Luke Kim, MD
- Clinical Fellow in Cardiology
- Greenberg Division of Cardiology
- Department of Medicine, New York
- Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Medical College
- of Cornell University
- New York, New York
The power during transmission (peak power) is 250 mW and so the average power level is 2 mW (see Section 2 herbs de provence substitute 60caps ayurslim with visa. Radio signals are reflected from buildings and other structures herbals vitamins discount ayurslim 60caps on-line, leading to multiple paths for a signal to follow from the transmitter to the receiver herbals for high blood pressure order ayurslim 60caps free shipping. The signal contributions arriving by these different paths travel different distances and so arrive at slightly different times herbs used for pain buy ayurslim 60caps visa. Also herbals dario bottineau proven ayurslim 60 caps, the path lengths differ by amounts that are larger than the wavelength (typically around 10 cm) bajaj herbals buy ayurslim with visa, meaning that the signal contributions can sum to reinforce or diminish at a given position. The consequence of multipath propagation is to create large variations in field strength over distances of the order of the wavelength, and also over short time intervals (fractions of a second). Fading implies that the exposure of a person is generally a dynamic quantity, even if the person is not moving, and the statistical characteristics of the fading in space and time have to be taken into account in how exposure is assessed. The radiative component is that part of the field which propagates energy away from the source, while the reactive component can be thought of as relating to energy stored in the region around the source. The reactive component dominates close to the source in the reactive near-field region, while the radiative part dominates a long way from it in the far-field region. Whilst reactive field components do not contribute to the radiation of energy, the energy they store can be absorbed and indeed they provide a major contribution to the exposure of people in the near-field region. The measurement of the reactive components of the field can be particularly difficult since the introduction of a probe can substantially alter the field. Since D is usually comparable in size to (or larger), 2D /is roughly 2 comparable to (or greater). Distances between /2and 2 D /form a transition region in which radiative field components dominate, but the angular distribution of radiation about the source changes with distance. Antennas with a high degree of gain, eg dish antennas, have large radiating near-field regions around them. As already noted, the power density of an electromagnetic wave, S, is equal to the product of the electric and magnetic fields, S = E H. The field structure in the reactive near-field region is more complex than that in the far-field region. Generally, the electric and magnetic fields are not at right angles to each other and they do not reach their largest values at the same points in space, ie they are out of phase. This region of the spectrum, together with optical frequencies, is therefore referred to as non-ionising. In contrast to ionising and ultraviolet radiations, where natural sources contribute the greater proportion of the exposure to the population, man-made sources tend to dominate exposure to time-varying electromagnetic fields over the spectrum shown in Figure 2. Over parts of the frequency spectrum, such as those used for electrical power and broadcasting, man-made fields are many thousands of times greater than natural fields arising from either the sun or the Earth (see Section 2. In recent decades the use of electrical energy has increased substantially for telecommunications purposes and it is clear that exposure of the population in general has increased. Many individuals will also be exposed to low level fields from microwave communications links, radar, and from domestic products, such as microwave ovens, televisions and display screen equipment. Some of the sources of electromagnetic fields and the estimated levels to which people are exposed, both at work and elsewhere, are shown in Table 2. The result of this coupling can be the induction of fields and, consequently, currents inside the body, or a rise in local or whole-body temperature. For exposure assessment purposes, both physical quantities of the electromagnetic fields (E, H and S) and dosimetric quantities (induced current density or rise in temperature, see Section 2. It is therefore important to assess the strength of the fields in order to protect the body from harmful effects. The physical quantities (E and H, and to some extent the induced current) can be directly measured outside the body, while the dosimetric quantities (induced current density or rise in temperature) are mainly assessed by indirect means inside the body. Here the methods used to measure electric and magnetic fields outside the human body are explained. In addition, the magnitude and direction of E and H vary throughout space and over time. Other factors affecting the measurements of electric and magnetic field strengths are: the frequency and power of the source; the modulation of the signal; the propagation and fading of the signal; the radiation pattern and direction of propagation; the polarisation of the field; and the physical environment. Measurement approaches also differ when the exposure is considered in the near-field or far-field regions. For all the factors mentioned above, it is important to follow a standard protocol for assessing the electromagnetic field strengths, in particular when the purpose of the assessment is to demonstrate compliance with exposure guidelines. Broadband instrumentation usually does not provide frequency information and will indicate field strength independently of frequency. Narrowband instrumentation enables assessment of both frequency and field strength information over a selected frequency bandwidth. Spectrum analysers are often used for this purpose and allow the field strength to be measured in a window of a certain bandwidth which is swept across a chosen frequency range. Narrowband instrumentation is used where frequency resolution and high sensitivity are required. Narrowband assessment is undertaken where measurements have to be made on a large number of frequencies with different limits and relatively small signal strengths. Dipoles, loops and horns, which are commonly used for field measurements, are polarisation sensitive and, to assess the total field strength, the antenna used is rotated in three orthogonal directions or orientated for maximum signal strength. Antennas that are large compared to the wavelength are unsuitable for evaluating rapidly changing amplitudes over small regions of space. Instruments covering a broad band of frequencies for field strength measurements consist of the field sensing probe and signal display equipment. Physically small dipoles are used in electric field probes and physically small loops in magnetic field probes. Usually probes are designed to indicate either one field component or the sum of all field components. Probes with a single sensor element respond to one field component only and require orientation to obtain the maximum value. Multiple sensor arrangements in suitable configurations can be used to sum the spatial field components and enable measurements independent of polarisation and direction of incidence. Sources that operate at relatively high current and low voltage, eg induction heaters, tend to be defined by measurement of the magnetic field. In situations where people couple closely to the transmitter, such as in the use of mobile phones, the external field strengths are not an appropriate indicator of exposure and comparison with exposure guidelines requires an assessment of the relevant internal dosimetric quantity. Also, the field strength at the body surface is heavily perturbed and different from the field strength that would be found at the same location in the absence