Sarah Gamble PhD
- Lecturer, Interdisciplinary

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/sarah-gamble/
Because a plant cannot be patented gastritis ka desi ilaj discount 1 mg doxazosin with amex, plants are researched for their active constituents gastritis symptoms livestrong buy discount doxazosin 1mg online, which are then isolated jenis diet gastritis discount doxazosin 1mg amex. Because it typically takes 10 to 18 years at a cost of hundreds of millions of dollars to obtain approval uremic gastritis symptoms discount 4 mg doxazosin otc, and also because of the lack of patent protection for natural plants gastritis diet x90 generic doxazosin 4 mg on-line, the American pharmaceutical industry has done very little research on plant extracts as medicinal agents gastritis xanax generic doxazosin 2mg with mastercard. In contrast, European governments have made it economically possible for companies to research and develop herbs as drugs. In Germany, herbal products can be sold with drug claims if they have been proved to be safe and efective. The German Commission E In Germany, a special expert commission called the German Commission E has developed a series of several hundred monographs. This commission is composed of physicians, pharmacists, pharmacologists, toxicologists, representatives of the pharmaceutical industry, and laypersons. After completing its work, the commission issued a monograph with a positive or negative recommendation regarding medicinal use. Several reputable American herbal companies use the monographs from the German Commission E in the preparation of their herbal supplements and follow the recommendations of the commission regarding dosage and potency. The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act The supplement industry continues to grow dramatically worldwide as more and more consumers seek natural methods of managing their health. For example, a company cannot say that glucosamine sulfate treats or cures arthritis, but it can say that it helps to build and support joint cartilage. To make these claims, manufacturers must document and substantiate their statements. They must also state that their supplements are not drugs; their labels must say that they are dietary supplements and have a supplement facts panel on them. The term nutraceutical is commonly used to describe supplements that combine several of these substances in a formulation. Products that are signifcantly cheaper than others; products that are not made by known, reputable companies; products that make claims of cure or miracle; or products the claims for which are not backed by scientifc studies should be avoided. Consumers who wish to use the growing market of supplementation would be wise to consult with a certifed herbalist, nutritionist, or other healthcare provider who is knowledgeable in the feld of supplementation. Special warnings should be given to clients who have diabetes or who are taking cardiac drugs, particularly anticoagulants, because of the increased risk of serious interactions and side efects. Knowledge of the interactions among dietary supplements and medications is in its infancy. Clients therefore should consult not only with their physicians, who have limited information in this area, but also with qualifed herbalists and nutritionists. Massage therapists should have such people involved as part of their network of healthcare professionals so that they can refer their clients to the best healthcare practitioner for their specifc needs. Numerous herbal and nutraceutical remedies are on the market today, and they are clearly beyond the scope of this appendix. Check the suggested reading list at the end of this appendix for additional sources of information. Coenzyme Improves blood circulation; increases Very safe, no serious side effects. Q10 tolerance to exercise; protects heart Numerous drugs impair the synthesis tissue from free-radical damage, of CoQ10 in the body. Echinacea Enhances resistance to infections, Side effects are rare; those allergic especially of the upper respiratory tract; to the Compositae family of plants assists in recovery from chemotherapy; might be allergic. There are no data anti-infammatory to suggest that long-term use of echinacea is harmful to immune function. Evening Anti-infammatory disorders, including Headaches, mild nausea; use caution Primrose Oil rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis; in persons with a history of epilepsy. Possible allergic dermatitis Fish Oils Lowers blood pressure, triglyceride Mostly safe for most people when (Omega-3 levels, and cholesterol, prevents heart taken in low doses (3 g or fewer Fatty Acids) disease and stroke, helps combat per day). Can cause Alzheimers disease, dry eyes, glaucoma belching, heartburn, nausea, and and age-related macular degeneration, loose stools. Hawthorn Atherosclerosis, cardiac arrhythmia, No contraindications; can act with congestive heart failure, angina, protects hypotensive drugs and increase their against myocardial damage; peripheral actions; modifcation of drug dosage vascular disease, hypertension can be necessary. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Unintentional Injury Prevention. Diferences in vitamin D status may account for unexplained disparities in cancer survival rates between African and white Americans. Opioid use disorder is increasing at alarming rates for both men and women in the United States. While the epidemic is being addressed at many different levels, much still needs to be done. Between 1999 and 2015, the rate of deaths from prescription opioid overdoses increased 471 percent among women, compared to an increase of 218 percent among men, and heroin deaths among women increased at more than twice the rate than among men. At the same time, the differences between how opioid misuse and use disorder impact women and men are often not well understood. Even in areas where differences between the sexes are apparent, such as women appearing to progress more quickly to addiction than men, very little is understood about why those differences occur. This Report highlights the key background and findings from the white paper, provides a summary of the September 2016 national meeting, and concludes with a section focused on findings and takeaways from both the national and regional meetings. This Final Report highlights the key background and findings from the White Paper, provides a summary of the national meeting, and concludes with a section focused on findings and takeaways from both the national and regional meetings. White Paperthe White Paper: Opioid Use, Misuse, and Overdose in Women was developed with the goal of ensuring that all stakeholders attending the September 2016 national meeting started from a shared level of understanding of how the unique aspects of this epidemic impact women across age, race, geography, and income. The White Paper was released on January 16, 2017, and is available at. Invitees participated in facilitated state-specific breakout sessions with resource experts on womens health and opioid addiction. This approach enabled states to identify key areas for improvement and action steps for change, as well as to develop a framework to apply lessons learned in other regions and states. Page 7 Background Opioid use disorder is increasing at alarming rates for both men and women in the United States. The prevalence of prescription opioid, heroin, and illicit synthetic opioid use among women is substantial. Between 1999 and 2015, the rate of deaths from prescription opioid overdoses increased 471 percent among women, compared with an increase of 218 percent among men, and heroin deaths among women increased