David A Meyerson, J.D., M.D.
- Director of Cardiology Consultation Services

https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0000675/david-meyerson
The most common pattern is given a grade of 1 (most like normal cells) to 5 (most abnormal) blood pressure medication questions buy benicar 20 mg cheap. If there is a second most common pattern heart attack complications buy benicar 20mg fast delivery, the pathologist gives it a grade of 1 to 5 blood pressure chart age 50 buy benicar cheap online, and adds the two most common grades together to make the Gleason score hypertension nos 40 mg benicar mastercard. High-grade tumors are more likely than low-grade tumors to grow quickly and spread prehypertension stress benicar 10 mg on-line. Staging is a careful attempt to find out whether the tumor has invaded nearby tissues blood pressure chart spreadsheet buy 10mg benicar fast delivery, whether the cancer has spread and, if so, to what parts of the body. You may receive contrast material by injection into a blood vessel in your arm or hand, or by enema. Sometimes contrast material makes abnormal areas show up more clearly on the picture. If cancer has reached these nodes, it also may have spread to other lymph nodes, the bones, or other organs. When cancer spreads from its original place to another part of the body, the new tumor has the same kind of abnormal cells and the same name as the primary tumor. For example, if prostate cancer spreads to bones, the cancer cells in the bones are actually prostate cancer cells. The tumor may have invaded the seminal vesicles, but cancer cells havent spread to the lymph nodes. The options include active surveillance (also called watchful waiting), surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemo therapy. Your doctor can describe your treatment choices, the expected results of each, and the possible side effects. You and your doctor can work together to develop a treatment plan that meets your medical and personal needs. You may want to see a urologist, a surgeon who specializes in treating problems in the urinary or male sex organs. Other specialists who treat prostate cancer include urologic oncologists, medical oncologists, and radiation oncologists. Your health care team may also include an oncology nurse and a registered dietitian. Before treatment starts, ask your health care team about possible side effects and how treatment may change your normal activities. For example, you may want to discuss with your doctor the possible effects on sexual activity. At any stage of the disease, supportive care is available to relieve the side effects of treatment, to control pain and other symptoms, and to help you cope with the feelings that a diagnosis of cancer can bring. Your doctor may suggest active surveillance if youre diagnosed with early stage prostate cancer that seems to be slowly growing. Your doctor may also offer this option if you are older or have other serious health problems. Having surgery or radiation therapy is no guarantee that a man will live longer than a man who chooses to put off treatment. If you and your doctor agree that active surveillance is a good idea, your doctor will check you regularly (such as every 3 to 6 months, at first). After about one year, your doctor may order another biopsy to check the Gleason score. Active surveillance avoids or delays the side effects of surgery and radiation therapy, but this choice has risks. Also, it may be harder to cope with surgery or radiation therapy when youre older. If you choose active surveillance but grow concerned later, you should discuss your feelings with your doctor. Before the surgeon removes the prostate, the lymph nodes in the pelvis may be removed. If prostate cancer cells are found in the lymph nodes, the disease may have spread to other parts of the body. If cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, the surgeon does not always remove the prostate and may suggest other types of treatment. A cutting tool at the end of the scope removes tissue from the inside of the prostate. Before surgery, you should discuss the plan for pain relief with your doctor or nurse. The time it takes to heal after surgery is different for each man and depends on the type of surgery. After surgery, some men may lose control of the flow of urine (urinary incontinence). You can talk with your doctor about medicine and other ways to help manage the sexual side effects of cancer treatment. If you wish to father children, you may consider sperm banking or a sperm retrieval procedure before surgery. Radiation Therapy Radiation therapy is an option for men with any stage of prostate cancer. Men with early stage prostate cancer may choose radiation therapy instead of surgery. It also may be used after surgery to destroy any cancer cells that remain in the area. In later stages of prostate cancer, radiation treatment may be used to help relieve pain. Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Many men receive 3-dimensional conformal radiation therapy or intensity-modulated radiation therapy. These types of treatment use computers to more closely target the cancer to lessen the damage to healthy tissue near the prostate. Dozens of seeds are placed inside needles, and the needles are inserted into the prostate. Youre likely to be very tired during radiation therapy, especially in the later weeks of treatment. Resting is important, but doctors usually advise patients to try to stay active, unless it leads to pain or other problems. If you have external radiation, you may have diarrhea or frequent and uncomfortable urination. Hormone Therapy A man with prostate cancer may have hormone therapy before, during, or after radiation therapy. Hormone therapy is also used alone for prostate cancer that has returned after treatment. Hormone therapy keeps prostate cancer cells from getting the male hormones they need to grow. Because the adrenal gland makes small amounts of male hormones, you may receive an antiandrogen to block the action of the male hormones that remain. This 24 combination of treatments is known as total androgen blockade (also called combined androgen blockade). Hormone therapy causes side effects such as impotence, hot flashes, and loss of sexual desire. Because these changes increase the risk of diabetes and heart disease, your health care team will monitor you for these side effects. Antiandrogens (such as nilutamide) can cause nausea, diarrhea, or breast growth or tenderness. Rarely, they may cause liver problems (pain in the abdomen, yellow eyes, or dark urine). Some men who use nilutamide may have shortness of breath or develop heart failure. If you receive total androgen blockade, you may have more side effects than if you have just one type of hormone treatment. If used for a long time, ketoconazole may cause liver problems, and aminoglutethimide can cause skin rashes. For some men, the cancer will be controlled for two or three years, but others will have a much shorter response to hormone therapy. In time, most prostate cancers can grow with very little or no male hormones, and hormone therapy alone is no longer helpful. At that time, your doctor may suggest chemotherapy or other forms of treatment that are under study. In many cases, the doctor may suggest continuing with hormone therapy because it may still be effective against some of the cancer cells. If your levels are low, your health care team may stop the chemotherapy for a while or reduce the dose of drug. Your health care team can give you medicines and suggest other ways to help with these problems. Other side effects include shortness of breath and a problem with your body holding extra water. Your health care team can give you medicine to protect against too much water building up in the body. Also, chemotherapy may cause a skin rash, tingling or numbness in your hands and feet, and watery eyes. Second Opinion Before starting treatment, you might want a second opinion about your diagnosis and treatment plan. You may even want to talk to several different doctors about all of the treatment options, their side effects, and the expected results. For example, you may want to talk to a urologist, radiation oncologist, and medical oncologist. Some people worry that the doctor will be offended if they ask for a second opinion. And many health insurance companies will pay for a second opinion if you or your doctor requests it. You can feel more confident about the decisions you make, knowing that youve looked at your options. It may take some time and effort to gather your medical records and see another doctor. You can ask your doctor, a local or state medical society, a nearby hospital, or a medical school for names of specialists. Your doctor, a registered dietitian, or another health care provider can suggest a healthy diet. Whatever physical activity you choose, be sure to talk to your doctor before you start. Also, if your activity causes you pain or other problems, be sure to let your doctor or nurse know about it. Checkups help ensure that any changes in your health are noted and treated if needed. Even when the cancer seems to have been completely removed or destroyed, the disease sometimes returns because undetected cancer cells remained somewhere in the body after treatment. Sources of Support Learning you have prostate cancer can change your life and the lives of those close to you. Concerns about treatments and managing side effects, hospital stays, and medical bills are common. You may also worry about caring for your family, keeping your job, or continuing daily activities. Often, social workers can suggest resources for financial aid, transportation, home care, or emotional support. In these groups, patients or their family members meet with other patients or their families to share what they have learned about coping with the disease and the effects of treatment. You may want to talk with a member of your health care team about finding a support group. They can send you a list of organizations that offer services to people with cancer. Ask your doctor about possible treatment of side effects and whether these effects are likely to last. Whatever the outlook, you and your partner may find it helps to discuss your concerns. Taking Part in Cancer Research Cancer research has led to real progress in prostate cancer detection, treatment, and supportive care.