of the body. Care is therefore required in the interpretation of the readings from body-worn instruments and a rigorous calibration should take account of the field perturbation by the body. When the body is exposed to radio waves, some of the energy is absorbed from the waves, a direct effect which leads to heating of the body tissues (World Health Organization, 1993). Shock is related to electrostimulation of tissues and burn occurs due to intense and rapid localised heating. At frequencies below 100 kHz, the physical quantity identifiable with most biological effects is the electric field strength in tissue, which is related to the current density. The absorption of energy from radio waves causes molecules to vibrate, which in turn leads to heating of body tissues. For a sinusoidally varying electric field, the factor of may be omitted and the rms (root mean square) value of the field substituted in this equation. It is a measure of the energy absorption inside the body and is often used as a proxy for the amount of heating or temperature rise in the body. Electrical burns can be much deeper than burns that result from contact with hot objects and they can occur at points where current exits the body as well as where it enters. The main factors that determine the potential for burn or shock are the power density and frequency of the radio waves, the grounding conditions, whether the structure has resonant dimensions and how much of the body is in contact with the conductor. Whilst constituting a hazard for those working near antennas, in medicine such contact burns are usefully applied for electrosurgery (see Section 2. It depends primarily on the output power of the radio transmitting device and the configuration of the transmitting antenna. As the distance from an antenna increases, the radio waves spread out and the power density ultimately decreases according to the inverse square law. The power density close to antennas varies in a complicated way with distance and is generally less than would be predicted from inverse square law considerations. High power broadcast and highly directional radar systems do not necessarily present a source of material exposure except to specialist maintenance workers or engineers. The field strengths typically decrease rapidly with distance from a particular source according to the inverse square law. The extent to which each of the processes occurs depends on the type of material and its thickness in relation to the frequency of the waves. When radio waves are incident on metal surfaces, reflection is the dominant process; some absorption will occur and there will be near-zero transmission. In the case of biological materials, there will be some reflection and the relative proportions of absorption and transmission will depend on the thickness of the material. Radio waves at telecommunications frequencies generally penetrate into the body tissues for a few centimetres and tend to be absorbed. In being absorbed, they give up their energy to the body tissues and this adds to the energy being produced by the bodys metabolism. On exposure to radio waves, energy is not deposited uniformly throughout the body, even if the incident radiation has uniform power density. When radio waves are incident on a homogeneous slab of material, the proportion of energy transmitted decreases exponentially with the thickness of the slab. Consequently more energy will be absorbed in the material towards the front surface facing the incoming waves than towards the rear. The electric field component of a wave penetrating into a material reduces to 37% of its initial value after a distance known as the skin depth (see Figure 2. The skin depth of tissues depends on their electrical permittivity and conductivity. The skin depths of tissues with low water content such as fat and bone are greater than those with higher water content such as muscle and skin. High water content tissues such as muscle and skin, however, are good conductors and these will absorb more strongly (see Table 2. At higher frequencies, the skin depth decreases, therefore absorption in the body becomes increasingly confined to surface tissues. Consequently most of the energy from the incident radiation is absorbed in one side of the head within a few centimetres of the handset. Body resonance the human body is particularly effective at absorbing radio waves under conditions of resonance, which occurs when the wavelength of radiation is comparable with the dimensions of the body (Dimbylow, 1997). The body then behaves as an antenna, absorbing energy in a resonant manner that depends upon the length of the body in relation to the wavelength. The frequency of resonance depends on a number of factors such as the height of the individual, their posture, how easily currents can flow from the feet to the ground, the conductivity of the earth beneath their feet, and the polarisation or orientation of the electric field with respect to the body. Smaller adults and children show the resonance characteristic at higher frequencies (Figure 2. In addition to whole-body resonance, it is possible for partial-body resonances to occur, eg in the limbs. This is based on the assumption that the body has an effective means of controlling core temperature, and that local temperature equilibration occurs through heat conduction and convection (including blood flow). Exposure guidelines, as those given in Appendix B, tend to permit higher exposures in small volumes of tissue in the head, body and limbs than are allowed when exposure is averaged over the whole mass of the body. The duration of exposure is another important factor in determining the amount of heating of the body. In a careful quantitative review of potential mechanisms, Sheppard et al (2008) have demonstrated that the dominant mechanism is dielectric relaxation and ohmic loss, giving rise to an associated increase in temperature, and that most other possible mechanisms, many based upon direct coupling to specific modes in molecules, cells or tissues, are implausible as means for independent energy deposition. Most potential candidates may be excluded because, to be biologically effective, they would be accompanied by temperature rises that would overwhelm any other biological response. Resonant molecular or sub molecular vibrational modes are precluded because they are too heavily damped, whilst other possible mechanisms involve energy that is far weaker than thermal background. Any molecule with a permanent dipole moment, when acted on by an alternating electric field, is forced to oscillate. This oscillation is hindered by the molecular environment and intermolecular forces, resulting in dielectric loss and the transfer of energy into heat. Dielectric dispersion, the dependence of the dielectric constant on frequency, arising from the change in phase between the oscillation and the applied field, gives rise to frequency dependent energy deposition and hence temperature rise. The energy deposition depends upon the local dielectric properties of the cells or tissue, and upon the local field properties. In principle, therefore, it would appear possible to create very high spatial gradients for heat generation within tissue, either because of localised microfield structure or because of local enhancements of dielectric property. Nevertheless, even if such unlikely conditions were to occur, thermal diffusion in tissue prevents the creation of high spatial gradients on the cellular scale, and any tendency to create localised hotspots cannot occur. Of specific interest in the context of the safety of mobile phones and other communications devices is the potential that non-linear demodulation of a lower, modulating or pulsing, frequency may create a low frequency electromagnetic field that may directly affect tissue. Any demodulated signal of biological significance would be accompanied by a carrier frequency of thermally destructive power. However, it is accepted that second-harmonic generation is a necessary and sufficient condition for demodulation.
