Dr Tony Rahman
- Consultant Gastroenterologist & ICU Physician
- Honorary Senior Lecturer,
- St. George?,
- University of London,
- London
The night-time urine production should be recorded over an (at least) two week period to diagnose an eventual differentiation between a high night-time production (more than 130% the age expected bladder capacity) versus a night-time overactive bladder blood pressure medication enalapril side effects cheap hydrochlorothiazide online amex. A physical examination should be performed with special attention to the external genitalia and surrounding skin as well as to the condition of the clothes (wet underwear or encopresis) heart attack zine order hydrochlorothiazide cheap online. Urine analysis is indicated if there is a sudden onset of bedwetting blood pressure lab buy hydrochlorothiazide visa, a suspicion or history of urinary tract infections blood pressure cuff name discount hydrochlorothiazide online mastercard, or inexplicable polydipsia heart attack young squage generic 12.5 mg hydrochlorothiazide free shipping. A uroflowmetry and ultrasound is indicated only if there is a history of previous urethral or bladder surgery blood pressure medication green pill buy hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg without prescription, straining while voiding, interrupted voiding, an abnormal weak or strong stream, a prolonged voiding time. If the comorbid factor of developmental, attention or learning difficulties, family problems, parental distress and possible punishment of the child, a referral to a psychologist should be advised and followed-up. However, in this approach, it is important to emphasise the fact that the child should wear diapers at night to ensure a normal quality of sleep. The goal is that the child wakes up by the alarm, which can be acoustic or tactile, either by itself or with the help of a care giver. The method of action is to repeat the awakening and therefore change the high arousal to a low arousal, specifically when a status of full bladder is reached. Initial success rates of 80% are realistic, with low relapse rates, especially when night-time diuresis does not exceed age expected bladder capacity. Imipramine, which has been popular for treatment of the enuresis, achieves only a moderate response rate of 50% and has a high relapse rate. Figure 5 presents stepwise assessment and management options for nocturnal enuresis. Although the several forms of neuromodulation and acupuncture have been investigated for nocturnal enuresis treatment, the present literature data precludes its use because of its inefficiency, or at least no additional benefit. Offer supportive measures in conjunction with other treatment modalities, of which 1 Strong pharmacological and alarm treatment are the two most important. Conservative treatment starting in the first year of life is the first choice, however, surgery may be required at a later stage to establish adequate bladder storage, continence and drainage later on [455-457]. With regard to the associated bowel dysfunction, stool continence, with evacuation at a social acceptable moment, is another goal as well as education and treatment of disturbance in sexual function. Due to the increased risk of development of latex allergy, latex-free products (e. About 12% of neonates with myelodysplasia have no signs of neuro-urological dysfunction at birth [460]. Newborns with myelodysplasia and initially normal urodynamic studies are at risk for neurological deterioration secondary to spinal cord tethering, especially during the first six years of life. Close follow-up of these children is important for the early diagnosis and timely surgical correction of tethered spinal cord, and for the prevention of progressive urinary tract deterioration [460]. Even today in a contemporary series around 50% of the patients are incontinent and 15% have an impaired renal function at the age of 29 years [465]. A recent systematic review concerning the outcome of adult meningomyelocele patients demonstrated that around 37% (8-85%) are continent, 25% have some degree of renal damage and 1. The term continence? is used differently in the reports, and the definition of always dry? was used in only a quarter of the reports [467]. The term myelodysplasia includes a group of developmental anomalies that result from defects in neural tube closure. Lesions include spina bifida aperta and occulta, meningocele, lipomyelomeningocele, or myelomeningocele. With antenatal screening spina bifida can be diagnosed before birth with the possibility of intrauterine closure of the defect [469, 470]. Traumatic and neoplastic spinal lesions of the cord are less frequent in children, but can also cause severe urological problems. Other congenital malformations or acquired diseases can cause a neurogenic bladder, such as total or partial sacral agenesis which can be part of the caudal regression syndrome [471]. Patients with cerebral palsy may also present with varying degrees of voiding dysfunction, usually in the form of uninhibited bladder contractions (often due to spasticity of the pelvic floor and sphincter complex) and wetting. Finally, a non neurogenic neurogenic? bladder, such as Hinman or Ochoa syndrome, has been described, in which no neurogenic anomaly can be found, but severe bladder dysfunction as seen in neurogenic bladders is present [473, 474]. The bladder and sphincter are two units working in harmony to act as a single functional unit. In patients with a neurogenic disorder, the storage and emptying phase of the bladder function can be disturbed. The bladder and sphincter may function either overactive or underactive and present in 4 different combinations. In those with a safe bladder during the first urodynamic investigation, the next urodynamic investigation can be delayed until one year of age. A thorough clinical evaluation is mandatory including the external genitalia and the back. If there is any sign of decreased