Luoping Zhang PhD, MS
- Adjunct Professor, Toxicology

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/luoping-zhang/
Fetal intrauterine growth restriction is a frequent and expected by product of uteroplacental ischemia muscle relaxant overdose treatment cheap nimotop american express. Interestingly spasms in 6 month old baby generic 30 mg nimotop amex, despite the increase in fetal growth restriction and prematurity muscle relaxant anesthesia buy nimotop 30 mg without prescription, preeclampsia is associated with a decreased risk of cerebral palsy (4) spasms coronary artery order nimotop online from canada. Because this condition is often asymptomatic spasms cure nimotop 30 mg, screening is indicated between 24 and 28 weeks gestation infantile spasms 6 weeks generic nimotop 30 mg online. Glucose management is strict with the recommendation to maintain levels between 60 and 120 mg/dl. It is well established that tight metabolic control is associated with a marked reduction in the fetal and neonatal complications associated with diabetes in pregnancy listed in the table below: Fetal and Neonatal Complications of Diabetes in Pregnancy: A. Macrosomia occurs in 25%-45% of pregnancies complicated by diabetes which is a direct result of fetal hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. Additional substances of abuse include cocaine, heroin, and miscellaneous other agents. As a general rule, the severity and frequency of fetal/neonatal side effects associated with maternal substance abuse is related to timing, dose, and duration of use. Pharmacotherapy for severe withdrawal symptoms include tincture of opium, phenobarbital, and methadone. Microcephaly, mild to moderate mental retardation, subtle cognitive and behavioral deficits have all been well described. No consistent or specific complications have been associated with the use of marijuana in pregnancy. Breastfeeding is contraindicated as cocaine intoxication has been demonstrated in breast fed infants. Selective drug screening of mothers and newborns takes place routinely at most perinatal centers. Decisions regarding who to screen is often related to other perinatal risk factors such as inadequate prenatal care, previous history of substance abuse, high risk clinical signs in the mother (inappropriate or unusual behavior), history of prostitution, history of preterm labor, and presence of sexually transmitted disease(s). It is important for the pediatrician to be fully aware of maternal risk factors so that he/she may be fully prepared to receive the newborn in the delivery room and provide ongoing care. Timely recognition of certain high-risk conditions during pregnancy often results in the transfer of the mother and fetus to a facility equipped to provide subspecialty care. True/False: Preeclampsia is a complication of pregnancy associated with hypertension and proteinuria. The mother was hospitalized at 27 weeks gestation due to cervical changes and received 2 doses of betamethasone two weeks prior to delivery. He has a normal precordium and a grade 2/6 holosystolic murmur at the upper left sternal border. Because of a persistent heart murmur, an echocardiogram is performed which reveals a moderate to large patent ductus arteriosus with normal cardiac anatomy and function. He continues on parenteral nutrition but his feedings had to be discontinued due to abdominal distention and the presence of excessive residual breast milk noted in a gastric aspirate obtained just prior to his next feeding. Neonatal transition is the process involved in physiologic adaptation of the fetus to extrauterine life. Premature babies are at higher risk for slower transition to neonatal life due to immaturity of organ systems and lack of body mass. This leads to a higher incidence of low Apgar scores and need for resuscitation in the delivery room. This can be avoided by providing exogenous heat with a radiant warmer during transition and minimizing heat loss by drying them quickly (evaporation of amniotic fluid on the skin is a potential cause of significant heat loss). These infants are at risk for hypoglycemia because of limited glycogen stores and relatively immature glucose homeostatic mechanisms. Respiratory problems are among the most common and important conditions related to prematurity. An additional factor is the incomplete development of the lungs (respiratory immaturity or immature lung disease). Some of the risk factors contributing to this injury include positive pressure/ventilator support (barotrauma), oxygen (oxygen toxicity), infections, and aspiration. The caloric intake required for the preterm infant to approach intrauterine growth rates is in the range of 120 to 150 Kcal/kg/d. Thus, the majority of premature infants are at total enteral feedings within the first three weeks of life. Parenteral nutrition is comprised of a mixture of dextrose (carbohydrates), amino acids (proteins) and intralipids (fat) along with electrolyte additives and multi-vitamin supplements. Specially prepared formulas for preterm infants also contain additional amounts of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamins. Risk factors include systemic infection, rapid advance of enteral nutrition, decreased intestinal blood flow (relative ischemia), the presence of catheters in umbilical vessels, and poor gut motility. Perforation presents clinically with pneumoperitoneum, peritonitis, abdominal wall discoloration, and/or portal venous air. Premature infants are not able to regulate their body temperatures as well as term infants. Factors that contribute to this problem are immaturity of the hypothalamic regulatory center, lack of subcutaneous fat (insulation shield), lack of brown fat (allows for thermogenesis in adverse climatic environmental conditions) and a relatively large body surface area to body mass ratio. Typically, temperature control is maintained by providing an external heat source (radiant warmers or incubators/isolettes). However, they remain at continued risk for poor thermal regulation at the extremes of environmental temperature. The occurrence of physiologic jaundice in otherwise healthy term newborn infants is well recognized. Whether premature infants are at greater risk for bilirubin neurotoxicity is unclear. In the absence of such complications, there appears to be no evidence to suggest that bilirubin is more neurotoxic to the premature brain. The most common cardiovascular problem in premature infants is the persistence of the ductus arteriosus. Clinically, infants may present with a varied constellation of signs and symptoms that, in addition to a systolic murmur heard best at the left upper sternal border, include tachycardia, active precordium, bounding pulses, and cardiomegaly with pulmonary congestion on chest x-ray. Patent ductus arteriosus can be managed medically by using fluid restriction and indomethacin (prostaglandin inhibitor) therapy or surgically, by ductal ligation. The germinal matrix is a unique vascular bed that is present in the region of the choroid plexus during development. In infants born prior to 32 weeks gestation, this area is prone to vascular accidents that can lead to intraventricular hemorrhage. One of the most important factors predisposing to hemorrhage in this area is hypoxic-ischemic injury. This type of intracranial hemorrhage tends to occur within the first week of life. The lesions of periventricular leukomalacia are visualized as discrete cystic lesions in the periventricular white matter on cranial ultrasound. With timely developmental intervention, there is evidence that neurodevelopmental outcomes can be improved. The majority of apnea events in premature infants are typically mixed (central and obstructive) in origin. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Ophthalmologists have jointly recommended a schedule for screening high risk premature infants for this disorder. Later on in life, prematurely born infants are at higher risk for refractive errors and, therefore, need to be closely monitored. Premature infants are at the same risk for developing anemia of infancy as are term infants. Anemia of prematurity may at least partially be overcome by the use of erythropoietin, which is used to stimulate erythropoiesis. Nevertheless, it is important to replenish the bodys iron stores and the provision of supplemental iron is critical until the hemoglobin levels reach normal values for age. In this respect, the iron supplementation during therapy should be at the levels used in the treatment of anemia at any other age (up to 6 mg/kg/d of elemental iron). The primary source of immunity for the neonate is passively derived antibodies from the mother and this tends to occur primarily in the third trimester. This mandates close monitoring for infectious complications, both during hospitalization, in the immediate neonatal period, and in subsequent months during the first year of life. The only exception to this rule is the hepatitis B immunization, which should be initiated only after the infants weight exceeds 2 kg. Despite lower titers of antibody response in these infants, there is no recommendation for additional doses of specific immunizations. In addition, and most importantly, it is critical that the parents/caregivers feel comfortable with the care of the infant in the home environment. Many of these infants will have additional needs and it is important that all of these needs and appropriate community resources are identified prior to discharge. At the time of discharge, the routine mandated screening for hearing and metabolic diseases should be completed with the results forwarded to the primary care physician. The long term outcome of premature infants is inversely related to gestational age (better outcomes in older infants), and directly related to the clinical course in the neonatal period, and the associated morbidities and diagnoses during their hospitalization. In general, these infants need close neurodevelopmental monitoring and early interventions for identified problems. They are at increased risk for repeated hospitalization for various residual problems of prematurity such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia, failure to thrive, and feeding problems. Developmental outcome is also related to the home environment and the ability of the family to properly nurture the infant. Unfortunately, the stress associated with parenting a high-risk infant often leads to dysfunctional family dynamics. Strategies to reduce thermal stress at birth should include (mark all correct answers): a. They are born with adequate glycogen stores but have immature homeostatic mechanisms to mobilize glucose. They are born with inadequate glycogen stores but have mature homeostatic mechanisms to mobilize glucose. In contrast to term infants, the following statements are true regarding physiologic jaundice in the premature infant in the neonatal period (choose one): a. The following statements regarding the persistence of ductus arteriosus are true in the premature infant (choose one): a. Over the next several hours, the infant develops progressively more distress and a greater oxygen requirement. This chapter will cover the common problems which cause respiratory distress in the newborn within the first week of life. Based on the clinical presentation, onset and gestational age, the most likely diagnosis can be determined. The most significant discriminatory findings are the onset of the illness and the degree of distress exhibited by the infant. Typically, the infant becomes tachypneic immediately after birth and has mild respiratory distress. If followed closely, infants remain stable for several hours and/or begin to improve. As a consequence, meconium aspiration is considered to be a relatively common event. Infants with aspiration syndromes may require more oxygen, and have greater degrees of tachypnea, retractions and lethargy. Pulmonary hypertension may be develop when meconium aspiration occurs in conjunction with varying degrees of in utero asphyxia. Pulmonary hypertension, which often results from hypertrophic pulmonary vascular muscular tissue, is a severe condition characterized by cyanosis from right to left shunting across the atrial septum and patent ductus arteriosus. As the disease process progresses, the symptoms and severity of hypoxemia increase over the subsequent hours. Aspiration can occur in utero or during the intrapartum period as well as during the early postpartum period. Since meconium aspiration is the most common problem, much effort has been made over the last 30 years to prevent this disease by reducing intrapartum and postpartum aspiration. Thorough suctioning of the oropharynx with a large bore catheter upon the delivery of the head is typically performed by the obstetrician. The pediatrician, needs to assess the quality of the meconium (thin, moderate or thick) and the state of the newborn before determining what is needed after birth. The sudden onset of significant respiratory distress should raise the possibility of an air leak syndrome. The most common air leak syndromes are pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax and pneumopericardium. The elevation of the thymus with a sail or bat wing sign suggests a pneumomediastinum. Hypotension and bradycardia occur rapidly in a tension pneumothorax or pneumopericardium (cardiac dysfunction is due to reduced venous return due to compression of the heart and mediastinal vascular structures). In cases other than a bronchopleural fistula, the air leak will usually seal within a few days. The classic findings of cyanosis, grunting, nasal flaring, intercostal and subcostal retractions and tachypnea are present. The chest radiograph reveals decreased lung inflation with diffuse symmetrical reticulogranular (ground glass appearance) lung fields and air bronchograms. While the lungs structural immaturity contributes to the pulmonary dysfunction, the major reason for this disorder is surfactant deficiency. This relationship states that as the radius of the air filled alveolus decreases, the pressure within the alveolus increases. This increased pressure requires an equivalent external opposing pressure to keep the alveolus inflated.