I asked my medical intuitive friend to check herbal medicine cheap ayurslim 60 caps with mastercard, and sure enough himalaya herbals nourishing skin cream purchase 60caps ayurslim amex, hes calcifying like a rock herbs lung cancer discount 60 caps ayurslim amex. If he doesnt take corrective action to pull that calcium out herbals stock photos order ayurslim uk, hes going to be in big trouble within a few years zordan herbals purchase ayurslim canada. Obviously herbals in the philippines trusted ayurslim 60caps, stopping all exposure to microwave energy fields needs to be at the top of his priorities. That means radiation is emitted 24 hours a day whether the phone is being used or sitting idle in its cradle. Studies also show that there is 100% increase in adult leukemia between 45 and 130 cm from the phone and a similar increase in childhood leukemia between 35 and 260 cm. Global neglect of the Precautionary Principle is opening the way to corporate profit but placing humans and ecosystems at risk, and delaying a paradigm shift towards safer connectivity. Although it is non-ionising, and does not destabilise molecules directly, evidence of other harm has been growing since 1950s studies on radar workers. According to the updated Bio-initiative Report (2012+) by 29 precautionary scientists, effects on biology feature in several thousand, peer-reviewed papers. Few of us realise that genetic effects and free radical damage both disease risks over time are the most common, cautionary findings. Device-crowded spaces, such as our peak commuter trains or all-wireless classrooms, may be creating a subtly toxic environment. Ground-breaking work by biochemistry professor Martin Pall, Washington State University winner of eight international awards reveals a viable mechanism for such harm. The long-term, ecological implications of our new, anthropogenic radiation are not known. But peer reviewed studies revealing harm to birds, tadpoles, trees, other plants, insects, rodents and livestock, offer clues. Untested, high microwave frequencies are being lined up to increase bandwidth, automation, and usage at great profit to the industry. These millimetre and centimetre waves, though too weak to heat us, may pose possible risks to our skin, and deeper surface tissue, including that of plants. A delegation of scientists have petitioned for such electrosensitivity to be recognised as an environmentally-induced illness, with an International Disease Code (2015). The pulsed, polarized, microwaves used by wireless technologies pose more biological risks than smooth or natural waves. Weak millimetre waves have a known potential to increase antibiotic resistance: what ecological effects might they risk, perhaps, if used universally Dr Joel Moskowitz, director of community health studies at the University of California, warns "precaution is warranted before 5G is unleashed on the world". Former government physicist Dr Ron Powell points out the plans "would irradiate everyone, including the most vulnerable to harm from radiofrequency radiation: pregnant women, unborn children, young children. This drive to mine the electromagnetic spectrum come-what-may has echoes of fracking, and other headlong trends. Microwaves, Science and Lies (2014), filmed by Jean Heches across Europe, exposes similar patterns that are driving our pulsed radiation to risky levels. Western "safety limits", based only on high levels that heat tissue, far exceed those of Russia, China, and some other nations. Stealthy pollution-raisers, such as the 5G Internet of Things with 30 billion tiny transmitters forecast for 2020 and also, sadly, wireless smart-meters [1, 2*], vetoed by the American Academy of Environmental Medicine, may run counter to a cherished Green goal: that of nurturing healthy environments. Court claims for wireless-meter health harm, supported by medical testimonies including by neurology professor Andrew Marino (Louisiana) are sweeping America. Data obtained by a judge revealed all-hour, house-piercing pulses every few seconds. New data-over wiring innovations (if free of "dirty electricity") may offer inspiring, alternative ways forward. Or taking pause, we may begin to call the industry to account plus governments lulled by it. And stark risks from passive exposure, bared by Leif Salford, medical professor at Lund University. It would irradiate everyone, including the most vulnerable to harm from radiofrequency radiation: pregnant women, unborn children, young children, teenagers, men of reproductive age, the elderly, the disabled, and the chronically ill. While it may give us uber automation and instantaneous immersive entertainment a lot of questions remain with regards to public health and safety of wireless devices. Will the adoption of this new 5G technology harm directly or indirectly the consumers and businesses it hopes to attract It could connect us in our homes, workplaces and city streets to over a trillion objects around the world. This communication network will form an expanded electromagnetic microwave blanket above each city and county, permeating the airspace and providing seamless connectivity where people and things will exchange data. Engineers and physicists are busy working out the details of carrier frequencies and the architecture of the new network. Manufacturing industries are already developing commonly used products that feature wireless integration that will connect to the densely clustered antennas. Marketing companies are now pushing ads for smart devices for smart people in smart cities. Even the healthcare industry is anticipating using some of these wearable devices for patients with cardiac conditions or to do remote surgery in other parts of the world. The economic opportunities are obvious and business will be booming in the tech industry. Concerns continue to rise however about the basic safety of our current use of wireless technologies not to mention adding layers of newer microwave frequencies that have not been tested for short term or long term safety. Important questions have not been addressed while industry and government policy have already moved forward. Some felt there should be maximum spectrum usage opening up even higher frequencies that are only experimental now in order to help the underserved. Industry did not mention any potential public or environmental health hazards regarding the use of these new frequencies. They asked How will it affect children, pregnant women and the elderly who are the most vulnerable in our population She experienced insomnia at first and did not know there was a cell tower until several years later when she then associated the timing of its placement with her symptoms. After smart meters were installed in her area (but not on her house) she became sensitive to her laptop on wireless and her cell phone. Comcast then placed a Wi-Fi hotspot within 400 feet of her house and she stated her symptoms increased to the point that if she was outside in her yard more than 20 minutes she developed increasing fatigue, headaches, heart palpitations and high pitched ringing in her ears. She wrote about her concerns and that the new frequencies may add to her symptoms and inability to leave