The ThinPrep Imaging System blood pressure levels usa cheap benicar 20mg visa, for example blood pressure lowering medications order benicar discount, integrates automated imaging with screening by cytotechnologists to identify fields that contain potentially relevant cellular abnormalities blood pressure numbers for seniors purchase 10mg benicar amex. If the cytotechnologist identifies significant abnormalities 5 htp arrhythmia purchase benicar 20mg fast delivery, the slide is examined by the cytopathologist heart attack acoustic purchase benicar 10mg mastercard. A slightly different and less expensive technique called the PapSpin uses a special brush placed in a collection device and centrifuged to provide a cellular concentrate for microscopic examination blood pressure 80 over 50 purchase benicar 40mg with visa. Similar to screening for all cancers, as more studies become available, guidelines change. Furthermore, different medical professional societies may differ on certain aspects of appropriate Pap smear guidelines. Such drugs as digitalis and tetracycline may alter the test results by affecting the squamous epithelium. Instruct the patient not to douche or tub bathe during the 24 hours before the Pap smear. Material is collected from the cervical canal by rotating a moist saline cotton swab or spatula within the cervical canal and in the squamocolumnar junction (Figure 32). The cells are immediately wiped across a clean glass slide and fixed either by immersing the slide in equal parts of 95% alcohol and ether or by using a commercial spray. The secretions must be fixed before drying because drying will distort the cells and make interpretation difficult. A, the vaginal speculum is shown in position to allow direct visualization of the cervix. If liquid-based cervical cytology is performed, the cervical specimen is placed in the fixative preservative solution. After being placed in this solution, cells can be evaluated any time within the next 3 weeks if kept frozen. After P Inform the patient that usually she will not be notified unless further evaluation is necessary. Diagnostically, paracentesis is performed to obtain and analyze fluid to determine the etiology of the peritoneal effusion. This is an important differentiation and is very helpful in determining the etiology of the effusion. Transudates are most frequently caused by congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, myxedema, peritoneal dialysis, and hypoproteinemia. However, collagen vascular disease, gastrointestinal diseases, trauma, and drug hypersensitivity also may cause an exudative effusion. Therapeutically, this procedure is done to remove large amounts of fluid from the abdominal cavity. Usually these patients experience transient relief of symptoms (shortness of breath, distention, and early satiety) because of the removal of fluid within the abdominal cavity. A catheter is placed through the skin and abdominal muscle wall and into the peritoneal cavity containing free fluid. Urea and creatinine may be measured if there is a question that the fluid may represent urine from a perforated bladder. Gross appearance Transudative peritoneal fluid may be clear, serous, or light yellow, especially in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Milk-colored peritoneal fluid may result from the escape of chyle from blocked abdominal or thoracic lymphatic ducts. Conditions that may cause lymphatic blockage include lymphoma, carcinoma, and tuberculosis involving the abdominal or thoracic lymph nodes. Bloody fluid may be the result of a traumatic tap, intraabdominal bleeding, tumor, or hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Bile-stained green fluid may result from a ruptured gallbladder, acute pancreatitis, or perforated intestines. Protein count Total protein levels greater than 3g/dL are characteristic of exudates, whereas transudates usually have a protein content of less than 3g/dL. It is now thought that the albumin gradient between serum and ascitic fluid can differentiate better between the transudate and exudate nature of ascites than can the total protein content. The total protein ratio (fluid/serum) has been used to differentiate exudate from transudate. Decreased levels may indicate tuberculous/bacterial peritonitis or peritoneal carcinomatosis. Amylase Increased amylase levels may be seen in patients with pancreatic trauma; pancreatic pseudocyst; acute pancreatitis; and intestinal necrosis, perforation, or strangulation. Ammonia High ammonia levels occur in ruptured or strangulated intestines and with a ruptured appendix or ulcer. Alkaline phosphatase Levels of alkaline phosphatase are greatly increased in infarcted or strangulated intestines. An exudate is identified with a higher degree of accuracy if the peritoneal fluid/serum protein ratio is greater than 0. It can be difficult to differentiate malignancy from severe inflammatory paracentesis 687 mesothelial cells. Cytology examination of the fluid is improved by spinning down a large volume of fluid and examining the sediment. Bacteria Usually the fluid is cultured, and the antibiotic sensitivities are determined. Gram stain and bacteriologic culture the presence of bacteria may indicate intraabdominal