Group 4 heard and reference planes were used to compare the differences between the anchor stimuli representing 3 spasms in your back buy nimotop 30 mg free shipping, and 5 on the rating scale and this resulted virtual plan and postoperative surgical result muscle relaxant and nsaid buy nimotop on line amex. The poorest correspondence was for Group 1 which did not hear any two-jaw orthognathic surgery were performed in this study muscle relaxant 503 best 30 mg nimotop. A median rating was computed across listeners for not use the osteotomy guide in surgery muscle relaxant drugs medication generic nimotop 30mg amex, and was thus excluded from analysis muscle relaxant vitamin order 30 mg nimotop fast delivery. Mean nasalance scores virtual plan and postoperative surgical result in maxilla and condyle were essentially the same for all stimuli rated 1 (26 muscle relaxant drug list purchase nimotop 30mg line. In other words, it appeared that listeners made distinctions on the study exhibited clinically acceptable precision for position of the maxilla mild-moderate end of the perceptual scale that the Nasometer did not. The intervention program included four clinical, billing and scheduling databases. Demographic, phenotypic, and phases; pre-intervention test, small group parent training, administration of clinical data, including birth, medical and surgical histories were ascertained parent-implemented intervention in childrens home for 3 months and from study visits, parental interview, photographs and medical records review. To investigate the effectiveness of the intervention facial asymmetry and preauricular/facial tags (tags) without microtia (2%); c) more validly, 7 children with cleft palate and their mothers involved in the facial asymmetry and tags or microtia plus other features (epibulbar dermoids, study as a control group and they participated in only test sessions and did not macrostomia, tags) (76%); d) other features excluding facial asymmetry or voluntarily receive parent training. Renal ultrasounds had been performed in 62 participants, and of standardized language tests and collection of 20-minute language samples spine radiographs in 39. Of the total group, 8% had a renal anomaly (all while mothers interacted with their children in their homes. Researchers who unilateral, 66% in right side), and 21% had vertebral anomalies (all from were blinded the purpose of the study, group type, and testing phase phenotypic groups c and d). Renal ultrasounds and spine radiographs transcribed and analyzed the language samples and provided mothers and frequency varied between groups a to d: 71%, 50%, 72%, 33% and 12%, 0%, childrens measures. These prevalences are likely underestimates given consonants, and the number of different syllable structures. The study has implications for establishing models for the delivery of wanted an outcome of all patients to have stopped having a bedtime drink early intervention program in the population. Following this, patients families were given preventative advice by the Contact Email: katherine rose@urmc. Data was collected nationally over described as microretrognathia, glossoptosis, and airway obstruction. Hospital charts were reviewed for sent out to families at 5 months to explain the importance of dental associated genetic syndromes, co-existing cleft palate/lip, airway assessment prevention. Secondly, a leaflet reminder is sent out just prior to their first via direct laryngoscopy, presence of gastroesophogeal reflux symptoms, use of birthday to reiterate the Stop the Bottle advice. A leaflet documenting for anti-reflux medications, feeding method(s) and amount, and weight parents the importance of stopping bottle feeding at 12 months has also been percentiles. Volume of oral intake, weight, and weight percentile Contact Email: shha610@gmail. We the relationship between racial/ethnic differences and psychosocial concerns present two patients with deletions at 17q21. The current study examined psychosocial factors gene illustrate the importance of including this condition in the differential in a pediatric craniofacial population, particularly as they related to race and diagnosis of other human facial dysostosis syndromes. The total sample included 278 children and adolescents, ages 5-17 microcephaly, microretrognathia, and midface hypoplasia. X-rays documented bilateral radioulnar synostosis and 11 significantly related to reported rates of bullying/teasing, with 61. Patient 2 is a 4 year old female with a history of differences were significantly related to reported rates of aggression, with a submucousal cleft palate, epilepsy, and speech apraxia. Examination of her extremities did not reveal abnormalities and her Finally, racial/ethnic differences were significantly related to reported rates of anthropometric measurements were normal, including head circumference. Future research should focus on the extent and effects Patient 2 provides evidence for the relationship between a lack of absolute of these disparities on the psychosocial wellbeing of children and adolescents microcephaly and favorable neurodevelopmental outcomes. This provides further evidence of the clinical overlap among human facial dysostoses. Furthermore, moderate to strong severity groups without a significant difference between the cohorts. Facial differences frequently result in negative life difference between the entire maxillary sinus volume (including non-bony experiences for children and adolescents. Left and right maxillary sinus and functioning in a sample of children with various craniofacial anomalies. Paired t-tests determined whether range of diagnoses included cleft lip, cleft palate, cleft lip and palate, maxillary size, airspace, sinusitis. Significant administered a self-report version of Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire. Interestingly, visibility was found to be encourage the presence of sinusitis, which may perturb maxillary positively related to prosocial behaviors based on parent reports. A similar but pneumatization during morphogenesis and growth to disrupt physical non-significant trend was also seen for self-report data. Transverse craniometric measures and lateral facial measurements alternative offered to patients younger than 6 months of age. Given lack of were reported and used to calculate mean ratios between affected and published data comparing open and endoscopic repairs of lambdoid unaffected sides. Statistical analysis was performed on craniometric craniosynostosis, the purpose of this study is to quantitatively analyze the measurements using Kruskal-Wallis and Wilcoxon signed-rank tests. Patients results was achieved by speech analysis by a speech pathologist and a treated with open reconstruction (n=6) were compared to those treated telephone enquiry relating to airway symptoms by a clinical nurse manager. Neither procedure achieves complete difficulties clearing the nasal passages when suffering from head colds were symmetry of the cranial vault. Louis, Federal University Minas Gerais Brazil, Belo horizonte, Minas Gerais, (3) St. This study investigates the anatomical relationship literature, with regard to the diagnosis of sinusitis in the cleft patient. This variability was greater in the study group than in the control and the sagittal suture ranged from 5. The maxillary sinus volume on the cleft side was sometimes decreased following surgical intervention though it remained significantly smaller and sometimes larger than the non-cleft side. Further studies are anticipated in examining the sinuses of patients with craniofacial conditions. Additional 15 scans of orthodontic seeking treatment subjects with ages important step during 3-dimensional (3D) virtual simulation of orthognathic 8-12 year old were also reviewed as a non-cleft control group. The purpose of this study was to introduce a method by automatic images were rendered and volume was measured in mm3. The digital dental models were integrated to significant different when the two groups were compared. The differences in morphology between the deviated