at more than twice the rate than among men. The differences in how prescription opioid and heroin use impacts women and men are often not well understood. Notably, new cases of hepatitis C among women increased more than 260 percent from 2010 to 2014,11 likely increasing the risk of perinatal hepatitis C transmission to their infants. In this section, we explore some of these issues as they relate to the prevention of opioid misuse and use disorder in women. Biological Pathways to Substance Use Disorder Womens paths to substance use are complicated, and relatively little information is available regarding biological pathways in women. The biological differences between men and women in substance use are better understood with regard to nicotine and alcohol than for opioids. For instance, women metabolize nicotine faster than men, which may be related to why women generally do not respond as well as men to nicotine replacement therapies. With alcohol, evidence shows that women often become intoxicated after fewer drinks and in a shorter amount of time than men. Women tend to have smaller amounts of water in the body due to higher proportions of body fat. This can lead to higher blood alcohol concentrations after drinking compared with men of similar weight. For example, one study demonstrated that women are more sensitive to cue-induced cravings for cocaine. Women are more likely to initiate hazardous drug use while in some type of intimate partner relationship, particularly after introduction of the substance by a boyfriend or spouse. Although these factors are often generally correlated with rates of opioid use and misuse, some differences appear to exist based on sex and gender. When controlling for gender, rates are generally highest in Appalachia, along with counties in Southern and Western states. All individuals act in many ways that fulfill the gender expectations of their society. With continuous interaction between sex and gender, health is determined by both biology and the expression of gender. Death rates from drug overdose for women are more pronounced in rural areas in the South and Midwest. Though Americans in general are living longer, death rates are increasing for white, non-Hispanic women. Death rates for white, non-Hispanic women ages 15 to 54 between 2005 and 2013 for accidental poisoning, a category that includes drug overdoses (largely comprised of prescription drug overdoses), increased 121 percent compared with 80 percent for men. The increase in death rates for white American women has coincided with a shift toward prescribing opioids for more types of chronic pain rather than purely acute pain and cancer treatments, as was the case in the late 1980s to mid-1990s. There is little epidemiological evidence as to why death rates among white women have increased while death rates among other racial groups have decreased. Further, white women, specifically in the middle class, are more likely to be treated for chronic pain compared with minority women, including increasing prescription of opioids. When pain is chronic and continuous, people can experience emotional responses including anxiety and depression, which can in turn lead to more pain. Some evidence suggests that women may experience more severe clinical pain (pain as a direct result of injury or ailment). Some studies have found a link between sex hormones and pain sensitivity, including changes in pain perception across the menstrual cycle. The Guideline also reports that patients within certain groups, including women, can be at risk for inadequate pain treatment and can experience persistent pain that is not well controlled. Three days or less will often be sufficient; more than seven days will rarely be needed. The guideline also discusses the need for education aimed at correcting misperceptions including that opioids are always required for postoperative pain, or that opioid use inevitably leads to addiction. There is some evidence that exercise can help manage various types of pain as well as reduce anxiety and depression, which, as previously noted, women cite as reasons for using opioids. Given the importance that women place on their role as family caregivers, they are more likely to seek and stay in treatment longer if they are able to maintain their caregiving role while in treatment, and they are more likely to either stay within the same Page 16 treatment services or retain relationships with treatment providers throughout the provision of services. Oftentimes, women will stop using harmful substances during pregnancy, only to begin hazardous substance use shortly after birth. More than half of those adolescents who misused pain relievers in the last year are female (n=518,000). Further, 122,000 adolescents age 12 to 17 had a use disorder due to prescription pain relievers in the last year. Only a small percentage of those who use these pain relievers obtain a prescription from a medical professional (18. A University of Michigan study found people who have taken prescription opioids for legitimate medical purposes during high school have a 33 percent greater risk of opioid misuse by the age of 23. Moreover, of the nonmedical users of prescription drugs, girls in this age range are more likely to become dependent. For individuals ages 18 and older, as previously stated, males are more likely than females to misuse prescription drugs. Older Adults Some 40 to 50 percent of adults age 65 and older report the presence of a chronic pain disorder. Specifically, among patients 65 and older, 19 percent of men and 23 percent of women take at least five prescription drugs. The majority of jails report that they do not provide medications for opioid detoxification and those that do often do not use evidence-based practices. Specifically, naloxone is administered during an opioid overdose to reverse life-threatening depression of the central nervous system and respiratory system, restoring normal breathing for the person experiencing the overdose. Naloxone is a prescription medication with no potential for physical or psychological dependence. Although traditionally administered by emergency response or hospital personnel, naloxone can be administered by Good Samaritans or minimally trained bystanders, such as family and peer networks, which makes it a valuable resource in reversing the epidemic of opioid overdose deaths. With multiple formulations now available, increased availability and usage will hopefully follow for both men and women. Given the trends in increased heroin use among women, increased Page 19 availability and usage of naloxone may soon be that much more critical to prevent death from overdose among women. This leads to insufficient dosing or limitations on the duration of use of these medications (when they are used at all), which often leads to treatment failure and the perception that the drugs are ineffective, further reinforcing the negative attitudes toward their use. For example, individual, group, and family therapy may help address psychosocial complications associated with family dynamics or guilt over the adverse effects of addiction on the family. When women do enter treatment for substance use disorder, they typically present with medical, behavioral, psychological, and social problems that are generally more severe than for men, suggesting a need for gender-specific treatment approaches. Women with children may also fear that their children will be removed from their custody. In addition, the responsibilities of caregiving, in addition to undergoing treatment, can become overwhelming for some women. Successful treatment programs may need to consider providing increased supports to address this barrier.
