anesthesia and significantly more staff with training in surgical techniques. In the end, the decision over whether a patient will have a chemi cal or surgical brow-lift comes down to what is right for that individual. The results tend to be much ap this year’s major revisions: preciated by patients. You need to Complete print set make sure you’re giving each patient Includes all 13 sections, plus the Master Index your best; that’s the key to success and $790 member / $1065 nonmember #02800950 ultimately a happy patient. Enrollment code for this Plan: Special Notice: the Plan will add a High Deductible Health Plan for 2019. This means you do not need to enroll in Medicare Part D and pay extra for prescription drug coverage. For example, if you go 19 months without Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage, your premium will always be at least 19 percent higher than what many other people pay. You will have to pay this higher premium as long as you have Medicare prescription drug coverage. In addition, you may have to wait until the next Annual Coordinated Election Period (October 15 through December 7) to enroll in Medicare Part D. Medicare’s Low Income Benefits For people with limited income and resources, extra help paying for a Medicare prescription drug plan is available. You can get more information about Medicare prescription drug plans and the coverage offered in your area from these places: No verbal statement can modify or otherwise affect the benefits, limitations, and exclusions of this brochure. If you are enrolled in this Plan, you are entitled to the benefits described in this brochure. If you are enrolled in Self Plus One or Self and Family coverage, each eligible family member is also entitled to these benefits. You do not have a right to benefits that were available before January 1, 2019, unless those benefits are also shown in this brochure. Benefit changes are effective January 1, 2019 and changes are summarized on page 17. The health coverage of this plan meets the minimum value standard for the benefits the plan provides. Fraud increases the cost of health care for everyone and increases your Federal Employees Health Benefits Program premium. You may be prosecuted for fraud for knowingly using health insurance benefits for which you have not paid premiums. It is your responsibility to know when you or a family member is no longer eligible to use your health insurance coverage.
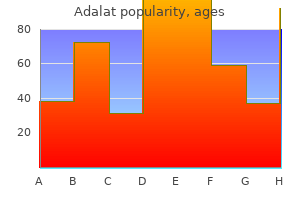
Trusted adalat 20mg. Resting Blood Pressure and Heart Rate.