pharyngeal wall boundaries relative to the audio signal. The Pearson correlation measured by calculating the accumulation error and through visual inspection. The ramus axis to the coronal plane became more structures of interest in the velopharyngeal area and were able to predict the upright bilaterally, while the gonial angle on the deviated side showed velar and pharyngeal configurations when provided with the audio signal. The non-deviated side showed applied to any speech task for normal or cleft palate anatomy. Although tertiary pediatric hospital was performed between the years of 2002-2012. Of the four patients with hypernasality, two were found to have structural Complete intraand extra-oral exams were performed by a licensed dentist issues requiring surgery (pharyngeal flap). The remaining when possible, intra-oral photographs, radiographs (including panoramic, two patients were found to have articulation error patterns that were periapical, and bitewing radiographs) and dental records provided by the considered more developmental in nature and both responded to speech participant, and alginate dental impressions. All patients had improvement in their polysomnogram or sleep symptoms after adenotonsillectomy. They still harbour cleft lip by narrowing the cleft width, aligning the alveolar segments, the burden of this defect with ill-developed speech due to velo-pharyngeal lengthening the columella, and improving nasal tip projection. Exclusion criteria included lip repair after 1 year-of-age and use of successful treatment approach includes surgery utilizing palatoplasty with parenteral or non-oral feeding. Data included gestational age, age at time of primary pharyngeal flap followed by speech therapy. Statistical comparisons were generated using a Mannsuperior-based pharyngeal flap versus two-flap palatoplasty alone in terms of Whitney test with significance set at a p value < 0. This was observed for both groups, with increasing improvement during post-operative course. Youngstrom (1965; 1966) hypothesized that compensatory articulation might change the temporal characteristics of speech. There was a high complication rate with semi-buried devices two-dimensional images. The goal of this study is to develop a method for in the cranial location in sheep; such device complications have not translated quantitatively describing the nasal morphologic changes using threeto humans. Purpose: the aim of this study was to examine inter-relationships among repositioning procedures. Surgical access was via a single 3-4 cm zigzag describe the nasal morphologic change as a results of maxillary repositioning. Following subgaleal dissection, a malleable lightsource allowed Data obtained through this methodology supplements the existing literature direct visualization of strip craniectomy. This approach is feasible for future wedge excisions were made with bone scissors to address associated outcome studies. This procedure is best large cranial defects that may allow treatment without use of permanent bone performed < 5 months of age. Compared to endoscopic investigated the use of complex, curvilinear distraction vectors that mimic procedures, the approach is simpler, leaves a smaller scar and yet allows for native calvarial contours. This study establishes a sheep model to evaluate the superior visualization and surgical control. Multivariable logistic regression models were used to examine the effects of several patient and surgeon related factors on outcomes. Wider clefts were associated with significantly higher Treatment protocols included: latency period, 4. There were complications in 46 did not have any blood loss, 23% had1 cc of blood loss, while 8% had a blood (16%) cases, but most were minor. We began in May 2013 and we currently have eight trained mentors and have matched nine mentees successfully. However, employing the Developmental Coordination Disorder is to train adolescent peer mentors. A secondary aim is to identify advantages and especially where the value of the second component was high. Types of stigma associated with cleft deformity included felt, internalized, enacted, felt normative, and symbolic stigma. Long term results are presented as well as technical hearing loss or any syndrome. None had oronasal fistula and one had alveolar modifications for differential multisegmental and multivectorial remodeling bone grafting. These results were compared to historical controls were native speakers of Persian. The speech stimuli consisted of the nonsense and similar reports in the literature words /sis/ and /shish/. Spectral moments of initial /s/ and /sh/ sounds were determined short follow up (<1 year). Mean spectral moment and frontal remodeling with hinge plates and counter-lever arms activated by differences between /s/ and /sh/ were 0. Intraoperative blood loss was third (skewness) and forth (kurtosis) spectral moments of /s/ (p<0. Operative times averaged 122 minutes (range 90-150 maxillary arch dimensions and/or structural anomalies of the oral cavity may minutes). Neurodevelopmental indicators showed marked improvement in be contributing factors in the misarticulation of alveolar sounds. About 82% of the mothers were palate and adults with normal anatomy at rest and during speech. Participants were scanned in the supine position with ashamed of having a child with cleft deformity. A time-efficient acquisition of a six-shot spiral pulse and friends because of the defect of their children. Data showed a higher risk of hearing loss at age 10 even after adjusting for total collection is currently ongoing to increase the sample size to 16. The timing of tube analyses will enable between and within group comparisons at the conclusion placement did not have a perceived effect on complication or hearing of data preparation. Furthermore, results indicate that complications increase with prior studies related to normal and abnormal anatomy in adults (Ettema with greater number of tube placement. Further data collection will provide improved potential negative outcomes of multiple tube placements and suggest the statistical model. A pharyngeal flap is considered to be effective procedure, with conditions success rates of 78 to 98 percent. The deviated internal carotid artery was located in the submucosal plane and near the level where the distal end of pharyngeal flap was expected. Patients with multiple orbit and midface fractures were to assess dental factors influencing timing of bone grafting for alveolar clefts included. Lateral cephalograms at longest-term follow up were traced, and 2) to determine the viability over time of retained teeth in the cleft region digitized, and averaged. Differences in x and y axes between assessed whether 1) the dentition in the cleft region or 2) the use of rapid test and control metrics were measured. Chi-square analyses were conducted to examine the relationships the specific aim of this project was to assess the efficacy of Dynacleft as a between bullying and other demographic and psychosocial variables.