Some babies with trisomy 18 tion is a Robertsonian translocation involving have little in the way of anomalies but may be small a fusion chromosome 14 and 21 (46 gastritis diet emedicine purchase genuine doxazosin,t14/21) gastritis mercola generic doxazosin 1 mg on-line, but for gestational age gastritis diet ��������� 4mg doxazosin fast delivery. Chromosome retardation and polyhydramnios is especially sug studies on the parents of a translocation Down gestive of trisomy 18 gastritis y colitis doxazosin 4 mg lowest price. The risk of recurrence where classical trisomy 13 baby will have microcephaly chronic gastritis diet guide order 4 mg doxazosin free shipping, one of the parents carries a balanced translocation iris coloboma gastritis diet treatment medications order 2mg doxazosin overnight delivery, abnormally shaped ears and cleft lip ranges from less than 1% to as high as 10% based on the type of translocation and the sex of the carrier 8 parent. A Down syndrome baby will occasionally be born with a 21/21 translocation (46,t21/21). The pa rents in such a situation usually have normal chromosomes, but rarely one of the parents will have 45 chromosomes and a balanced 21/21 trans location. This is an uncommon situation in which there will be a 100% risk for a child with Down syndrome. The two possibilities at conception are either Down syndrome or monosomy 21, which is typically not compatible with live birth. Essentially, all babies with trisomy 21 will be mentally retarded, usually in the moderate range. Parents often ask about this, and if mosaicism is present, they will ask whether the level of cognitive skills will be higher. This is a hard question to Figure 2 Cleft lip, overlapping ngers, abnormal answer. If mosaicism is present, it will vary from position of the thumb and polydactyly in trisomy 13. Lipson Turner syndromethe most common nding in Turner syndrome is a single X chromosome and a missing second sex chromosome (45,X0). Its frequency at conception is high, but there is erce natural selection against it. In female fetuses spontaneously aborted in the mid second trimester due to cystic hygroma and gen eralised edema, most are 45,X0. Signicant short stature, elbow cubitus valgus and a short fourth metacarpal are not present. Coarctation of the aorta in a female newborn should raise a suspicion of Turner syndrome. A renal anomaly, particularly Figure 3 Growth retardation, microcephaly, short horseshoe kidney, is characteristic but certainly palpebral ssures, ptosis, micrognathia, short sternum, not universal. Short stature is usually present by clenched hands and rocker-bottom feet in trisomy 18. The typical baby with Turner syndrome are available, and the American trisomy 18 will have microcephaly, malformed Academy of Pediatrics has published health super ears, a prominent occiput and a small mouth and vision guidelines. Other birth defects in trisomy 13 includethe chromosome ndings in Turner syndrome heart defects, albeit not usually life-threatening vary signicantly. In only about half the cases is ones, omphalocele, postaxial polydactyly, micro the karyotype 45,X0. Changes involving the struc phthalmia/anophthalmia, cutis aplasia, cryptor ture of one of the X chromosomes are common, chidism and holoprosencephaly. Trisomy 18 can particularly isochromosome of the long arm of X have many of the same anomalies, but eye and (46,X,i(Xq)). Functionally, this leads to monosomy skin malformations are less common, whereas of the short arm of one of the X chromosomes. A neural tube and limb reduction defects are more myriad of other chromosome patterns constitute common. Families search for a Y chromosome cell line is essential, have been described with anomalies suggesting since these patients are at increased risk for trisomy 13 or trisomy 18 but with normal chromo 14 a malignant tumor at a young age. The literature more strongly supports a mendelian 9 Noonan syndrome phenocopy of trisomy 13. The mortality rate is equally high for There are some clinical similarities between this both trisomies, most infants dying in a few months condition and Turner syndrome. As with Down syndrome, mo despite the fact that Noonan syndrome occurs in saicism occasionally occurs, but making meaning both the sexes. Nonetheless, the two conditions ful predictions based on its presence is perilous. In the newborn period, the Common neonatal syndromes 225 Figure 4 Edema of the foot in Turner syndrome. Facially, the typical patient has low-set and mildly dysplas Profound hypotonia tic ears, down-slanting palpebral ssures and ptosis. A short or webbed neck and pectusthe differential diagnosis of profound hypotonia is excavatum/carinatum are also typical. A detailed history is required to assess threatening renal anomalies are seen, and disor prenatal or delivery circumstances such as a te 15 ders of lymphatic vessels are more common. Growth hormone treatment has A family history can be useful in determining 16 been reported. Cognitive function is usually whether a condition is autosomal recessive (a normal and can be high, although there is an similarly affected sibling) or X-linked (similarly increased chance of needing special education. Many cases are new illustrative conditions in the differential of hypo mutations. Males syndrome become harder to identify as one ages, usually have undescended testicles. Small hands careful evaluation of the parents is necessary and feet, and almond-shaped eyes, are not useful before concluding that a sporadic case has oc diagnostic features in newborns. A few families have been reported with the long arm of chromosome 15 is involved in the multiple affected siblings and unaffected consan etiology of PradereWilli syndrome. Since ious ways depending on age and gross motor there are many mitochondria in each ovum, the risk milestone acquisition. Some allows counseling of the parents about the short specic disorders can be diagnosed prenatally via ened life expectancy, autosomal recessive inheri chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis, but tance and 25% recurrence risk. Other ndings such as facial features Myotonic dystrophy is an autosomal dominant suggestive of Down syndrome, hepatomegaly and disorder. When seen in newborns, it typically calcic stippling of the patella and epiphyses are causes respiratory distress, feeding difficulties also present. The mother absence of peroxisomes, single-membrane organ is nearly always affected, but she is commonly not elles in the cell that contain many essential aware of this. The condition is usually myotonic dystrophy, with different causation 25 lethal within a few years and has an autosomal genes. The disorder is caused by mutations in muscle weakness is proximal rather than distal. Mitochondrial myopathies refer to a group of There are primary muscle disorders that can conditions that affect the energy production in the present in the newborn period with hypotonia. Symptoms are Common neonatal syndromes 227 typically not immediately present at birth but usually arise within hours or days. In questionable cases, X-rays should be carried out, looking for vertebral defects and subtle defects of the radial side of the hand and forearm. Aberrant embryonic development of the Several additional names are used in the literature third and fourth phalangeal pouches explains to describe conditions with similar ndings: hemi many of the features of DiGeorge syndrome, such facial microsomia, oculoauriculoverterbral syn as varying degrees of maldevelopment of the drome and facioauriculovertebral syndrome. Mild facial dysmorphic features families have been described with suspected au and mild mental retardation are common. Core ndings in cases of DiGeorge syndrome are caused by a small clude hypoplasia of the bony structures of one side deletion of a specic area on the long arm of of the face, benign tumors on the external surface chromosome 22 (del22q11. This deletion is of the eye (epibulbar dermoids) and malformed often not seen with a standard banded karyotype ears. Cogni cleft lip, heart defects such as tetralogy of Fallot tive function is usually normal unless there is and ventricular septal defects, slender hands and a structurally abnormal brain. Lipson