her house. What many of us deal with currently is trying to survive in an environment that is hostile to us biologically. We have lost all of our rights, our finances, our homes, our ability to earn a living due to this ubiquitous exposure. We are being tortured every second of every day and have been reduced to simply trying to survive the moments we are alive. Others have been unable to do so and have opted to not stay living on this planet of torture. You may wonder, however, more and more people from all ages, professions and walks of life are relating similar symptoms in the presence of wireless devices. He goes to great lengths to continue his profession, interact with his collegues and maintain a healthy existence. More scientific evidence links biologic effects with increased reports of health related effects including electrosensitivity. The symptoms recorded were headaches, eyestrain, fatigue, dizziness, disturbed sleep at night, sleepiness in daytime, moodiness, irritability, unsociability, hypochondriac reactions, feelings of fear, nervous tension, mental depression, memory impairment, pulling sensation in the scalp and brow, loss of hair, pain in muscles and heart region, breathing difficulties, increased perspiration of extremities. Belpomme, in 2015, completed the most comprehensive study of electrosensitivity, investigating 1216 people: 71. Effects have been demonstrated on cell membranes causing a shift in the voltage gated calcium channels. Sperm studies have consistently found genotoxic, morphologic and motility abnormalities in the presence of cell phone radiation. The most recent and compelling evidence has come from the 2016 National Institutes of Health, National Toxicology Program. The studies were robust, collaborative, well controlled and with double the number of rats required to reveal a significant effect, if present. These were the same two types of tumors shown to increase in human epidemiological studies on long term use of cell phones. Lennart Hardell and others have demonstrated a consistent pattern of increased incidence of ipsilateral (same side) acoustic neuromas (vestibular schwannomas) and gliomas with each 100 hours of cell phone use. The experiment has been done and, after extensive reviews, the consensus is that there was a carcinogenic effect. Surface effects, however, can be quite substantial on an organism as stimulation of skin receptors can affect nerve signaling causing a whole body response with physiological effects on heart rate, heart rhythm, and the immune system. In a 1998 review article, Pakhomov (123) looked at the bio effects of millimeter waves. Some effects were clearly thermal as millimeter microwaves are rapidly absorbed by water which is abundant in living organisms. Many of the millimeter frequency studies however showed effects without heating of tissues and at low intensities. Research was variable and showed both regenerative effects and also adverse effects depending on frequency, power and exposure time. Chernyakov induced heart rate changes in anesthetized frogs by microwave irradiation of remote skin areas. He noted that microwaves of different wave-lengths can induce the development of cataracts. Commercial production often precedes research on consumer protection and health effects. If we become ill, we do not question or identify the daily or weekly chemical exposures that could have contributed to that cancer or arthritis or lung disease or Alzheimers. Research shows that wireless microwave radiation adds yet another dose of toxic exposure to our daily lives. While very cool to use Google Glass and Virtual Reality may have dangerous consequences to our eyes, brain function or immune systems with long term use, especially to children. This is an obsolete standard and not considering current science showing cellular and organism harm from non-thermal effects. There is a large gap in safety data for 5G biological effects that has been demonstrated in older studies including military. Rau says a strategy to consider for those experiencing electrical sensitivity symptoms is to remove the electromagnetic hot spot in the head created by the presence of metal fillings. Concern is thus not only for the neurotoxic aspect of mercury in fillings, an increasingly understood hazard, but because fillings themselves act as antennas in the presence of electromagnetic fields from cell phones and cell towers, wi-fi networks, portable phones, and other sources of radiofrequency radiation. Rau says the removal of dental fillings can be an important early step in reducing electrical sensitivity, allowing some people to live in homes they otherwise could not tolerate. Cultures have shown beneficial bacteria grows more slowly in the presence of electromagnetic fields, says Rau, allowing pathological organisms to dominate. Thus, a strategy with electrically sensitive patients, or with those facing chronic conditions, is the aggressive supplementation with probiotics and other Biological Medicine approaches to balance intestinal flora. Linked to many acute and chronic illness conditions, electrical sensitivity is a serious emerging public health issue globally and a subject in which most doctors have no training. Rau says exposing children in schools to radiation, known to impair brain function and learning, is criminal. We know that power stations for electromagnetic waves like mobile phones are hurting the brains of children, so to put such stations into schools is reallyvery, very bad. Rau says, the question is, Does the school, or does the society, really want to have intelligent, well-educated children, or not It is estimated that 3-8% of populations in developed countries experience serious electrohypersensitivity symptoms today, and 35% experience mild symptoms. With increasing electromagnetic field exposures, these numbers, along with the suffering involved for people who are impacted, and the health care costs involved, are bound to go up. Above this level we could say electrosmog pollution is present, unless in the midst of a large solar storm. Johansson, these levels might only be seen in a cave or specially designed military installation. However, it is instructive to see the great distance between what we evolved to tolerate and the suggested guidelines above. Is it any wonder that bioeffects and health impacts would be observed under these alarming conditions The radiation levels reach the ambient levels at a distance of about 100 ft (32 meters) from the front of the meters. Practical suggestions to reduce electrosmog, based on current science cited in the BioInitiative Report 2012: the following may seem difficult to achieve in todays world (2013) but we can assure you that it is possible to take control of your environment and greatly reduce your (and your loved ones) exposure to electrosmog by applying the following suggestions. All of the above should be removed from the home and other occupied spaces during pregnancy.