infection. Fungi Fungi may indicate infections with histoplasmosis, candidiasis, or coccidioidomycosis. A scalpel may be used to make a stab wound in the skin to allow the cannula or needle to enter. The other end of the tubing is placed in the collection receptacle (usually a container with a pressurized vacuum). Usually the volume removed is limited to about 4L at any one time to avoid hypovolemia if the ascites is rapidly reaccumulated. Although local anesthetics eliminate pain at the insertion site, tell the patient that he or she will feel a pressure-like pain as the needle is inserted. This test is useful in establishing a diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism and distinguishing nonparathyroid from parathyroid causes of hypercalcemia. Of course, surgical ablation P of the parathyroids is another cause of hypoparathyroidism. It is important for the surgeon planning resection of the parathyroid abnormality to know how many parathyroid glands are involved and their locations. Preoperative parathyroid scanning is the most accurate method of providing this information. A parathyroid adenoma or cancer, however, causes enlargement of only one parathyroid gland and suppression of the other three glands. However, parathyroid anatomic location varies considerably, and they may be located anywhere from the upper neck to the lower mediastinum. Parathyroid scanning is also done immediately prior to surgery to help the surgeon identify the parathyroid glands and particularly the pathologic glands. In this test, the scan is performed on the parathyroid glands as described previously. In the operating room, if the preoperative scan result is abnormal, the surgeon scans the suspect area of the neck with a gamma ray detector probe. P Increased counts are noted in the regions where the parathyroid abnormalities are located. For planar images, the detector is passed over the neck and upper chest area, and the radioactive counts are recorded and displayed. After Assure the patient that the dose of radioactive technetium used in this test is minute and therefore harmless. These actions prolong the intrinsic clotting pathway for approximately 4 to 6 hours after each dose of heparin. The effects of heparin can be reversed immediately by the administration of 1mg of protamine sulfate for every 100 units of the heparin dose. This drug is often given during cardiac and vascular surgery to prevent intravascular clotting during clamping of the vessels. Often, small doses of heparin (5000 units subcutaneously every 12 hours) are given to prevent thromboembolism in high-risk patients. These coagulopathies are not usually associated with excessive bleeding or thromboembolism. Remember, if the patient is receiving anticoagulants or has coagulopathies, the bleeding time will be increased. Check for blood in the urine and all other excretions and assess the patient for bruises, petechiae, and low back pain. Abnormal findings Increased levels Decreased levels Acquired or congenital Early stages clotting factor deficiencies of disseminated. Many of the severe manifestations of B19 viremia relate to the ability of the virus to infect and lyse red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow. Erythema infectiosum is the most common manifestation of B19 infection and occurs predominantly in children. Parvovirus B19 has also been associated with a number of other clinical problems, including joint inflammation, purpura, hydrops fetalis, and aplastic anemia. Because of the recently discovered spectrum of disease caused by parvovirus B19, laboratory diagnosis has come into great demand. Acute infections can be determined by B19-compatible symptoms and the presence of IgM antibodies that remain detectable up to a few months. Past infection or immunity is documented by IgG antibodies that persist with IgM antibodies. Inform the patient that it normally requires approximately 2 to 3 days to get test results. Abnormal findings Increased levels Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) Joint arthralgia and arthritis Hydrops fetalis Fetal loss Transient aplastic anemia Chronic anemia in immunodeficient patients Bone marrow failure notes pelvic ultrasonography 697 pelvic ultrasonography (Pelvic ultrasonography in pregnancy, Obstetric ultrasonography, Vaginal ultrasound) Type of test Ultrasound Normal findings Normal fetal and placental size and position Test explanation and related physiology Ultrasound examination of the female patient is a harmless, noninvasive method of evaluating the female genital tract and fetus. It should be noted that pelvic ultrasonography can be performed with the transducer placed on the anterior abdomen (see Figure 1, p. Vaginal ultrasound adds significant accuracy in identifying paracervical, endometrial, and ovarian pathology that otherwise may not be detected with the anterior abdominal probe. Major heart defects, trisomy 21, and other genetic defects are associated with increased edema in this location at this age of gestation. Assure the patient that this study has no known deleterious effects on maternal or fetal tissues. Give the patient three to four glasses (200 to 350mL) of water or another liquid 1 hour before the examination, and instruct