palate may lead to the diagnosis being made in the particularly the proximal long bones, leading to newborn period. Late-onset hypocalcemia and the condition being classied as one of the seizures sometimes occur in this syndrome e rhizomelic skeletal dysplasias. There are another sign of the overlap with DiGeorge syn many radiographic features of the condition. There is normally an increase in arteriosus, tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary valve the interpedicular distance from L1 to L4. If a deletion is found, parental studies achondroplasia, this measurement either stays are indicated since the deletion is inherited a small the same or decreases. Nearly all C(coloboma), H (heart disease), A (atresia of the affected people, regardless of ethnic group, have choanae), R (retarded growth and development an identical mutation in the gene. At least four of these major ndings 31 skeletal dysplasia (thanatophoric dysplasia) and should be present to conrm the diagnosis. Other a number of syndromes associated with craniosy features can include oral clefts and facial palsy. If a mid second trimester fetal survey ultrasound has been carried out, it is almost always normal. The shortening of the proximal long bones does not usually fall below the 3rd centile until the start of the third tri mester. The fetal chest measurement remains in the normal range, and the length is not signi cantly short at birth. The typical frontal bossing and scooped-out nasal bridge are not striking Figure 6 Relative macrocephaly, at nasal bridge and in newborns. The risk of recurrence is 50% if a parent has achondroplasia but quite low if the parents are of normal stature. Osteogenesis imperfecta this condition, a disorder of collagen metabolism, 34 is generally classied into four main types. If prenatal ultrasound in the mid second trimester is performed, ndings of short extremities, under mineralisation of the bones and fractures will be found. Severe short stature and spinal deformity are the result, al Figure 8 Short, broad long bones and multiple though cognitive function is normal. Osteogenesis genesis imperfecta is generally caused by dominant imperfecta can usually be condently diagnosed on the basis of the nature of the type I collagen abnormality seen in cultured skin broblasts. The more severe types of osteogenesis imperfecta are characterised by qualitative defects of type I collagen. Lipson Syndrome identication in the nursery takes References place in a setting of high emotion and anxiety. Goals, bene tion syndrome is made or considered, the involve ts, and outcomes of genetic counseling: client and genetic ment of a geneticist is essential so that proper counselor assessment. Ford B, Rupps R, Lirenman D, van Allen M, Farquharsm D, asking a series of questions about family Lyons C, et al. Renalecoloboma syndrome: prenatal de history tection and clinical spectrum in a large family. Chromosome abnormalities and multiple birth defects are present, and genetic counseling. Fritz B, Hallermann C, Olert J, Fuchs B, Bruns M, Aslan M, the babys chromosome study shows non et al. Ring X and other structural X material is present chromosome abnormalities: X inactivation and phenotype. Bleeding diathesis in Noonan Absence of widening of the lumbar inter syndrome: a common association. Genetic heterogeneity in with achondroplasia Noonan syndrome: evidence for an autosomal recessive Keep in mind the possibility of parental form. Cellular and molecular aspects of Zellweger syndrome and other peroxisome biogenesis Research is needed to determine clinical disorders. Very long-chain fatty acids in diagnosis, when standard chromosome study is normal pathogenesis, and therapy of peroxisomal disorders. Trinucleotide instability: a re genetic basis of broblast growth factor receptor 3 peating theme in inherited disorders. Annu Rev Med 1996; disorders: the achondroplasia family of skeletal dysplasias, 47:201e9. Am J Med Genet 1991; lethal osteogenesis imperfecta due to parental mosaicism 38:46e51. Here, we summarize how one such programme led to the development of the proton-pump inhibitor omeprazole (Losec, Prilosec), a conceptually new drug that proved clinically superior to previous antisecretory drugs in the treatment of acid-related disorders, and which became the worlds best-selling drug in the late 1990s. We then describe how the antisecretory and clinical effects were further improved by the development of esomeprazole (Nexium), a single enantiomer of omeprazole, which was launched in 2000. Cimetidine, condition with or without absorption, as well as providing some protection against and later comparable compounds with the same mecha change in tissue structure that bacterial infections. However, inappropriate levels of nism of action, have a marked gastric acid inhibitory results from the reflux of gastric acid into the esophagus. Treatment company Astra was also pursuing a programme options then, however, were limited. After H 124/26 had been identified, it None of the subsequently developed proton-pump was discovered that it was already covered by a patent inhibitors based on the omeprazole structure (but owned by an Hungarian company, which described the outside the original chemical patents) introduced by compound as a drug for the treatment of tuberculosis. Thiourea compounds are well-known inhibitors ity of esomeprazole was higher bioavailability, which of iodine uptake in the thyroid. A literature search of resulted in higher plasma concentrations than achiev the chemistry of thiourea compounds showed a few able with the R isomer. At the parietal-cell level, both substituted mercapto-benzimidazoles having no effect isomers are equally effective, as both are transformed to on iodine uptake, and the introduction of these sub the same active inhibitor within the parietal cell. Tests on several substituted benzi ment of omeprazole, focusing on the key discoveries midazoles showed that separation of the inhibition of and challenges, and then describe the subsequent acid secretion from the inhibition of iodine uptake development of esomeprazole (a more detailed history was obtained in a specific range of lipophilicity of of the development of omeprazole can be found in the these compounds5.
Thethe internal capsule is a broad band of projection strip of cortex bordering the central sulcus is called the bers that lies between the thalamus medially and the primary somatosensory cortex (areas 1 gastritis diet ��� buy doxazosin cheap, 2 gastritis raw food diet doxazosin 2mg without a prescription, and 3) because basal ganglia laterally (see gastritis fundus purchase doxazosin 1 mg visa. It contains all of it receives very discrete sensory information from the lat the bers that connect the cerebral cortex with deeper eral nuclei of the thalamus gastritis no appetite purchase 1 mg doxazosin with visa. Just behind the primary sen structures gastritis symptoms tagalog doxazosin 4 mg with amex, including the basal ganglia gastritis diet ����������� purchase discount doxazosin on-line, thalamus, mid sory cortex is the som atosensory association cortex (a r ea s brain, pons, medulla, and spinal cord. The two cerebral hemispheres for perceiving the meaningfulness of integrated sensory are lateral outgrowths of the diencephalon. Localized lesions of this region can cephalon by a small opening called the interventricular result in the inability to recognize the meaningfulness of foram en (see. Nevertheless, the person cannot integrate the sen processing of olfactory information occurs. The corpus callosum is a massive commissure, or bridge, of myelinated axons that connects the cerebral The m p o r a l L o b. The temporal lobe lies below the lat cortex of the two sides of the brain (see. Two eral sulcus and merges with the parietal and occipital smaller commissures, the anterior and posterior com lobes. The primary auditory cortex (area 41) is impor missures, connect the two sides of the more specialized tant in discrimination of sounds entering opposite ears. It receives auditory input projections by way of the infe-the surface of the hemispheres, which contains the rior colliculus of the midbrain and a ventrolateral tha six-layered