Male circumcision the resection of the prepuce is the definitive surgical treatment herbs books buy generic ayurslim on line. Dorsal nerve block is reinforced by infiltration of the underside of the penis between the corpus spongiosum and the corpora cavernosa herbals during pregnancy buy 60caps ayurslim with amex. If the prepuce can be retracted herbs direct purchase discount ayurslim, carefully clean the glans and the preputial furrow with soap and water sriram herbals discount 60caps ayurslim amex. If the prepuce cannot be retracted herbs for depression cheap ayurslim amex, gently stretch the preputial opening Figure 9 herbals biz purchase ayurslim on line. Check that the lower blade really is lying between the glans and prepuce and has not been inadvertently passed up the external meatus. Then excise the prepuce by extending the dorsal slit obliquely around on either side to the frenulum, and trim the inner preputial layer, leaving at least 3 mm of mucosa (Figure 9. Insert a similar traction stitch to unite the edges of the prepuce dorsally (Figure 9. Complications the most serious complication of operation is haematoma due to failure to secure the artery to the frenulum sufficiently or to dehiscence of the stitches as a result of an early morning erection. Diagnose it by recognizing Paraphimosis should be treated a retracted, swollen and painful foreskin. The glans penis is visible, and is urgently with manual reduction surrounded by an oedematous ring with a proximal constricting ring (Figure of the foreskin or dorsal slit 9. Phimosis is prevented by reduction of the foreskin and Differential diagnosis includes: cleansing of the glans penis on a regular basis Inflammation of the foreskin (balanitis) due, for example, to infection Phimosis may be treated Swelling caused by an insect bite. Reduction of the foreskin 1 Sedate the child and prepare the skin of the genitalia with a bland antiseptic. Isolate the penis with a perforated towel and inject local anaesthetic in a ring around its base (Figure 9. Exert continuous pressure, changing hands if necessary, until the oedema fluid passes proximally under the constricting band to the shaft of the penis (Figure 9. Phimosis and paraphimosis are definitively treated with circumcision, but can be treated with a dorsal slit of the foreskin Dorsal slit can be performed with direct infiltration of the foreskin with xylocaine 1% without epinephrine (adrenaline) Clamp the foreskin with two artery forceps and make an incision between them (Figure 9. The In torsion, the testicle can predisposing factors are congenital scrotal abnormalities which include: become gangrenous in 4 hours; Long mesorchium, a horizontal lie of the testis within the scrotum treatment is thus an emergency Ectopic testis. The non-affected side should be fixed at the same time as the the presentation is one of sudden onset of lower abdominal pain, pain in the subsequent incidence of torsion on the opposite side is high affected testis and vomiting. Important differential diagnoses orchidectomy should be include: performed to protect the other Epididymorchitis: the patient often has urinary symptoms, including testis from loss due to autoimmune disease urethral discharge One testicle is enough for Testicular tumour: the onset is not sudden. Treatment the treatment is urgent surgery to: Untwist the torsion Fix the testis Explore the other side and similarly fix the testis to prevent the normal testis from undergoing torsion subsequently. Do not rush into performing orchidectomy even if, at exposure, you think that the testis is already gangrenous. Wrap the affected testis with warm wet swabs, wait for a minimum of 5 minutes and check for any improvement in colour. Do not hurry this stage; give yourself plenty of time, provided you have already untwisted the torsion. However, if the testis is dead, it should be removed, as autoimmune responses can result in loss of function of the other testis. The swelling that results is often enormous and usually Does not extend above the uncomfortable. In adults, the hydrocoele fluid is located entirely within the inguinal ligament Transilluminates Does not reduce Does not transmit a cough impulse In children, the hydrocoele often communicates with the peritoneal cavity; it is a variation of hernia and is managed as a hernia Non-communicating hydrocoeles in children under the age of 1 year often resolve without intervention the surgical management of adult hydrocoele is not appropriate for children. Treatment Aspiration is not recommended, as the relief is only temporary and repeated aspirations risk infection. Injection of sclerosants is not recommended, as it is painful and, although inflammation is reduced, it does not effect a cure. Of the various alternative operations, eversion of the tunica vaginalis is the simplest, although recurrences are still possible. Wash the scrotal skin and treat any lesions, for example wounds made by traditional healers, with saline dressings. The presence of skin lesions is not a contraindication to surgical treatment, so long as there are healthy granulations with little or no infection. Technique 1 Perform the procedure with local infiltrate, spinal or general anaesthesia. Continue incising through the layers of the scrotal wall down to the tunica vaginalis. With gauze and scissors, continue separation to the termination of the spermatic cord where it is attached to the hydrocele (Figures 9. If the sac is inadvertently opened, catch the edges of the opening with forceps and introduce a finger into the sac to stretch it and the overlying tissues as an aid in dissection. Catch the edge of the hole with forceps and, after making sure that the epididymis is not adherent to its posterior surface, slit the sac vertically with scissors (Figure 9. Biopsy the testicle, then refer the patient if tuberculosis or schistosomiasis is suspected. Reunite the edges of the everted sac behind the cord and epididymis with a few interrupted stitches of 2/0 absorbable suture (Figure 9. Maintain careful haemostasis throughout; it is important to stop even the slightest bleeding to minimize the risk of haematoma formation. Insert a latex drain, bringing it out inferiorly through a counter incision, and fix it to the skin with a stitch (Figure 9. Close the dartos muscle with interrupted 2/0 absorbable suture and the skin with interrupted 2/0 non-absorbable suture (Figure 9. If haematoma develops despite every care having been taken to 9 stop bleeding during surgery, remove a few stitches from the wound, open the edges with a pair of large artery forceps and express the clots from the wound. Antibiotics do not always prevent infection; if it does occur, give appropriate antibiotic therapy and drain the wound. Emphasize that the operation is almost always successful, but that sterility cannot be guaranteed since there is a small chance of failure. Stress that sterility will not be immediate; it can take up to 8 weeks for the patient to become completely sterile. Technique 1 Vasectomy is usually carried out with the patient under local anaesthesia. Infiltrate the deeper tissues, picking up each layer in turn to inject anaesthetic. The cut ends will be characteristically conical, with the outer fibromuscular tissues retracting from the lumen. Turn the proximal end back on itself and ligate it so that it lies outside the sheath. Close the 9 scrotal wound with a few 2/0 absorbable stitches, making sure to include