renal function, physicians should be encouraged to optimise the treatment as much as possible. If there are any clinical changes in between, another ultrasound should be performed. Bladder wall thickness has been shown not to be predictive of high pressures in the bladder during voiding and storage and cannot be used as a non-invasive tool to judge the risk for the upper urinary tract [484]. Especially in newborns, performing and interpretation of urodynamic studies may be difficult, as no normal values exist. During and after puberty bladder capacity, maximum detrusor pressure and detrusor leak point pressure increase significantly [486]. If there is a significant bacteriuria, antibacterial treatment should be discussed; especially in older patients a single shot may be sufficient [488]. In the infant period information on detrusor filling pressure and the pressure and bladder volume at which the child voids or leaks can be obtained [485]. Detrusor leak point pressure is more accurate than abdominal leak point pressure, but keeping the rectal probe in an infant in place can be challenging [485]. In those with cerebral palsy, non-neurogenic-neurogenic bladder or other neurological conditions allowing active voiding it may be a practical tool. The main limitation of uroflowmetry is a compliant child to follow instructions [489-492]. In contemporary series, renal scars can be detected in up to 46% as patients get older [496-498]. During the treatment it should be also taken into account with spina bifida patients, that QoL is related to urinary incontinence independent from the type and level of spinal dysraphism and the presence or absence of a liquor shunt [500]. Foetal open and endoscopic surgery for meningomyelocele are performed to close the defect as early as possible to reduce the neurological, orthopaedic and urological problems [501]. Despite some promising reports [502-505], caregivers need to be aware about the high risk of developing a neurogenic bladder as demonstrated by the Brazilian group [506]. In infants without any clear sign of outlet obstruction, this may be delayed but only in very selected cases. Looking at the microbiological milieu of the catheter, there was a trend for reduced recovery of potentially pathogenic bacteria with the use of hydrophilic catheters. Also, a trend for a higher patient satisfaction with the use of hydrophilic catheters was seen [516]. Based on the current data, it is not possible to state that one catheter type, technique or strategy is better than another. Oxybutynin is the most frequently used in children with neurogenic bladder with a success rate of up to 93% [521, 522]. Dose dependent side-effects (such as dry mouth, facial flushing, blurred vision heat intolerance etc. Intravesical administration has a significant higher bioavailability due to the circumvention of the intestinal first pass metabolism, as well as possible local influence on C-fiber-related activity can be responsible for the different clinical effect [523, 524]. Intravesical administration should be considered in patients with severe side-effects, as long-term results demonstrated that it was well tolerated and effective [525, 526]. The transdermal administration leads also to a substantial lower ratio of N-desethyloxybutynin to oxybutynin plasma levels, however, there are treatment related skin reactions in 12/41 patients [527]. There are some concerns about central anticholinergic adverse effects associated with oxybutynin [528, 529]. A double blinded cross-over trial, as well as a case control study, showed no deleterious effect on children?s attention and memory [530, 531]. Tolterodine, solifenacin, trospium chloride and propiverine and their combinations can be also used in children [532-538]. Except for oxybutynin, all other anticholinergic drugs are off label use, which should be explained to the caregivers. Early prophylactic treatment with anticholinergics showed a lower rate of renal deterioration as well as a lower rate of progression to bladder augmentation [507, 509, 539]. Up to date, there is almost no experience with this drug [540], therefore no recommendation can be made. Botulinum toxin A injections: In neurogenic bladders that are refractory to anticholinergics, the off-label use of suburothelial or intramuscular injection of onabotulinum toxin A into the detrusor muscle is a treatment option [544, 545]. In children, continence could be achieved in 32-100% of patients, a decrease in maximum detrusor pressure of 32% to 54%, an increase of maximum cystometric capacity from 27% to 162%, and an improvement in bladder compliance of 28%-176% [544]. Onabotulinum toxin A seems to be more effective in bladders with obvious detrusor muscle over-activity, whereas non-compliant bladders without obvious contractions are unlikely to respond [546, 547]. Also, the injections into the trigone seems to be save in regard of reflux and upper tract damage, if it has some benefit is not further investigated [548]. The most commonly used dose of onabotulinum toxin A is 10 to 12 U/kg with a maximum dose between 200 U and 360 U [544]. The optimal dose in children as well as the time point when to inject which child is still unclear. Onabotolinum toxin A can be effective between three to twelve (0-25) months and repeated injections are effective up to ten years in one study [545, 550, 551]. Urethral sphincter onabotulinum toxin A injection has been shown to be effective in decreasing urethral resistance and improve voiding. The evidence is still too low to recommend its routine use in decreasing outlet resistance, but it could be considered as an alternative in refractory cases [552, 553]. Neuromodulation Intravesical electrical stimulation of the bladder [554-556], sacral nerve stimulation [557, 558] and transcutaneous neuromodulation [559] are still experimental and cannot be recommended outside from clinical trials. The same is true for the intradural somatic-to-autonomic nerve