neocortex, can be described as lateral (side), lamic nucleus. The auditory association area (area 22) medial (area between the two sides of the brain), and functions in the recognition of certain sound patterns basal (ventral). A gyrus is the ridge between ral cortex is less de ned functionally but apparently is two grooves, and the groove is called a sulcus or s important in long-term memory recall. The cerebral cortex is arbitrarily divided into lobes larly true with respect to perception and memory of com named after the bones that cover them: the frontal, pari plex sensory patterns, such as geometric gures and faces etal, temporal, and occipital lobes. The occipital lobe lies posterior to the rounds the connection between the lateral and third temporal and parietal lobes. The innermost band just above and below visual cortex (area 17), stimulation of which causes the cut surface of the corpus callosum is folded out of the experience of bright lights called phosphenes in sight but is a three-layered cortex ending as the hip the visual eld. Just outside the folded association cortex (areas 18 and 19), which is required area is a band of transitional cortex, which includes the for gnostic visual function, by which the meaningful cingulate and the parahippocampal gyri. Overall, this region of the brain is the somatosensory and the visual cortices, have a func involved in emotional experience and in the control of tion in relating the texture, or feel, and location of an emotion-related behavior. Between the auditory and in this system can lead to feelings of dread, high anxi visual association areas, the parieto-occipital region is ety, or exquisite pleasure. It also can result in violent necessary for relating the meaningfulness of a sound and behaviors, including attack, defense, or explosive and image to an object or person. Th e s ku ll is o p e n to s h o w Amygda la the falx cerebri and the right and left portions of the tentorium Uncus cerebelli, as well as som e of the cranial venous sinuses. T h e l i m b i c s y s t e m i n c l u d e s t h e l i m b i c cortex (cingulate gyrus, parahippocam pal gyrus, uncus) and the arachnoid mater is a continuous sheath of strong associated subcortical structures (mammillary body, amygdala). The cranial dura often splits into two layers, with the outer layer serving as the perios Inside the skull and vertebral column, the brain and teum of the inner surface of the skull. The surfaces of the spinal cord, brain, and rates the cerebral hemispheres and fuses with a second segmental nerves are covered with a delicate connec transverse fold, the tentorium cerebelli. The tive tissue layer called the pia m ater (Latin for deli tentorium cerebelli separates the anterior and middle cate mother). The surface blood vessels and those that depression in the skull (cranial fossae), which contains penetrate the brain and spinal cord are encased in this the cerebral hemispheres, from the posterior fossa, found protective tissue layer. A second, very delicate, non interiorly and containing the brain stem and cerebellum. The arachnoid layer is Ve n t ri c u l a r S y s t e m a n d Ce re b ro s p i n a l Fl u i d named for its spider-web appearance. The system comprises four ventricles: right and left Superior sagittal sinus lateral ventricles (the rst and second ventricles), third Ara chnoid villi ventricle, and fourth ventricle. Cerebrospinal uid is a S kin clear, colorless ultra ltrate of blood plasma, composed of 99% water with other constituents, making it close Subdural Periosteum space to the composition of the brain extracellular uid. A r a c h n o i d v i l l i, s h o w n plexus, which projects into the ventricles. Here, the waterproof arachnoid mater Ara chnoid villi l A Superior sagittal acids, and potassium ions during routine daily activi the inner dura and venous walls of the superior sagittal barrier, provide the means for maintaining the stable d i b sinus Subarachnoid space Choroidal Lathe ra l ve n tric le plexus third (see. The arachnoid villi function as Pons Inthe r ve n tric u la r Cerebellum fo r a m e n B Arthe rio le Capillary Ve in Lathe ra l ve n tric le A ations in pH and concentrations of hormones, amino t r a l o Choroida l plexus Luschka, are located at the lateral corners of the fourth fo u r th ve n tr ic le ties such as eating and exercising. The third, the median foramen of M agendie, M aintenance of a chemically stable environment is is in the midline at the caudal end of the fourth ventricle essential to the function of the brain. In most regions of the body, extracellular uid undergoes small uctu nal cord, mainly on its dorsal surface, and moves back up to the cranial cavity along its ventral surface. In adults, the mature blood-brain bar the transport of other substances between the brain and rier prevents bilirubin from entering the brain, and the the blood is slower and more controlled. Water is transported and by the processes of previously described supporting through the choroid epithelial cells by osmosis. The high sodium and low potassium contents of tems remove materials from the brain. Because the brain and spinal cord have no lym high ionic charge, such as many of the catecholamines. One area is at the nicotine, and heroin are very lipid soluble and rapidly caudal end of the fourth ventricle, where specialized enter the brain. In severely jaun blood glucose levels, contributing to hunger and eating diced infants, bilirubin can cross the immature blood behaviors. On transverse section, the spinal cord has an oval shape, and the internal gray matter has the appearance of a butter y or letter H. The ventral horns contain the output association neurons and lo w e r m o to r n e u ro n s th a t le a ve th e co rd b y th e ventral roots. Tight junctions of Th e re a re 31 p a ir s o f s p in a l n e rve s (8 ce rvica l, overlapping capillary 12 thoracic, 5 lum bar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal), endothelial cells each communicating with its corresponding body As trocyte segments. Each spinal nerve is formed by the end feet com bination of nerve bers from the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord. T h e t h r e e c o m p o n e n t s o f t h e b l o o d b r a i n carry afferent sensory axons entering the dorsal barrier: the astrocyte and astrocyte end feet that encircle the horn of the gray matter, while the ventral roots ca p illa ry, th e ca p illa ry b a s e m e n t m e m b ra n e, a n d th e tig h t ju n ctio n s th a t jo in th e o ve rla p p in g ca p illa ry e n d o th e lia l ce lls. Universal Free E-Book Store C H A P T E R 3 4 Organizationand Controlof NeuralFunction 847 an ever-changing physical environment. The term auto carry efferent axons from m otor neurons located nomic (self-governing) re ects the independent nature of this part of the nervous system or functioning largely within the ventral horn of the gray matter. It is strongly Th e b ra in ca n b e d ivid e d in to th re e re g io n s: th e affected by emotional in uences and is involved in many hindbrain, the midbrain, and the forebrain. The of the expressive aspects of behavior, including blushing, hindbrain, consisting of the medulla oblongata, pallor, palpitations, clammy hands, and dry mouth. The functions of the sympathetic nervous system include maintaining body temperature, respiration, Th e d ie n ce p h a lo n co n ta in s th e th a la m u s a n d digestion, elimination, and adjusting blood ow and hypothalamus. All sensory pathways have direct blood pressure to meet the changing needs of the body. The premotor area and primary ter of the urethra constrict, and the rate of secretion of motor cortex are located in the frontal lobe; the exocrine glands that are involved in digestion diminishes. In contrast to the sympathetic nervous system, the functions of the parasympathetic nervous system are Th e b ra in is e n clo s e d a n d p rothe cte d b y concerned with conservation of energy, resource replen connective tissue sheaths called the meninges, ishment and storage, and maintenance of organ function which consist of three layers: the dura mater, during periods of minimal activity. Exceptions are func the brain from substances in the blood that