the dartos layer (Figure 9. The less experienced practitioner may find it easier to identify the vas by pinching it between the thumb and finger at the lateral side of the neck of the scrotum, incising the skin directly above it, catching the vas with a pair of tissue forceps before it slips away. As an alternative, fix each vas under the skin by inserting a hypodermic needle after effecting local anaesthesia with 1% lidocaine. Make a vertical incision 1 cm long over the vas on one side, and hook it out with forceps. Obtain information about the nature of the object causing injury; sharp objects may have penetrated adjacent organs. Anaesthesia may be required to perform a thorough examination and repair of severe injuries. For vulval haematomas, 9 infiltrate the area with local anaesthesia and evacuate the clots. Complications Complications include: Infection Haematoma in the parametrium Rectovaginal fistula Dyspareunia. Rape If there is allegation of rape, make detailed records of your findings and comply fully with local legal requirements. The majority of cases are performed with non-sterile razors by Acute complications include: untrained personnel. Healed mutilation wounds with vaginal or perineal stenosis may need specialized gynaecology care. Differential diagnosis of labial masses includes: Cysts of the vaginal process Labial hernia. Treat Bartholins cysts with marsupialization but, if an abscess is present, incision and drainage is sufficient. An abscess is diagnosed by evidence of: Localized pus Throbbing pain Marked tenderness Fluctuation. Technique Incision and drainage is easy to perform, almost bloodless and provides the best chance of a cure. Pack the cavity with petroleum or saline soaked gauze and apply an external gauze dressing. The patient complains of amenorrhoea with cyclical abdominal pain or acute retention of urine. Differential diagnosis includes: Pregnancy Tuberculous peritonitis Pelvic kidney Ovarian cyst. Evert the edges of the wound and stitch them to the adjacent vaginal tissue with interrupted sutures of 2/0 absorbable suture (Figures 9. Patients present with scrotal swelling and with pain out of proportion to the physical findings. Treatment Treat with systemic broad spectrum antibiotics, fluid resuscitation, tetanus prophylaxis and complete surgical debridement, which may need to be extensive. Periurethral abscesses Infections of the male periurethral glands secondary to gonococcal urethritis or urethral stricture may lead to abscess formation. Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy include: Pregnancy induced hypertension Chronic hypertension Pre-eclampsia Eclampsia. Hypertension is diagnosed when the systolic blood pressure is 140 mmHg and/or the diastolic blood pr essure is 90 mmHg on two consecutive readings taken 4 hours or more apart. A time interval of less than 4 hours is acceptable if urgent delivery must take place, or if the diastolic blood pressure is equal to or greater than 110 mmHg. Diastolic blood pressure is a good indicator of prognosis for the management of hypertensive diseases in pregnancy. A falsely high reading is obtained when the inflatable part of the cuff does not encircle at least three-quarters of the circumference of the arm. Hypertension is classified as pregnancy induced hypertension if it occurs for the first time: After 20 weeks of gestation During labour and/or within 48 hours after delivery If it occurs before 20 weeks of gestation, it is classified as chronic hypertension. If the blood pressure prior to 20 weeks of gestation is unknown, differentiation may be impossible; in this case, manage as pregnancy induced hypertension. The presence of proteinuria changes the diagnosis from pregnancy induced hypertension to pre-eclampsia. Catheterization for the sole purpose of testing is not justified due to the risk of urinary tract infection. Women with multiple pregnancies, diabetes and underlying vascular problems are at higher risk of developing pregnancy induced hypertension. The spectrum of the disease includes: Hypertension without proteinuria Mild pre-eclampsia Severe pre-eclampsia Eclampsia. Women with pregnancy-induced hypertensive disorders may progress from mild disease to a more serious condition. When pregnancy induced hypertension is associated with proteinuria, the condition is called pre-eclampsia. Mild pre-eclampsia could progress to severe pre-eclampsia; the rate of progression could be rapid. The risk of complications, including eclampsia, increases greatly in severe pre-eclampsia. Eclampsia Eclampsia is characterized by convulsions, together with signs of pre-eclampsia. Convulsions can occur regardless of severity of hypertension, are difficult to predict and typically occur in the absence of hyperreflexia, headache or visual changes. Convulsion may be followed by coma that lasts minutes or hours, depending on the frequency of seizures. Eclampsia must be differentiated from other conditions that may be associated with convulsions and coma, including epilepsy, cerebral malaria, head injury, cerebrovascular accident, intoxication (alcohol, drugs, poisons), drug withdrawal, metabolic disorders, meningitis, encephalitis, hypertensive encephalopathy, water intoxication and hysteria. Monitor blood pressure, urine (for proteinuria) and fetal condition weekly If blood pressure rises or proteinuria occurs, manage as mild pre eclampsia If there are signs of fetal compromise, admit the woman to the hospital for assessment and possible expedited delivery Counsel the woman and her family about danger signals indicating pre-eclampsia or eclampsia If all observations remain stable, allow to proceed with normal labour and childbirth. Mild pre-eclampsia Gestation less than 36 weeks If signs remains unchanged or normalize, follow up twice a week as an outpatient: Monitor blood pressure, urine (for proteinuria), reflexes and fetal condition Counsel the woman and her family about danger signals indicating pre eclampsia or eclampsia Encourage the woman to eat a normal diet; discourage salt restriction Do not give anticonvulsants, antihypertensives, sedatives or tranquillizers. If follow-up as an outpatient is not possible, admit the woman to the hospital or set up a hostel beside your hospital where high risk mothers may stay and attend the hospital for regular checks Provide a normal diet without salt restriction Monitor blood pressure (twice daily) and urine for proteinuria (daily) Do not give anticonvulsants, antihypertensives, sedatives or tranquillizers unless blood pressure increases Do not give diuretics; these are harmful and only indicated for use in pre-eclampsia with pulmonary oedema or congestive heart failure If diastolic pressure decreases to normal levels or the womans condition remains stable, send her home: Advise her to rest and watch out for significant swelling or symptoms of severe pre-eclampsia See her twice weekly to monitor blood pressure, proteinuria and fetal condition and to assess for symptoms and signs of severe pre-eclampsia If diastolic pressure rises again, readmit her.
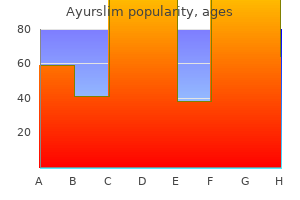
Ayurslim 60 caps without a prescription. Liver Disease and Anxiety and Depression - Liver Disease in the News.