Valproate is a useful alternative muscle relaxant at walgreens cheap nimotop 30 mg mastercard, with an intravenous is noted in most patients (159) quetiapine muscle relaxer purchase nimotop american express, and an improved response to preparation available for rapid loading (138) spasms 24 30mg nimotop with visa. Radiosurgical who have tonic seizures may respond to carbamazepine; howcorpus callosotomy may ultimately prove to be a promising ever muscle relaxant new zealand order genuine nimotop, it can aggravate atypical absence seizures in patients with alternative (161) muscle relaxant voltaren order 30 mg nimotop free shipping. Seizure frequency spasms upper right abdomen purchase nimotop 30 mg, improvement in seizure severity, and 50% responidentification directs not only the evaluation for the underlying der rate for total seizures with adjunctive use when compared to condition or disease process, but also aids in classifying the most Chapter 16: Atypical Absence Seizures, Myoclonic, Tonic, and Atonic Seizures 213 appropriate treatments (5). Generalized epilepsy with spike-and-wave discharge: a reinterpretation of its electrographic and clinical manifestations. Absence epilepsy with onset before age three years: a heterogeneous and often severe condition. The etiology and diagnosis of atypical absence seizures, myoclonic, tonic, and atonic status epilepticus. A proposed diagnostic scheme for people with epileptic seizures (Dravet syndrome). Ictal clinical electroencephalographic findings of of the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. The Treatment of Epilepsy; Practice terminology and nosological position amongst the secondary generalized and Principals. Epilepsy: A Comprehensive myoclonic manifestations associated with typical absences in childhood Textbook. Tonic-automatism complex: cases with eralized epilepsy: an answer to the considerations of Lyon and Gastaut. Positional candidate approach neuroimaging findings in patients with midline spikes. Neurobiological and full-term neonates: clinical correlates, associated brain lesions, and risk Approaches. Hypnic tonic postural seizures in healthy children trazol seizure patterns in rats after precollicular transections. Asymmetric tonic seizures with anomaly as a possible cause of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Tonic seizures: their significance intractable drop attack seizures, and sleep-related electrical status epileptifor lateralization and frequency in different focal epileptic syndromes. Polygraphic and clinical study colepsy: identification of cataplexy-related cells in the medial medulla. Cortical electrical stimulawith generalized spike-and-slow wave complexes: video-polygraphic study tion in humans. A study of unilateral brief focal atonia in of medically resistant epilepsy: preliminary results in a pediatric populachildhood partial epilepsy. Chapter 16: Atypical Absence Seizures, Myoclonic, Tonic, and Atonic Seizures 215 114. Refractory grand mal seizures with onset during infancy approach to medically intractable epilepsy. A prospective study of the modiCharacteristics of valproic acid resistant juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Myoclonus associated with the use tion in children with medically refractory epilepsy. Vagus nerve stimulation and drug double-blind, crossover study comparing the efficacy and safety of three reduction. Treatment of seizures in subcortical laminar epilepsy in infancy: a randomised placebo-controlled syndrome-dedicated heterotopia with corpus callosotomy and lamotrigine. The seizure starts with a phasic contraction that are quite varied, and although the prognosis is frequently lasts for less than 2 seconds, followed by an ensuing tonic guarded and often grave, a small proportion of children may contraction for 2 to 10 seconds, although only the phasic conshow complete recovery without sequelae. In flexion placed among the generalized seizure disorders in the first spasms, the trunk, arms, legs, and head flex. Many children have more than one type, even in the age-related features further characterized. Even if the same muscle were initially medical or surgical management that significantly impacts on activated with every spasm, the ensuing sequence or pattern of the shortand long-term prognosis. Between spasms, most children cry, the ontogenetic expression of drug-induced limbic seizures, although this is probably not an ictal phenomenon but may have shown a similar age-dependent phenomenology in addibe a result of surprise or pain (16). Up to 60% of all patients tion to high after-discharge thresholds that suggest a relative have respiratory pauses, while pulse changes occur less often. Spasms are usually asymmetric on the side contralateral to a unilateral lesion such as hemimegalencephaly. These findin spasms is faster than that in tonic seizures but slower than ings have been described in 30% to 89% of patients and that in myoclonic seizures (26,27). Tonic seizures can occur may be considered a prognostic factor for underlying brain simultaneously with or precede spasms and may be difficult to injury as 85% to 90% of this group will eventually have differentiate, requiring videotelemetry to define the seizure developmental delay (14,28,32,33). Tonic seizures last longer than spasms and lack the initial umented mental retardation in 75% and cerebral palsy in phasic component. Loss of visual tracking may reflect before, during, or after a spasm and frequently precede a clusthe degree of epileptic encephalopathy present and appears ter of spasms (18). Most spasms occur on awakening or after feeding, less often during sleep, and the typical clustering lasting less than 1 to 5 seconds have been documented (16). The spasms decrease in intenA variety of disorders can cause infantile and epileptic spasms sity at the end of longer clusters; however, the number and that drive management, prognosis, and overall outcome. Pretype of spasms may vary markedly from week to week with existing brain damage has been demonstrated in 60% to 90% less day-to-day variation (16,28). Symptomatic patients usually asymmetric spasms with the predominant side conforming to have more focality on neurologic examination, a history of that of the preceding partial seizure. Prenatal causes include congenital malformation, congenbeen recently studied in children with well-defined pure culital infections, neurocutaneous disorders, chromosomal abnortures of temporal and extratemporal lobe focal epilepsy (30). There is some radinerve growth factor (59), which may reflect brain damage ologic evidence that a larger tuber burden is more likely to profrom the spasms or that stress hormones may play a role in the duce spasms rather than partial seizures, but this may also pathogenesis of spasms. Sex-linked dominant but these usually have a better prognosis than other symptoinheritance may be seen in incontinentia pigmenti, double matic causes (48). Some families have been monly Down syndrome (43,49), represent approximately 13% reported with an X-linked transmission that has been mapped of prenatal etiologies; these children usually do not have a poor to regions Xp11. Some of the issues are periventricular leukomalacia are typically hypsarrhythmic and interspecies differences in brain development and the lack of located more posteriorly than anteriorly (27,54). Results of neurepresent a nonspecific age-dependent reaction of the immature roimaging and laboratory evaluations are frequently normal. Brainstem origin has also been postulated on the translates from the Greek as high-amplitude irregular waves. Because hypsarrhythmia occurs mainly moment to moment in localization, amplitude, and duration during sleep and the brainstem controls sleep cycles, this sleep (19). In other charges may generalize, but it is not common to have rhythwords, the cortical lesion interacts with developing brainstem mic, repetitive, and synchronously organized runs of spike pathways, causing motor spasms that are similar to startle or discharge patterns that resemble the petit mal variant or cortical reflex myoclonus (71,72). These patients have normal development, and the mental response can also be seen in the absence of a clinical spasms usually remit after a short period. Diffuse attenuation, which is symmetric; and a family history of seizures is comgeneralized spike wave, paroxysmal fast activity or fast fremon. Tonic seizures usually coexist with and are lasting for approximatley 1 second, while longer patterns are more marked during this stage of the syndrome. This evolution has been reported sustained ictal event rather than brief, repetitive seizures (93). A firm diagnosis is necessary before initiation of the subclinical discharges (27,50). Delayed myelination in 27% of patients did not appear will invariably demonstrate either developmental regression or to be associated with any specific etiology (Table 17. Nearly half of all of the etiologic nosed with chromosomal microarrays and specific mutational diagnoses are established or suspected by the historical and studies. Neuroimaging Complete blood count, electrolytes (looking for an anion gap), and glucose determinations are appropriate. Dosing is complicated by the existence Lumbar Puncture of natural and synthetic forms of corticotropin. More than 100 years after James Wests overall long-term response rate ranged from 53% to 91%. If spasms are controlled and hypCorticotropin and, as of 2009, vigabatrin are approved by the sarrhythmia disappears, I taper the dose over 1 to 4 months, Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States. Constriction of peripheral visual megalovirus infection are major infections that have been fields, which substantially limits the drugs use, was not reported. Corticotropin exacerbates the seizures in a few reported until 1997 (125) and now affects from 15% to 50% infants, and treatment for more than a few weeks leads to of patients. In one report (126), constriction occurred in more steroid insufficiency if the drug is stopped abruptly (114). Most and mortality risks (reported at approximately 2% to 5%) studies have suggested that the constriction is not reversible; before the therapy begins, and these must be balanced against however, eight of 12 patients who underwent full withdrawal the virtual certainty of mental retardation if the spasms are improved significantly; none of the 12 who continued taking not rapidly controlled. The problem is mild enough that most surements of blood pressure, electrolytes, and urinalysis is patients are unaware of the disturbance, which becomes mandatory. The current risk-to-benefit assessment favors corapparent only on perimetric studies. Following response to steroids or corticotrophin, the relapse rate is high and variably reported Valproic Acid between 33% and 56% (34). In a 1981 report, valproic acid produced between 14% and 58%, particularly in patients with a cryptoan excellent response in four of 18 patients treated with genic etiology (116). A year later, seven of 19 patients achieved good control (11 had also been treated with corticotropin) (129). Other patients later responded but also received dexamethasone or this drug has been reported to be highly effective in the treatcarbamazepine, so the effect of valproic acid was less clear. In Japan, high-dose vitamin B6 has been associates (122) treated 75 patients with 18 to 36 mg/kg/day the drug of choice (135,136), with reported response rates of (low dose) and 67 patients with 100 to 148 mg/kg/day (high 10% to 30%. Eight low-dose patients and 24 high-dose modest compared with the side effects of corticotropin or patients achieved complete control. Two retrospective reports of 40 children suggest control of spasms in 20% to 35% of patients with otherwise intractable disease Nitrazepam (152,153). Children younger than 1 year of age can achieve ketosis and may benefit from the diet. Many reports noted an increase in oral secretions effective nonantiepileptic drug therapy that may be effective in and a higher incidence of aspiration and pneumonia with a variety of seizure disorders, especially when associated with nitrazepam. Actual efficacy is unclear, however, and the most appropriate doses and duration have not been determined. Zonisamide that should be selected early for surgery as there is compelling was well tolerated, but 20% of the patients in one study expeevidence that earlier surgery and shorter duration of epilepsy rienced anorexia and one patient lost weight (146). Because aplastic anemia has not been noted Prognostic features are overall difficult to assess. Signs of in prepubertal patients, felbamate may be as safe as some brain injury usually preclude complete recovery even in cases other drugs and could be recommended if other medications where seizure remission is achieved. Use of a low dose is important because rash, the major with a severe epileptic encephalopathy and carry a grave side effect, depends to some extent on how rapidly the dose is prognosis associated with significant morbidity and also morincreased. Intractable epilepsy, mental retardation, and autism are 2 months to the minimum expected therapeutic dose. In addition, the the very low dose is effective, however, lamotrigine becomes a long-term mortality may be high: a 25to 35-year follow-up fallback drug (151). Long-term prognosis of 150 cases the severe cognitive sequelae of this epileptic encephalopathy. Visual inattention in West Syndrome: a neuropsychological and neurofunctional imaging study.
Patients who have hypertension or Alagille syndrome usually have a storage disease characteristic facies (beaked nose muscle relaxant used in surgery discount 30mg nimotop mastercard, should be sushigh forehead) spasms right side of back buy generic nimotop, butterfly vertebrae spasms with stretching buy nimotop with paypal, a pected muscle relaxant order nimotop in united states online. Normurmur on cardiovascular auscultamally muscle relaxant for joint pain purchase 30mg nimotop, the liver tion due to peripheral pulmonic steedge is round nosis spasms due to redundant colon buy genuine nimotop line, and a posterior embryotoxon and soft and on ophthalmologic examination. The onset of sympthe presence of toms (such as vomiting) following fibrosis or cirthe introduction of a new food conrhosis. The taining galactose or fructose could latter condition suggest galactosemia or hereditary also often is fructose intolerance. Palpation of Infants who have cholestasis often the liver in the suffer from intense pruritus, which are detergent molecules that lower epigastrium signifies either the presis characteristic of obstructive liver the superficial tension of solutions, ence of cirrhosis or Riedel lobe disease, that primarily is manifested thereby creating visible foaminess. Among edema that is responsible for the the laboratory findings of liver this plethora of physical findings, perceived pain localized to the liver. Hepatomegaly often is allow the clinician to detect vascular obstructive bile duct injury and the only manifestation of liver disbruits due to anatomic malforma2) hepatocellular or liver cell injury. Ascites, if present, overlap between injury types in a normal variations in contour, body suggests increased portal venous patient who has liver disease. Therefore, meamay indicate a storage disorder or a cannot be excreted because of occlusurement of liver span is a useful malignancy, although a particularly sion or obstruction of the biliary adjunct to palpation at initial presenimpressive hepatomegaly in isolation tree. The liver often is associated with congenital of substances (bile pigments, span is the distance between the hepatic fibrosis. This usually is assoenzymes, bile salts) that normally liver edge and the upper margin of ciated with minimal liver dysfuncare present within or eliminated via dullness obtained by percussion at tion, despite the worrisome hepatobile will increase in cholestatic conthe right midclavicular line. Table 8 lists our recwith cholestatic disease, it is espedegree of hepatocellular dysfunction ommended sequence of data colleccially important to be able to recogbecause of the noxious accumulation tion in the evaluation of an infant nize, differentiate, and attempt to of bile within the hepatocytes and who has suspected cholestasis. In hepatocellular expedited evaluation is suggested for ary atresia) when cholestasis is disease, the reduced bile flow infants who present at 2 months of present. In hepatocellular of liver disease is diagnosed by long before overt clinical findings. It provide information about prognosis, lestasis inevitably leads to a certain is most important to recognize the response to therapy, and extent of 380 Pediatrics in Review Vol. Goals of a Liver Failure Physical Findings Staged Evaluation of Associated With Liver Infants Who Have Jaundice Neonates and Infants Disease Infections: herpesviruses, echo/ Recognize cholestasis (versus adenoviruses, sepsis Infants unconjugated, physiologic Microcephaly: congenital hyperbilirubinemia) Metabolic disorders: hereditary fructose intolerance, cytomegalovirus, rubella, Assess severity of the liver mitochondrial diseases, toxoplasmosis injury