tions, such as sweating and regulation of arteriolar blood would disrupt brain function. For example, vascular smooth muscle previously discussed somatic nervous system, provides a tone is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. In this case, the toni sympathetic actions tend to be more diffuse than those cally active parasympathetic nervous system exerts a of the parasympathetic nervous system, in which there constraining or braking effect on heart rate, and when is a more localized distribution of bers. The pregangli parasympathetic out ow is withdrawn, similar to onic bers of the sympathetic nervous system may tra releasing a brake, the heart rate increases. The increase verse a considerable distance and pass through several in heart rate that occurs with vagal withdrawal can be ganglia before synapsing with postganglionic neurons, further augmented by sympathetic stimulation. In some ganglia, the ratio of preganglionic to postganglionic cells may be 1:20; Au t o n o m ic Effe re n t Pa t h w ays because of this, the effects of sympathetic stimulation are diffuse. The cell body of the contrast to the sympathetic nervous system, the para rstmotorneuron,calledthepreganglionic neuron, lies in sympathetic nervous system has its postganglionic neu the brain stem or the spinal cord. The preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous M ost visceral organs are innervated by both sympa system are located primarily in the thoracic and upper thetic and parasympathetic bers. T h e a u t o n o m i c n e r v o u s system with the parasympathetic division Splenic flexure Colon of colon Colon (cra n io s a cra l) in d icathe d in re d o n th e right and the sym pathetic division Pelvic (th o ra co lu m b a r) in d icathe d in b lu e o n Urinary Urinary bladder splanchnic bladder the left. These pregangli innervate the liver, stomach, and other visceral organs onic neurons have axons that are largely myelinated and. The postganglionic neurons of the sym the sympathetic ganglia contain interconnecting neurons pathetic nervous system are located in the paravertebral similar to those associated with complex circuitry in the ganglia of the sympathetic chain that lie on either side brain and spinal cord, many of which inhibit modulate of the vertebral column, or in prevertebral sympathetic preganglionic-to-postganglionic transmission. Sympathetic communicans preganglionic bers (blue) le a ve Splanchnic the spinal cord by way of the nerves ventral root of the spinal nerves, enter the ventral primary rami, and White ra mus Synapse communicans pass through the white rami to the prevertebral or paravertebral ganglia To s t o m a c h a n d of the sympathetic chain, where other abdominal they synapse with postganglionic vis ce ra Prevertebral neurons (black). Oth e r p re g a n g lio n ic ganglion neurons (red dotted lines) tra ve l directly to their destination in the Be low L2 various effector organs. Local re ex circuits relating visceral afferent and and leave the spinal nerve through white rami of the rami autonomic efferent activity are integrated into a hierar communicantes to reach the paravertebral ganglionic chic control system in the spinal cord and brain stem. In the sympathetic chain of ganglia, Progressively greater complexity in the responses and preganglionic bers may synapse with neurons of the gan greater precision in their control occur at each higher glion they enter, pass up or down the chain and synapse level of the nervous system. M ost visceral re exes with one or more ganglia, or pass through the chain and receive input from the lower motor neur ons that inner move outward through a splanchnic nerve to terminate in vathe skeleta l muscles a s par t of their response pat ter ns. The adrenal medulla, which thalamus, which has connections with the cerebral is part of the sympathetic nervous system, contains post cortex, the limbic system, and the pituitary gland, ganglionic sympathetic neurons that secrete sympathetic is in a prime position to receive, integrate, and trans neurotransmitters directly into the bloodstream. The neurons concerned with thermoregulation, thirst, Pa ra s y m p a t h e t ic N e rv o u s S y s t e m and feeding behaviors are found in the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus also is the site for integrating neuro As is true in the sympathetic nervous system, efferent para endocrine function. H ypothalamic releasing and inhib sympathetic nerve signals are carried from the central ner iting hormones control the secretion of the anterior vous system to their targets by a two-neuron pathway. The central regions duce complex combinations of autonomic and somatic of origin are the midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, and efferent functions required for the cough, sneeze, swal sacral part of the spinal cord. The out ow from the mid low, and vomit re exes, as well as for the more purely brain passes through the oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve autonomic control of the cardiovascular system. As with other spinal re exes, these arethe vagus nerve provides parasympathetic innervation for modulated by input from higher centers. When there is loss the heart, trachea, lungs, esophagus, stomach, small intes of communication between the higher centers and the spi tine, proximal half of the colon, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, nal re exes, as occurs in spinal cord injury, these re exes kidneys, and upper portions of the ureters. Sacral preganglionic axons leave the S2 to S4 seg mental nerves by gathering into the pelvic nerves. The sacral para are self-propagating action potentials with transmission sympathetic bers also supply the venous out ow from of impulses across synapses and other tissue junctions the external genitalia to facilitate erectile function. The membranes of the cells of sympathetic preganglionic bers pass uninterrupted to many smooth muscle bers are connected by gap junc short postganglionic bers located in the organ wall. In tions that permit rapid conduction of impulses through the walls of these organs, postganglionic neurons send whole sheets of smooth muscle, often in repeating waves axons to smooth muscle and glandular cells that modu of contraction. Schem atic illustration of (A) parasym pathetic cholinergic and (B) sym pathetic noradrenergic neurotransmitter synthesis, release, receptor binding, neurotransmitter degradation, and metabolite transport back into the presynaptic neuron (acetylcholine) and reuptake (norepinephrine). Ac e t y lch o lin e a n d Ch o lin e rg ic Re c e p to rs Cell membrane receptors that respond to acetylcholine are called cholinergic receptors. Some skeletal cholinergic neurons from choline and acetyl coenzyme A muscle relaxants, such as succinylcholine and tubocura (acetyl CoA) by a single step reaction catalyzed by the bio rine, can be used to induce muscle relaxation and short synthetic enzyme choline acetyltransferase. Muscarinic acetylcholine recep into vesicles that are concentrated on the inner surface of tors are present on the innervational targets of postgangli the presynaptic neuron. Because it is a muscarinic-blocking line molecule is transported back into the nerve ending, drug, it exerts little effect at nicotinic receptor sites. The excitatory or inhibitory responses of organs to sympathetic neurotransmitters arethe catecholamines constitute a class of neurotransmit mediated by interaction with cell membrane receptors. The adrenergic receptors neurological, psychiatric, endocrine, and cardiovascular have been further subdivided into 1 and 2 receptors, diseases. Catecholamines are characterized by a catechol and adrenergic receptors into 1, 2, and 3 receptors. Norepinephrine is released at most including those of the skin, gastrointestinal tract, kidney sympathetic nerve endings. The 2 receptors are mainly located presyn is a modi ed neural crest tissue, produces epinephrine aptically and can inhibit the release of norepinephrine along with small amounts of norepinephrine. The 1 receptors are principal inhibitory transmitter of interconnecting neu primarily found in the heart; they mediate an increase in rons in the sympathetic ganglia.