These infections can include pneumonia wicked herbals amped ayurslim 60caps with amex, meningitis herbals for prostate buy ayurslim 60caps fast delivery, bacteremia herbals in tamilnadu ayurslim 60 caps cheap, as well as sinus and ear infections herbs de provence walmart cheap ayurslim online mastercard. Mode of Transmission: Transmission occurs primarily through contact with nose or throat secretions from an infected person herbs direct order ayurslim in united states online. Period of Communicability: A person can spread the bacteria as long as the organism is in the respiratory tract or until 24 hours after the initiation of antibiotic therapy herbals on wholesale buy ayurslim us. Exclusion/Reporting: There are no specific exclusion provisions found in Indiana communicable disease laws or rules for pneumococcal disease. The local health department should be notified of suspected and/or documented cases of pneumococcal disease if the number of cases is in excess of what is normally experienced in your school or occur with a common connection (same class, sports team, etc. Rubella is characterized by a rash that often fades or turns red and is most evident after a hot shower. Symptoms can include fever, joint pain (in adolescents and adults), and enlarged and tender lymph nodes at the back of the neck. Incubation Period: the incubation period is normally from 12 23 days, usually from 16 18 days. Mode of Transmission: Transmission occurs through direct or droplet contact with infectious nasopharyngeal secretions. Period of Communicability: An infected person is contagious from seven days prior to the appearance of the rash through seven days after the rash appears. Exclusion/Reporting: Whenever rubella is strongly suspected or confirmed, notify the local health department immediately. Students who have not presented proof of immunity against rubella are excluded until acceptable proof of immunity is presented, or in the case of medical or religious exemptions, until 23 days after the onset of the last reported rubella case. Prevention/Care: Vaccinate with rubella vaccine at 12 15 months of age and again at 4 6 years of age. Exposed pregnant women should be tested for rubella immunity, if unknown, and should consult their healthcare provider. All women of childbearing age who are contacts of a person with a suspected or confirmed case should have their pregnancy status determined. If a pregnant woman is infected with rubella, immediate medical consultation is necessary. If a pregnant woman lacks laboratory evidence of rubella immunity, precautions should be taken to prevent any type of exposure to persons infected with rubella. Early symptoms can include fever and fatigue which begin about 10 21 days after exposure. These symptoms are followed by the appearance of flat, red spots which progress to an itchy rash with fluid-filled vesicles that are characteristic of the disease. Lesions appear in crops over several days and lesions will be present in several stages of development. As varicella vaccine coverage increases, most cases are now break-through cases, which are often less severe (less than 50 lesions and do not progress to the vesicular stage). Varicella can cause serious complications including pneumonia, encephalitis, secondary bacterial infections, and even death. Incubation Period: the incubation period normally ranges from 10 21 days, but most commonly 14 16 days. Mode of Transmission: Transmission occurs primarily through contact with infectious respiratory secretions and airborne droplets. Period of Communicability: A person can spread the herpes zoster virus 1 2 days before the onset of the rash until all of the lesions have crusted over or faded, typically seven days. Exclusion/Reporting: Infected persons are excluded from schools and day care centers, public gatherings, and contact with susceptible persons until vesicles become dry, or in cases of mild, break-through disease, until the lesions have faded or disappeared. Prevention/Care: Vaccinate with a single dose of live, attenuated varicella vaccine at 12 15 months of age and revaccinate with a second dose at 4 6 years of age. An outbreak of varicella is defined as five (5) or more cases epidemiologically linked in persons younger than 13 years of age; or three (3) or more epidemiologically linked cases in persons over 13 years of age. Non belongings from others, student School environment visual inspection of reportable condition. May estimated to be 3 sexual, with infected to be communicable vaccines are licensed. Refer to page 75 Impetigo Skin lesions (red 1-3 days for Direct contact with In untreated cases as Recommended to Cover draining lesions bumps) usually streptococcal infection secretions from long as drainage from keep child home until and wear disposable around the nose, and 4-10 days for lesions lesions occurs. Norovirus infection Watery diarrhea, 24-48 hours (range of Fecal-oral While shedding, up to Exclude while Hand washing stomach cramps, 12-72 hours) 72 hours after symptomatic. Lice with resultant lice able person who has live present or eggs in hair laws for exclusion. Contacts of a Confirmed Case: Antibiotic prophylaxis Exclude for 5 days for direct contacts while receiving antibiotic therapy. Eggs food, or other articles remain infective in an (including toilet seats) indoor environment for Refer to page 66 contaminated with about 2 weeks. R chest, weight loss or develop therapy that produces Tu failure to gain a significant reduction ber weight, fatigue, in symptoms) cul Refer to page 68 chills, etc. Avoid exposure to fever, headache, bite of infected infectious to other mosquitoes during myalgia, weakness, mosquitoes. West humans except through hours of biting (from R and often abdominal Nile virus may be blood/organ donation. Within 21 days secondary lesions spread over the trunk and extremities Secondary lesions are red and scaly Rash is usually itchy Rash begins on face and Low-grade fever, joint pain Rubella virus 7 days prior to the onset of Index Case: Rubella progresses to trunk within (adolescents and adults), rash through 4 days after the 24 hours Exclude from school and contact (Link to picture of enlarged and tender lymph rash appears Flat and raised pink, disease) with individuals outside the home discrete, rash that may be nodes at the back of the for 7 days after the onset of rash absent and often fades or neck turns red without Contacts: desquamation. Most evident after hot shower Students without proof of Slight to no itch immunity are excluded until 23 days after the onset of last rubella case Pregnant women with illness or exposure need to seek medical advice 112 Rash Illnesses: Description & Information Table Period of Exclusion/ Illness Rash Description Other Symptoms Agent Communicability Attendance Rash is manifested as Scratching of rash can Sarcoptes scabiei From time of infection until 1 Exclude from school until 1 day Scabies crusts, vesicles, pustules, become infected with day after treatment after treatment. The tongue is 48 hours after treated with after beginning antibiotic therapy neck and extremities (Link to picture of covered with white fur antibiotics within 24 hours disease) Pinkish-red pinhead spots before peeling and that blanch under pressure developing into strawberry and feel similar to tongue. The surveillance of disease is the discipline of continuously gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information and data about diseases and conditions. School nurses play a vital public health role by providing ongoing surveillance of those diseases and conditions that are seen on a daily basis in the school setting; looking for any situation that is outside of the normally expected level of disease in their population. Discovering occurrences or increases in disease and reporting these findings to the local health department are the first important steps toward identifying an outbreak and controlling the further spread of that disease. As infections may occur and spread rapidly, it is important that school personnel be prepared to put processes and policies into place quickly to mitigate the spread of disease; to communicate with staff, parents and their communities in a timely manner; to continue to provide instruction and services to their student population; and above all to keep their students safe. The following are suggested points to consider and steps to take at the beginning of each school year in preparation for a possible infectious disease outbreak. To avoid the possibility that they may be excluded during an outbreak, request that all school staff contact their healthcare provider to verify their immunization history or to request appropriate laboratory testing to determine immunity status. Review student immunization records and identify those students who are not in compliance with the immunization requirements for school entry for that school year. A sample letter Parent Exclusion Notice that you may use to explain this possibility of exclusion can be found at bit. Review student immunization records and identify those students who have a religious or medical exemption on file. In an outbreak situation, it is likely that students and/or staff will be required to be excluded from attending school and school related activities (in some cases for an extended length of time), or a school may be required to close as