the patient not to void until after the procedure is completed. This will permit visualization of the bladder, which is used as a reference point in pelvic anatomy. The patient is taken to the ultrasound room and placed in the supine position on the examining table. The ultrasonographer applies a greasy conductive paste to the abdomen to enhance sound transmission and reception. If a vaginal probe is used, it is inserted via the vagina and angled to identify the various parts of the pelvis. Inform the patient that no discomfort is associated with this study other than having a full bladder and the urge to void. When exposed to gastric acid, pepsinogen is converted to pepsin, an active enzyme that is proteolytic and promotes digestion. Pepsinogen I has been used as a subclinical marker of increased risk for stomach cancer. Tell the patient that antacids or other medications affecting stomach acidity or gastrointestinal motility should be discon tinued, if possible, for at least 48 hours before collection. Abnormal findings Decreased values Pernicious anemia Gastric atrophy Chronic gastritis Peptic ulcer disease notes pericardiocentesis 701 pericardiocentesis Type of test Fluid analysis Normal findings Less than 50mL of clear, straw-colored fluid without evidence of any bacteria, blood, or malignant cells Test explanation and related physiology Pericardiocentesis, which involves the aspiration of fluid from the pericardial sac with a needle, may be performed for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Therapeutically, the test is performed to relieve cardiac tamponade by removing fluid and improving diastolic filling. Diagnostically, pericardiocentesis is performed to remove a sample of pericardial fluid for laboratory examination to determine the cause of the fluid. Atropine may be given to pre vent the vasovagal reflex of bradycardia and hypotension.
Swallowing and breathing difficulties can be life threatening and there have been reports of For Injection: 100 Units or 200 Units vacuum-dried powder in a single-dose vial death blood pressure medication make you cold buy benicar toronto. Warnings and Precautions arterial blood purchase benicar with visa, Bronchitis and Upper Respiratory Seek immediate medical attention if respiratory arteria sacralis order benicar 10 mg without prescription, speech or swallowing Tract Infections in Patients Treated for Spasticity (5 hypertension nephrology associates order 40mg benicar overnight delivery. Revised: 09/2020 * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed blood pressure medication raynaud's disease discount 20mg benicar with mastercard. These may include asthenia blood pressure chart what your reading means trusted 10mg benicar, generalized muscle weakness, diplopia, ptosis, dysphagia, dysphonia, dysarthria, urinary incontinence and breathing difficulties. Swallowing and breathing difficulties can be life threatening and there have been reports of death. The risk of symptoms is probably greatest in children treated for spasticity but symptoms can also occur in adults treated for spasticity and other conditions, particularly in those patients who have an underlying condition that would predispose them to these symptoms. In unapproved uses and in approved indications, cases of spread of effect have been reported at doses comparable to those used to treat cervical dystonia and spasticity and at lower doses [see Warnings and Precautions (5. Limitations of Use Safety and effectiveness have not been established for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine (14 headache days or fewer per month) in seven placebo-controlled studies. In treating adult patients for one or more indications, the maximum cumulative dose should not exceed 400 Units, in a 3-month interval. In pediatric patients, the total dose should not exceed the lower of 10 Units/kg body weight or 340 Units, in a 3-month interval [see Dosage and Administration (2. An understanding of standard electromyographic techniques is also required for treatment of strabismus, upper or lower limb spasticity, and may be useful for the treatment of cervical dystonia. License number 1145 is not present on the vial label and carton labeling [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]. Draw up the proper amount of diluent in the appropriate size syringe (see Table 1, or for specific instructions for detrusor overactivity associated with a neurologic condition, see Section 2. Air bubbles in the syringe barrel are expelled and the syringe is attached to an appropriate injection needle. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration and whenever the solution and the container permit. Patients should discontinue anti-platelet therapy at least 3 days before the injection procedure. Patients on anti-coagulant therapy need to be managed appropriately to decrease the risk of bleeding. Overactive Bladder An intravesical instillation of diluted local anesthetic with or without sedation may be used prior to injection, per local site practice. The needle should be inserted approximately 2 mm into the detrusor, and 20 injections of 0. After the injections are given, patients should demonstrate their ability to void prior to leaving the clinic. The patient should be observed for at least 30 minutes post-injection and until a spontaneous void has occurred. Figure 1: Injection Pattern for Intradetrusor Injections for Treatment of Overactive Bladder and Detrusor Overactivity Associated with a Neurologic Condition Detrusor Overactivity associated with a Neurologic Condition An intravesical instillation of diluted local anesthetic with or without sedation, or general anesthesia may be used prior to injection, per local site practice. If a local anesthetic instillation is performed, the bladder should be drained and irrigated with sterile saline before injection. Draw the remaining 2 mL from each vial into a third 10 mL syringe for a total of 4 mL in each syringe. The bladder should be instilled with enough saline to achieve adequate visualization for the injections, but over-distension should be avoided. The needle should be inserted approximately 2 mm into the detrusor, and 30 injections of 1 mL (~6. After the injections are given, the saline used for bladder wall visualization should be drained. Chronic Migraine the recommended dilution is 200 Units/4 mL or 100 Units/2 mL, with a final concentration of 5 Units per 0. The recommended dose for treating chronic migraine is 155 Units administered intramuscularly using a sterile 30-gauge, 0. Injections should be divided across 7 specific head/neck muscle areas as specified in the diagrams and Table 2 below. A one inch needle may be needed in the neck region for patients with thick neck muscles. With the exception of the procerus muscle, which should be injected at one site (midline), all muscles should be injected bilaterally with half the number of injection sites administered to the left, and half to the right side of the head and neck. The recommended dilution is 200 Units/4 mL or 100 Units/2 mL with preservative-free 0. The lowest recommended starting dose should be used, and no more than 50 Units per site should generally be administered. Localization of the involved muscles with techniques such as needle electromyographic guidance or nerve stimulation is recommended. Adult Upper Limb Spasticity In clinical trials, doses ranging from 75 Units to 400 Units were divided among selected muscles (see Table 3 and Figure 2) at a given treatment session. When treating both lower limbs or the upper and lower limbs in combination, the total dose should not exceed the lower of 10 Units/kg body weight or 340 Units, in a 3-month interval [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5. Additional general adult spasticity dosing information is also applicable to pediatric spasticity patients [see Dosage and Administration (2. Pediatric Upper Limb Spasticity the recommended dose for treating pediatric upper limb spasticity is 3 Units/kg to 6 Units/kg divided among the affected muscles (see Table 5 and Figure 4). Limiting the total dose injected into the sternocleidomastoid muscle to 100 Units or less may decrease the occurrence of dysphagia [see Warnings and Precautions (5. The recommended dilution is 200 Units/2 mL, 200 Units/4 mL, 100 Units/1 mL, or 100 Units/2 mL with preservative-free 0. In general, no more than 50 Units per site should be administered using a sterile needle. Localization of the involved muscles with electromyographic guidance may be useful. Clinical improvement generally begins within the first two weeks after injection with maximum clinical benefit at approximately six weeks post-injection. In the double-blind, placebo-controlled study most subjects were observed to have returned to pre-treatment status by 3 months post-treatment. The hyperhidrotic area to be injected should be defined using standard staining techniques. Repeat injections for hyperhidrosis should be administered when the clinical effect of a previous injection diminishes. Patient should be resting comfortably without exercise or hot drinks for approximately 30 minutes prior to the test. The hyperhidrotic area will develop a deep blue-black color over approximately 10 minutes. To minimize the area of no effect, the injection sites should be evenly spaced as shown in Figure 6. Avoiding injection near the levator palpebrae superioris may reduce the complication of ptosis. Avoiding medial lower lid injections, and thereby reducing diffusion into the inferior oblique, may reduce the complication of diplopia. This can be prevented by applying pressure at the injection site immediately after the injection. In general, the initial effect of the injections is seen within three days and reaches a peak at one to two weeks post-treatment. Each treatment lasts approximately three months, following which the procedure can be repeated. At repeat treatment sessions, the dose may be increased up to two-fold if the response from the initial treatment is considered insufficient, usually defined as an effect that does not last longer than two months. However, there appears to be little benefit obtainable from injecting more than 5 Units per site. Injection without surgical exposure or electromyographic guidance should not be attempted. The paralysis lasts for 2-6 weeks and gradually resolves over a similar time period. About one half of patients will require subsequent doses because of inadequate paralytic