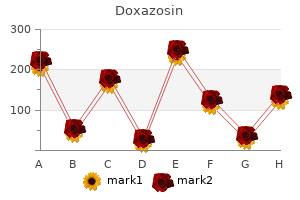
Multiple gestation12 gastritis diet ������ order doxazosin 1 mg overnight delivery,57 include the ability to perform the procedure in an outpatient 12 setting and without an incision gastritis diet for children order doxazosin paypal. Use of oral anticoagulants during pregnancy 80 waiting period until tubal occlusion is conrmed gastritis upper left abdominal pain doxazosin 2 mg visa. Mechanical valve prosthesis57 for the male partner is another efficacious option gastritis en ingles buy 2mg doxazosin, but the long term prognosis of the female partner must be taken into Modied from Siu et al gastritis joghurt quality 4mg doxazosin. The rst trime Contraceptive methods include combined hormonal contracep ster is the safest time for elective pregnancy termination gastritis upper right back pain doxazosin 1 mg without a prescription, which tives (oestrogen/progestin), progestogen-only methods, intrauter should be performed in hospital, rather than in an outpatient facil ine devices, and emergency contraception. Gynaecologists routinely medroxyprogesterone acetate are inappropriate for patients with advise antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent post-abortal endometritis, heart failure because of the tendency for uid retention. It should be borne in mind that 5% of patients Up to 7 weeks gestation, mifepristone is an alternative to experience vasovagal reactions at the time of implant; therefore, for surgery. When prostaglandin E compounds are given, systemic those with highly complex heart disease. Antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended at the time of Saline abortion should be avoided because saline absorption can insertion or removal since the riskof pelvic infection is not increased. Tubal ligation is usually accomplished safely, even in relatively high Thrombo-embolism may complicate in vitro fertilization when high 86 risk women. Because of the associated anaesthesia and abdominal oestradiol levels may precipitate a prothrombotic state. Congenital heart disease and pulmonary hypertension Table 9 General recommendations In many women with congenital heart disease, pregnancy is well tolerated. The risk of pregnancy depends on the underlying Recommendations Classa Levelb heart disease as well as on additional factors such as ventricular Pre-pregnancy risk assessment and counselling and valvular function, functional class, and cyanosis. The miscar is indicated in all women with known or riage rate is higher in more complex disease 1). High risk patients should be treated in I C Offspring complications, including offspring mortality (4%), are specialized centres by a multidisciplinary team. Diagnosis Echocardiography should be performed in any pregnant patient with unexplained or new I C Usually, congenital heart diseases will be known and diagnosed cardiovascular signs or symptoms. Pre-pregnancy assessment including medical Before cardiac surgery a full course of history, echocardiography, and exercise testing is indicated in all corticosteroids should be administered to the I C patients, with other diagnostic tests indicated on an individual mother whenever possible. Functional status before pregnancy and history of For the prevention of infective endocarditis in pregnancy the same measures as in non I C previous cardiac events are of particular prognostic value (see pregnant patients should be used. Diagnostic procedures that can be used during pregnancy are When gestational age is at least 28 weeks, 21 outlined in Section 2. This occurs even in patients with little or no dis hypoxia, and acidosis which may precipitate refractory heart ability before or during pregnancy. Supplemental oxygen therapy should be given if there is are: late hospitalization, severity of pulmonary hypertension, and 87 hypoxaemia. The risk probably increases with more elev occasionally used antenatally and peripartum to improve haemody ated pulmonary pressures. In patients where the indication for anticoagulation basis of all available diagnostic modalities in a specialized centre. In portal hypertension, anticoagulation is not recommended in view of the risks of anaesthesia this should be performed in a patients with increased risk of bleeding. It oxygen saturation is,85%, a substantial maternal and fetal mor should be recognized that potentially signicant drug interactions tality risk is expected and pregnancy is contraindicated. Plannedthe degree of maternal hypoxaemia is the most important predic caesarean delivery and vaginal delivery are favoured over emer tor of fetal outcome. If, however, maternal oxygen saturation is,85%, the chance of a live birth is 91 3. Maternal risk Eisenmenger patients need special consideration because of the Management association of pulmonary hypertension with cyanosis due to the Follow-up. Systemic vasodilatation increases the plemental oxygen (monitoring oxygen saturation) are rec right-to-left shunt and decreases pulmonary ow, leading to ommended. Because of the increased risk of paradoxical increased cyanosis and eventually to a low output state. The litera embolism, prevention of venous stasis (use of compression stock ings and avoiding the supine position) is important. Thrombo-embolism is a major risk for Obstetric and offspring risk cyanotic patients, therefore patients should be considered for pro Cyanosis poses a signicant risk to the fetus, with a live birth unli phylaxis after haematology review and investigations for blood kely (,12%) if oxygen saturation is,85%. When pregnancy occurs, the risks should be discussed cated and managed in the same way as in patients with Eisenmen and a termination of pregnancy offered; however, termination ger syndrome. If the patient wishes to continue with preg nancy, care should be based in a specialist unit. Thrombo-embolism is a major risk for cyanotic patients, fetal condition deteriorates, an early caesarean delivery should be therefore patients should be considered for prophylaxis after hae planned. In view of the risks of anaesthesia this should be per matology review and investigations for blood haemostasis. Antic formed in a tertiary centre experienced in the management of oagulation must be used with caution, as patients with these patients. In others, timely hospital admission, planned elec Eisenmenger syndrome are also prone to haemoptysis and throm tive delivery, and incremental regional anaesthesia may improve maternal outcome. The risks and benets of anticoagulation must there fore be carefully considered on an individual patient basis. It may be valvular, supravalvular, or caused by oxygen saturation measurement and full blood count are indicated. The manage ment of supravalvular and subvalvular stenosis is only described in Delivery. If the maternal or fetal condition deteriorates, an early case reports during pregnancy and is probably similar to the man caesarean delivery should be planned. In view of the risks of anaes thesia this should be performed in a tertiary centre experienced in agement of patients with valvular stenosis, although balloon valvu 92 the management of these patients. Although patients need pregnancy evaluation of the presence of a (residual) defect, to be informed about the (often small) additional risk, pregnancy cardiac dimensions, and an estimation of pulmonary pressures is should not be discouraged. The Obstetric and offspring risk follow-up plan should be individualized taking into account the Pre-eclampsia may occur more often than in the normal complexity of the heart disease and clinical status of the patient. The risk of heart failure is low and only exists in women with severe regur gitation or impaired ventricular function. Offspring mortality has been reported in 6%, primarily due to the occurrence of complex con 99 genital heart disease. For a secun Management dum defect, catheter device closure can be performed during preg Follow-up. Follow-up during pregnancy is advisable at least once nancy, but is only