a part of the efforts to control the spread of the disease. It is recommended that consideration be given to establishing guidelines and an outline for an alternate educational plan that can be used to provide continued educational services to those students who are impacted, whether a select number of students or the entire student body. This same consideration should be given for the situation where staff may be excluded as well. For information and assistance as it relates to developing an alternate educational plan, contact the Indiana Department of Education, Program Coordinator for Health Services at (317) 232-0541. It is the responsibility of the local health department, not the school nurse, to determine if the circumstances at hand represent an outbreak, or near outbreak situation. For either situation, guidance and instruction for next steps should come from the staff at the local health department. Close communication with the local health department is very important and will contribute to a successful and least disruptive resolution as possible to an infectious disease outbreak. If the local health department has determined the school is nearing outbreak status, follow these steps: Immunizations: 1. If they have not been addressed, implement the immunization-related steps listed above in the Preparation section. Determine the number of students that will be impacted by the outbreak (for a vaccine preventable disease outbreak it would be those whose immunization records are not complete and those who have religious or medical exemptions on file) and develop a tracking system to be used throughout the outbreak. Notify any teachers, students, and staff who may be pregnant or immunocompromised of the disease situation in the school, and refer them to their physician for guidance regarding immunizations and/or exclusion. Timely and accurate communication with staff, families, and the greater community is a critical component of the response and recovery phases of an infectious disease outbreak. During a crisis, communication with parents, staff, families, students, and the media is important and each group may require different, yet consistent, messages. Department of Education Emergency Response and Crisis Management Technical Assistance Center recommends that schools consider the following: (1) identifying the appropriate spokesperson to communicate with the media, assuring consistent and accurate messaging, (2) establishing media briefing schedules, (3) developing procedures for writing and approving news releases and (4) developing messages with consistent content for dissemination by the various agencies. Once an outbreak has been declared, close and frequent communication with the local health department is especially important! During this call, information regarding any required exclusions or other protocols for disease management will be discussed. If the steps listed above in the Immunization section of Preparation have not been implemented, it is necessary to do so at this time. Using the tracking system established earlier, document the students and staff involved in the outbreak and include the necessary information requested by the local health department. For vaccine preventable disease outbreaks this information will likely include: (1) student name and contact information; (2) date of birth; (3) dates of immunizations received related to the infectious disease of the outbreak; (4) relationship to the index case. Encourage those students and staff who may be pregnant or immunocompromised to contact their health care provider for instructions regarding immunization or exclusion options. Depending upon the infectious disease involved, these individuals may be required to be excluded from school for the length of time specific to the outbreak protocol for the disease. Items and tasks that are frequently the responsibility of school staff include: Assisting in the determination of the location for the clinic or clinics and securing the facility(ies), which may be a school building or other corporation-owned facility As necessary, arranging for bus transportation of students and staff to attend the clinic if those impacted are a part of more than one location Assisting in the security of the building and the flow of patient traffic through the facility during the clinic Assisting in identifying and notifying the students and their parents about the clinic Assisting in the distribution and collection of permission slips, immunization records, or other requested paperwork required by the local health department Communications: 1. As stated earlier, timely and accurate communication with staff, families and the greater community is a critical part of the successful management of an infectious disease outbreak. Implementing the corporations communication plan at this point will assure success. The local health department has the expertise, as well as access to other resources, that allows them to provide the most current medical advice available regarding communicable diseases. Frequently the question is raised by schools if communication with parents and the community. Taking into account that every infectious disease has specific modes of transmission and degrees of communicability and that every school corporation and community has its own history and expectations, the following points should be considered in the decision making process: o Transmission of the disease. This is a scenario where those who are at risk have been identified, contacted, and directed toward care. No other students or staff were determined to be at risk of acquiring the disease; therefore, sending communication to the entire school would not be needed or recommended. Those students and staff who were exposed to the student while they were in class have been identified and directed to receive the appropriate care. However, an unknown number of students, staff and members from other schools within the corporation or members of the community, because of vacation, extracurricular activity, or bus activity of the student, may be at risk for exposure. This is a scenario where those who are known to be at risk are identified, contacted, and directed toward care. However, because of the unknown number of individuals who might have been exposed, sending communication to the entire school and possibly corporation or community may be advised. As appropriate, implement the alternate education plan that was previously developed. Through strong, collaborative relationships, schools and local health departments can successfully manage an infectious disease outbreak, assuring that the health and safety of the students, staff and community is maintained with minimal disruption to the educational process. The Rule provides reporting instructions for physicians, hospital administrators (or their designee), and laboratories for diseases or laboratory results. It also incorporates by reference various documents that provide case definitions and guidance on measures to prevent further spread of the diseases. Those diseases listed in this rule must meet one or more of the following six criteria: 1) a nationally reportable disease, 2) a vaccine-preventable disease, 3) an emerging infectious disease, 4) an organism with significant emerging drug resistance, 5) a disease with high bioterrorism potential, and/or 6) a disease that requires a public health response based on severity and ease of transmission. As a general rule, access to student information without parent permission is limited to a specific group of school officials and those with a legitimate educational interest in the student. Recent new guidance found in the Guide for Developing High-Quality School Emergency Operations Plans (2013), from the U. Departments of Education, Health and Human Services, Homeland Security, Department of Justice, the Federal Bureau of Investigation, and the Federal Emergency Management Agency provides schools with information pertaining to the development of school safety plans and the implications for schools regarding the sharing of student personal information in emergency situations. According to the Guide, school officials have the obligation to balance both safety and student privacy interests. In applying the health and safety exception, note that: Schools have discretion to determine what constitutes a health or safety emergency. It does not allow disclosures to address emergencies that might occur, such as would be the case in emergency preparedness activities. Additionally, as it is also noted above, schools have the discretion to determine what constitutes a health or safety emergency, and thus the steps necessary for the sharing of student information. Although many of the diseases and/or conditions that are frequently found in the school setting are not found on the list of reportable diseases, it is recommended that if the number of cases seen of those diseases in the school exceeds what is typically found, it is good public health practice to notify the local health department of this situation as well. They include: the following links provide information related to Indiana Immunization Requirements: o. Develop, in consultation with the school nurse, a local attendance system for reporting symptoms and health syndromes from outbreaks or suspected outbreaks of diseases or other health conditions.