tyrosinemia, galactosemia, Characteristic facies: Separate specific entities neonatal iron storage disease arteriohepatic dysplasia (eg, metabolic versus viral Ischemia/shock: congenital (Alagille syndrome) versus anatomic) cardiac disease, myocarditis, Cataracts: galactosemia Differentiate biliary atresia severe hypotension Retinal pigmentation and from idiopathic neonatal Drugs/toxins: valproate, posterior embryotoxon: hepatitis acetaminophen Alagille syndrome Differentiate idiopathic Children and Adolescents Abnormal auscultation of neonatal hepatitis from Infections: hepatitis, lungs: cystic fibrosis progressive familial herpesviruses, echo/ intrahepatic cholestasis and Neuromuscular abnormalities adenoviruses, sepsis bile duct paucity (tremors, flaccidity): lipid Drugs/toxins: valproate, storage disease, Wilson acetaminophen, mushrooms disease, disorders of oxidative (Amanita) phosphorylation serum and urinary bile acid levels Malignancy will aid in eliminating the possibility Children of an inborn error of bile acid Ischemia/shock: congenital Pruritus: chronic cholestasis metabolism. Urinary succinylacetone cardiac disease, myocarditis, Hemangiomas: levels may indicate the presence of severe hypotension hemangiomatosis of the liver tyrosinemia. A urinalysis and urine Metabolic: Wilson disease, culture always should be obtained in Kayser-Fleischer rings: Wilson fatty liver of pregnancy disease any infant who has jaundice because urosepsis commonly is associated Glossitis: cirrhosis with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia dysfunction. However, the term Enlarged kidneys: congenital (eg, E coli urinary tract infection). All of the other Arthritis, acne, fatigue: parameters are essentially indirect Of all laboratory tests performed, measures of liver function, and some autoimmune hepatitis bilirubin fractionation is the most of these values are altered in setimportant, especially in any infant tings other than liver disease. For who has more than 2 weeks of jaunexample, elevations in aspartate amisuggests a defect in beta-oxidation dice. For a infants, may indicate an organic aciorganizations are not measuring convariety of reasons (cumbersome demia, glycogen storage disease, or jugated bilirubin levels, even after equipment and methodologies, a deficit in gluconeogenesis. An 2 weeks of life in the presence of expense, lack of established normal increase in anion gap metabolic acijaundice. Hypoand hyperthyroidism ease unlikely, but the infant may caine metabolism, do not yet have may be associated with jaundice. A sweat chloride determination may hemolysis, congenital disorders of Biochemical abnormalities associbe necessary to rule out cystic fibrobilirubin metabolism (eg, Criglerated with liver disease are not limsis. Stepwise Evaluation of Infants Who Have exact value of conjugated bilirubin Suspected Cholestatic Liver Disease in some institutions requires the addition of the delta value to that of Confirm cholestasis the conjugated bilirubin. Urobilinogen, which is formed from the degradation of conjugated bilirubin by bacteria present in the intestinal generally is considered pathologic. Most When the serum conjugated biliruthe blood and mediates conjugation urobilinogen is excreted in the stool bin value is greater than of unconjugated bilirubin with two as coprobilinogen; 20% undergoes 17 mcmol/L (1 mg/dL) or greater molecules of glucuronic acid. Only a than 15% of the total bilirubin gation of bilirubin turns an essensmall fraction escapes into the urine, value, it should be considered abnortially liposoluble substance (unconbut it is increased in the presence of mal and evaluated immediately. Clearly, urinary urobilinogen is (eg, from hemolysis) or a delay in aqueous medium. It is the liposolunearly absent in the presence of an hepatic bilirubin conjugating capacble nature of unconjugated bilirubin obstructive process because less biliity. Although harmless in the older that allows it to cross the bloodrubin enters the intestine and less is patient, unconjugated hyperbilirubrain barrier and potentially to cause converted to urobilinogen. However, the conjugated referred to as direct and indiexcreted in urine and, therefore, fraction is associated with serious rect. Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia bin was detected historically by cholestatic insult because its disapshould not be confused with physiousing the Van den Bergh reaction, in pearance depends on the degradation logic jaundice of the newborn (in which a water-soluble medium (Ehrof the albumin-bilirubin complex. These enzymes catabosuch as during pubertal growth trophic and choleretic bile acids or lize the reversible transfer of the spurts. Particularly high values overproduction of hepatotoxic bile alpha-amino group of the amino should lead to the suspicion of posacids. Proper functioning of this sysever, it also is present in the panof acetaminophen toxicity. However, tem promotes a balance between creas, spleen, brain, breast, small they are useful in monitoring the absorption of bile acids from the intestine, and especially the kidney. It suggests a decreased funcin whom bilirubin levels still may possible liver disease. In certain diseases, cially when laboratory tests are atypical bile acids such as lithoobtained at nonpediatric hospitals or cholic acid accumulate instead of clinics. When bile acids are not excreted decreased hepatic production due to A nonfunctional or a poorly funcinto the intestine, fat-soluble vitadecreased liver function following tioning liver cannot carry out mins are malabsorbed. However, a gamma carboxylation appropriately, vitamin A and E esters require low serum albumin concentration is despite the presence of vitamin K. When this is the basis for parenteral bile acid-dependent intestinal esterit is present, it suggests chronic disadministration (not oral) of vitamin ase catalyzes this reaction. The liver also is responworrisome, although such a decrease still is within normal limits, and the sible for one of the hydroxylation in patients who have ascites simply deficiency most likely is due to steps required to metabolize vitamin may reflect a change in the overall obstruction. Untreated hypoprothrombinemia may lead to spontaneous bleeding and intracranial hemorrhage. Untreated hypoprothromthe measurement of liver size, verifithy are classic findings of liver failbinemia may lead to spontaneous cation of changes in liver texture, ure, and there is a labile correlation bleeding and intracranial and documentation of the presence between the degree of encephalopahemorrhage. These cannot be used to detect calcium trypsin deficiency, which now is radiotracers are concentrated within deposits or in patients who have recognized easily as a specific cause the bile, thereby providing an image implanted metal devices. Simiof the tracer within the intestinal Percutaneous liver biopsy is the carlarly, as the metabolism of bile acids region by 24 hours virtually dinal method by which to arrive is defined more clearly and specific excludes biliary atresia, but the conquickly at a diagnosis of underlying defects are being identified, many verse is not true. It is fast, safe, and infants previously deemed to have tracer in the gut may not represent effective and usually does not neonatal hepatitis now are being an obstructive defect, but rather a require operating room time or overjudged to have a defect in bile acid parenchymal disease process in night hospital admission. To facilitate bile chyma can be examined, and infants and neonates are highly susflow, patients often receive phenoglycogen, copper, iron, and other ceptible to injury due to age-related barbital (5 mg/kg per day divided in components within the liver tissue immaturity of metabolic processes, two daily doses) for 3 to 5 days can be quantified exactly. This timeage disease, or neonatal iron storage tiation or perpetuation of cholestasis. The histologic infants who have neonatal hepatitis high false-positive (ie, no excretion) appearance of the tissue provides is to conduct an exhaustive search