response of the muscle to the initial dose, or because of mechanical factors such as large deviations or restrictions, or because of the lack of binocular motor fusion to stabilize the alignment. Initial Doses in Units Use the lower listed doses for treatment of small deviations. The symptoms are consistent with the mechanism of action of botulinum toxin and may include asthenia, generalized muscle weakness, diplopia, ptosis, dysphagia, dysphonia, dysarthria, urinary incontinence, and breathing difficulties. Swallowing and breathing difficulties can be life threatening and there have been reports of death related to spread of toxin effects. The risk of symptoms is probably greatest in children treated for spasticity but symptoms can also occur in adults treated for spasticity and other conditions, and particularly in those patients who have an underlying condition that would predispose them to these symptoms. In unapproved uses and in approved indications, symptoms consistent with spread of toxin effect have been reported at doses comparable to or lower than doses used to treat cervical dystonia and spasticity. Patients or caregivers should be advised to seek immediate medical care if swallowing, speech or respiratory disorders occur. In several of the cases, patients had pre-existing dysphagia or other significant disabilities. Hypersensitivity Reactions Serious and/or immediate hypersensitivity reactions have been reported. These reactions include anaphylaxis, serum sickness, urticaria, soft tissue edema, and dyspnea. One fatal case of anaphylaxis has been reported in which lidocaine was used as the diluent, and consequently the causal agent cannot be reliably determined. Increased Risk of Clinically Significant Effects with Pre-Existing Neuromuscular Disorders Individuals with peripheral motor neuropathic diseases, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or neuromuscular junction disorders. Patients with pre existing swallowing or breathing difficulties may be more susceptible to these complications. In most cases, this is a consequence of weakening of muscles in the area of injection that are involved in breathing or oropharyngeal muscles that control swallowing or breathing [see Warnings and Precautions (5. Deaths as a complication of severe dysphagia have been reported after treatment with botulinum toxin. Dysphagia may persist for several months, and require use of a feeding tube to maintain adequate nutrition and hydration. Aspiration may result from severe dysphagia and is a particular risk when treating patients in whom swallowing or respiratory function is already compromised. Treatment with botulinum toxins may weaken neck muscles that serve as accessory muscles of ventilation. This may result in a critical loss of breathing capacity in patients with respiratory disorders who may have become dependent upon these accessory muscles. There have been postmarketing reports of serious breathing difficulties, including respiratory failure. Patients with smaller neck muscle mass and patients who require bilateral injections into the sternocleidomastoid muscle for the treatment of cervical dystonia have been reported to be at greater risk for dysphagia. Limiting the dose injected into the sternocleidomastoid muscle may reduce the occurrence of dysphagia. Injections into the levator scapulae may be associated with an increased risk of upper respiratory infection and dysphagia. Patients treated with botulinum toxin may require immediate medical attention should they develop problems with swallowing, speech or respiratory disorders. These reactions can occur within hours to weeks after injection with botulinum toxin [see Warnings and Precautions (5. This may require protective drops, ointment, therapeutic soft contact lenses, or closure of the eye by patching or other means. It is recommended that appropriate instruments to decompress the orbit be accessible. In pediatric patients treated for lower limb spasticity, upper respiratory tract infection was not reported with an incidence greater than placebo. Urinary Retention in Patients Treated for Bladder Dysfunction Due to the risk of urinary retention, treat only patients who are willing and able to initiate catheterization post-treatment, if required, for urinary retention. Instruct patients to contact their physician if they experience difficulty in voiding as catheterization may be required. The duration of post injection catheterization for those who developed urinary retention is also shown. The duration of post-injection catheterization for those who developed urinary retention is also shown. Human Albumin and Transmission of Viral Diseases this product contains albumin, a derivative of human blood. Localized pain, infection, inflammation, tenderness, swelling, erythema, and/or bleeding/bruising may be associated with the injection. Needle-related pain and/or anxiety may result in vasovagal responses (including syncope, hypotension), which may require appropriate medical therapy. Local weakness of the injected muscle(s) represents the expected pharmacological action of botulinum toxin.
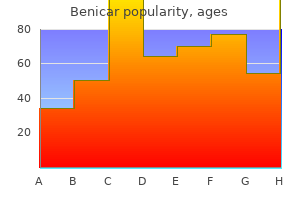
Order cheapest benicar. Why Drink Butter Coffee? The Science of Bulletproof Coffee.