indicated when the condition of the mother is each trimester. Clinical and echocardiographic follow-up is indi deteriorating (with transoesophageal or intracardiac echocardio cated monthly or bimonthly in patients with moderate or severe graphic guidance). For rec Because of the increased risk of paradoxical embolism, in ommended preventive measures for thrombo-embolism, see women with a residual shunt, prevention of venous stasis (use of Section 3. Pregnancy is often well tolerated in women after repair of coarcta Spontaneous vaginal delivery is in most cases appropriate. Other risk factors for this complication include aortic dilatation and bicuspid aortic valve, and they 3. The Obstetric and offspring risk rate of progression of stenosis in these young patients is lower 107 An excess of hypertensive disorders and miscarriages has been than in older patients. Hypertension should be treated, undergo imaging of the ascending aorta before pregnancy, and although aggressive treatment in women with residual coarctation surgery should be considered when the aortic diameter is must be avoided to prevent placental hypoperfusion. The use of covered stents may lower the risk In unrepaired patients, surgical repair is indicated before preg of dissection. Spontaneous vaginal delivery is preferred with use of epi pregnancy have been reported in up to 12% of patients. Pre women with marked dilatation of the right ventricle due to pregnancy relief of stenosis (usually by balloon valvuloplasty) severe pulmonary regurgitation, pre-pregnancy pulmonary valve should be performed in severe stenosis (peak Doppler gradient 19 19,68,105 replacement (homograft) should be considered. Severe pulmonary regurgitation has been identied as an inde Obstetric and offspring risk pendent predictor of maternal complications, especially in patients 76,106the risk of offspring complications is increased. Follow-up every trimester is sufficient in the majority of prosthesis) should be considered. In women with severe pulmonary regurgitation, monthly or bimonthly cardiac evaluation with echocardiography is indi Obstetric and offspring risk cated. Transcatheter valve hypertension-related disorders including (pre-)eclampsia, may be implantation or early delivery should be considered in those 103 who do not respond to conservative treatment. The incidence of offspring compli 103 cations also appears to be higher than in the general population. The preferred mode of delivery is vaginal in almost all Pulmonary regurgitation generally carries no additional offspring cases. The incidence of arrhythmias may rise during preg have an increased risk of developing complications such as arrhyth nancy and is associated with a worse prognosis. Women with Ebsteins anomaly and interatrial shunting can develop shunt reversal and cyanosis in pregnancy. There is also a risk of paradoxical emboli (see Obstetric and offspring risk Section 3. Maternal risk Though many women tolerate pregnancy relatively well, after an Delivery. In asymptomatic patients with moderate or good ventri atrial switch operation (Senning or Mustard repair) patients have cular function, vaginal delivery is advised. If ventricular function an increased risk of developing complications such as arrhythmias deteriorates, an early caesarean delivery should be planned to avoid the development or worsening of heart failure. There is probably a higher maternal risk if the Fontan circuit is Obstetric and offspring risk not optimal, and careful assessment pre-pregnancy is indicated. The offspring risk includes premature birth, small for gestational age, and fetal death in up to 50%. In asymptomatic patients with moderate or good ventricu lar function, vaginal delivery is advised. If ventricular function deteriorates, an early caesarean delivery should be planned to Management avoid the development or worsening of heart failure. It is recommended that Fontan patients have frequent surveillance during pregnancy and the rst weeks after delivery Arterial switch operation (every 4 weeks), and care in a specialist unit is recommended. Even though thrombo-embolic complications were not described in a literature seems low in these patients when there is a good clinical condition review on pregnancy in Fontan patients, the risk must be con pre-pregnancy. The thrombo-embolic risk may be lower in patients treated with a total cavopulmonary Fontan correction. If ventricular Maternal risk function deteriorates, an early caesarean delivery should be In patients with congenitally corrected transposition of the great planned in an experienced centre to avoid the development or arteries (also called atrioventricular and ventriculo-arterial worsening of heart failure. Aortic diseases during pregnancy which lead to histological changes in the aorta, 120 increasing the susceptibility to dissection. Dissection occurs Several heritable disorders affect the thoracic aorta, pre-disposing most often in the last trimester of pregnancy (50%) or the early post patients to both aneurysm formation and aortic dissection. Also other forms of con tion are at high risk of aortic complications during pregnancy. Therefore, all women with genetically proven Marfan syn and nally non-heritable aortic pathology may occur. Risk factors drome or other familial aortic pathology should have counselling on for aortic pathology in the general population are hypertension the risk of dissection and the recurrence risk, and have a complete and advanced maternal age. Pregnancy is a high risk period for evaluation including imaging of the entire aorta before pregnancy all patients with aortic pathology, and aortic pathology is reported (see Section 2. A number of imaging procedures and genetic tests are Patients with Marfan syndrome and a normal aortic root available, and are discussed in Sections 2. Dissection is rarethe risk of (pre)eclampsia is increased, and treatment of hyperten with an aortic diameter,40 mm, although a completely safe diam sion is important, especially during pregnancy. Following elective aortic root replacement, patients remain at risk for dissec Follow-up and medical therapy. Pregnancy should be supervised by a cardiol an increase in mitral regurgitation may occur and may lead to com ogist and obstetrician who are alert to the possible complications. However, in a recent regurgitation before pregnancy (see also Section 5 on valvular meta-analysis,132 including mostly studies with non-pregnant disease). In spite of these uncertainties, the Task Force recommends the use of b-blockers in patients with Marfan syndrome during pregnancy to prevent dis 4. Fetal growth maximal in the distal part of the ascending aorta, which cannot should be monitored when the mother is taking b-blockers. Caesarean section should be hernias, and varicosities, and suffer rupture of large vessels or performed in a hospital in which cardiothoracic surgery and neo rupture of the uterus. Because of the risk of uterine rupture, natal intensive care facilities are available. The role cardiothoracic, cardiology, obstetric, and anaesthetic physicians of prophylactic surgery is less well established in this patient must act rapidly to deliver the fetus (if viable) by caesarean delivery in cardiac theatres and proceed directly to repair of the dissection. The primary aim of intrapartum man dency to haemorrhage extensively, and poor wound agement in patients with ascending aorta enlargement is to reduce healing. Caesarean delivery may also be considered in these no quantitative evidence exists on the risk of dissection attribu patients, based on the individual situation. Regional anaesthesia table to pregnancy in women with Turner syndrome, the risk techniques can be difficult in Marfan patients, depending on the probably is increased and is higher if the woman has additional presence and severity of scoliosis and presence of dural risk factors such as bicuspid aortic valve, CoA, and/or hyperten ectasia.
Order 4 mg doxazosin visa. Helicobacter pylori.