and false-negative (ie, an apparent useful information about the degree for recognizable or treatable causes excretion of tracer into the intestine) of fibrosis or presence of cirrhosis of the clinical condition. Jaundice yields (at least 10%) and is not very and permits the diagnosis of biliary may be present from birth or appear effective when serum bilirubin levatresia, neonatal hepatitis, congenital in the first 3 months of life. Percutaneous liver hepatic fibrosis, and alpha 1-antitunately, the classic findings of chobiopsy never should be postponed to trypsin deficiency. However, they may be useful passage of acholic stools and dark in specific situations. Aminotransferase levels almost and characterize liver masses this relatively specific syndrome is always are elevated, but to varying clearly. In most cases, howof abnormality correlates with the nizing chemical differences in tisever, idiopathic neonatal hepatitis severity of disease at the initial presues and identifying tumors and represents a very general category sentation. Ultrasonography usually infiltrates without the injection of a that includes all cases of neonatal reveals the presence of a gall bladcontrast agent or exposure of the liver dysfunction for which an etiolder and the absence of a cystic malpatient to ionizing radiation. The tobiliary scintigraphy, if performed, titis, infants who have biliary atresia presence of succinylacetone in the reveals delayed transport of radionupresent with signs of cholestasis. A severely abdominal ultrasonography can rule hydrolase (which catalyzes the final damaged liver may have difficulty out the presence of a choledochal step in the oxidative catabolism of in taking up the radionuclide, which cyst. Liver biopsy tion of it into the intestine, even be screened for by protein inhibitor usually provides the definitive diag24 hours later. Excessive storage of involves supportive measures and necessary if there is progressive iron is seen on biopsy in infants avoiding the consequences of malabhepatic decompensation, refractory who have neonatal iron storage dissorption by ensuring adequate nutrigrowth failure, hepatic synthetic ease. Congenital hypothyroidism, tion and delivery of fat-soluble vitadysfunction, and the development of which may present with unexplained mins and medium-chain triglycerides a coagulopathy or intractable portal hyperbilirubinemia, is ruled out by until recovery (which occurs in the hypertension with recurrent gastroinassessment of thyroid function. Liver transplantation is an testinal hemorrhage or hyperalternative for those who do not splenism. Liver Disease of the Older Child the major causes of liver disease observed after infancy are the major causes of liver disease toxic, infectious, metabolic, autoimmune, vascular, and observed after infancy are toxic, infiltrative. Furthermore, process that affects intraand extrainfant may be diagnosed by a comthe relative frequency of each disorhepatic bile ducts. It leads to fibrosis bination of general tests, such as der varies with the age of the and obliteration of the biliary tract, ultrasonography, and more specific patient. Structural abnormalities of the patients of all ages, as does the liver biliary cirrhosis. It occurs worldbiliary tree, such as congenital disease due to cardiac or collagen wide, affecting an estimated 1 in hepatic fibrosis or choledochal cysts, vascular diseases. Disorders of fat 12,000 live births, and is the most usually are detected by ultrasonogrametabolism present in late infancy frequent indication for liver transphy. Liver biopsy shows the characand early childhood; Wilson disease plantation among infants and chilteristic ductal plate malformation usually is detected in late childhood dren. The need for liver transplantafinding in infants who have congenior adolescence. Any history tent intrahepatic inflammatory of maternal exposure to , or infection process. The clinical presenwhich permits improved nutrition viral infection, both serum immunotation of viral hepatitis varies with and maximal growth. Urine often sents most often as a flu-like illness, rection of biliary atresia is most will be positive for cytomegalovirus. Patients 3 months of age, which underlines of tyrosine metabolism, is suggested often are febrile and can be very the need for prompt and precise by disproportionate abnormalities of jaundiced. The pathogen spreads diagnosis of the cause of observed hepatic synthetic function, mild primarily via the oral-fecal route. Definiepidemics in parts of the world that with piecemeal necrosis, distortion tive diagnosis requires evaluation of have poor sanitary conditions. Cases of lobular architecture, and even 24-hour urinary copper excretion diagnosed in North America have bridging fibrosis in severe cases. Sclerosing cholangitis is characterwith a hemolytic crisis due to the ized by a chronic inflammatory protoxic effect of copper on red blood cess of the intraor extrahepatic cells. It may be primary with penicillamine, which allows for this traditionally is defined as an (without evidence of another underits excretion into the urine. Because inflammatory condition of the liver lying disease and of unknown etiolthe prognosis depends on early treatin which the biochemical and histoogy) and usually is associated with ment and individual responsiveness logic abnormalities persist for more inflammatory bowel disease. However, irreversondary sclerosing cholangitis results to consider this diagnosis in every ible changes may occur in children from stones, postoperative strictures, child who has signs of chronic liver within those 6 months. Typiof the diseases causing chronic hepshow a typical concentric fibrosis cally, aminotransferases are elevated Pediatrics in Review Vol. Nontransplant Options for Children Who Have is the availability of multiple nonLiver Disease transplant options for the treatment of liver disease (Table 9). In view of these Molecular manipulations (eg, inhibition of polymerization of alpha 1exciting prospects, it becomes of antitrypsin) great importance to assess the presReceptor-based, targeted enzyme replacement therapy ence of liver disease correctly and quickly in children to allow them to Gene therapy grow and be as healthy as possible Hepatocyte transplantation (eg, fulminant liver failure) until they can reach an age at which definitive therapy may be available. In: Suchy F, ed: Liver Disease in Chilthe liver during one of the aforenoma tends to occur later in life dren. Nontransplant option for the infectious hepatitis, but it is distinalpha-fetoprotein levels usually are treatment of metabolic liver disease: saving livers while saving lives. Chronic liver disease in readily in the child who presents the initial presentation is of cardinal children. Less commonly, babies who have biliary atresia is opportunities for effective surgery. A 15-year-old girl who is being evalconjugated fraction of 102 mcmol/L firm liver with a span of 5 cm and uated for poor school performance (6. Which of the following palpable 3 cm below the right costal and acting-out behaviors is noted to clinical features is most suggestive of margin; splenomegaly; total bilirubin, have a large, firm liver. I think the best thing has been the privilege to represent the profession of child neurology Aside from the day job There are frequent requests have on policy, children, professional to review new practice guidelines, policy education, scientic research, career statements, budgets, and the impacts of development, and international collaboration pending legislation on child neurologists. I dont know that I can call it the most difficult aspect has been time an accomplishment yet, but I think we have community of child management. While many aspects of the role made important strides increasing diversity in neurologists who are predictable, there are others that require our leadership, especially at the committee share common goals, attention at unexpected times.
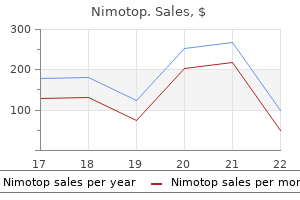
Quality nimotop 30 mg. TMJ 10 - Causes of TMJ - Emotions and Louise Hay.