anastomosis [560, 561]. Urethral Dilatation the aim is to lower the pop-off pressure by lowering the detrusor leak-point pressure by dilatation of the external sphincter under general anaesthesia up to 36 Charr. Some studies showed, that especially in females, the procedure is safe and in selected patients, effective [562-564]. Especially in the young infant with severe upper tract dilatation or infections, a vesicostomy should be considered. Faecal incontinence may have an even greater impact on QoL, as the odor can be a reason for social isolation. The aim of each treatment is to obtain a smooth, regular bowel emptying and to achieve continence and impendence. Beside a diet with small portioned fibre food and adequate fluid intake to keep a good fluid balance [518], follow-up options should be offered to the patients and caregivers. At the beginning, faecal incontinence is managed most commonly with mild laxatives, such as mineral oil, combined with enemas to facilitate removal of bowel contents. To enable the child to defecate once a day at a given time rectal suppositories as well as digital stimulation by parents or caregivers can be used. Today, transanal irrigation is one of the most important treatments for patients with neurogenic bowel incontinence. Regular irrigations significantly reduce the risk for faecal incontinence and may have a positive effect on the sphincter tonus as well as the rectal volume [570]. The risk of irrigation induced perforation of the bowel is estimated as one per 50,000 [571]. Later in some of them, transanal irrigation becomes difficult or impossible due to anatomic or social circumstances. Stomal complications occurred in 63% (infection, leakage, and stenosis) of patients, 33% required surgical revision and 6% eventually required diverting ostomies [574]. In addition, patients need to be informed, that the antegrade irrigation is also time consuming with at least 20 60 minutes. Reflux Secondary reflux in patients with neurogenic bladder increases the risk for pyelonephritis. Those with early and post-therapy persistent reflux during videourodynamic studies at low pressure have a higher risk of pyelonephritis [589]. Patients with a high-grade reflux before augmentation have a higher risk for persistent symptomatic reflux after the enterocystoplasty [590]. Therefore simultaneous ureteral re-implantation in high grade symptomatic reflux especially in those with low-pressure high grade reflux should be discussed with the patient/caregivers. Endoscopic treatment has a failure rate of up to 75% after a median follow-up of 4. The prevalence of precocious puberty is higher in girls with meningomyelocele [594]. Erectile function can be improved by sildenafil in up to 80% of the male patients [598, 599]. Neurosurgical anastomosis between the inguinal nerve and the dorsal penile nerve in patients with a lesion below L3 and disturbed sensation is still to be considered as an experimental treatment [595, 600]. Only 17% to 1/3 of the patients talk to their doctors about sexuality, 25 68% were informed by their doctors about reproductive function [593]. Therefore, early discussion about sexuality in the adolescent is recommended and should be promoted by the paediatric urologist taking care of these patients. Gastric segments are rarely used due to its associated complications like the haematuria-dysuria syndrome as well as secondary malignancies, which arise earlier than with other intestinal segments [602-605]. Good socially acceptable continence rate can be achieved with or without additional bladder outlet procedures [607].
In recent years hypertension heart disease purchase hydrochlorothiazide cheap online, the clinical focus has shifted towards functional impairments and outcomes hypertension the silent killer generic 25mg hydrochlorothiazide, with improvement of overall life quality as the main goal [330 blood pressure chart age 13 discount 25mg hydrochlorothiazide, 331] heart attack female trusted hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg. Medications are an important aspect of treatment and assist the facilitation of changes in these areas by improving focus pulse pressure hypovolemia buy hydrochlorothiazide line, self-regulation and decreasing impulsivity/hyperactivity and thus allowing the individual to use psychosocial strategies more effectively [335 hypertension uptodate 12.5 mg hydrochlorothiazide sale, 336]. Psychosocial treatment is the treatment approach preferred by many individuals over medications and is recommended as a first line for preschoolers by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Choosing Wisely Canada campaign (choosingwiselycanada. Psychosocial interventions play a particularly crucial role during key life transitions, for instance in the move from adolescence to adulthood [291, 337-339]. They can provide or support some of these interventions in a timely manner either on their own (with community resource supports) or in co-ordination with other medical specialists, health-care providers and professionals from the educational system. A solid therapeutic alliance is best achieved by spending time listening to a patient?s concerns and understanding their perspective and goals. This guide provides a quick treatment options, strategies for overview of the components of psychoeducation along with a summary optimizing functioning). For example, the following myths are adapted from the Take Ten Series? from the CanLearn Society, Calgary. They are, for example, often able to hyper focus on stimulating activities, like video games, or creative activities such as Lego or drawing. An unhealthy lifestyle, including poor diet, can influence attention and functioning [351]. A multi modal? or comprehensive approach is most beneficial and includes appropriate diagnosis, improve personal and family understanding of the disorder, behavioural interventions and educational supports. They can impulsively over-react verbally or physically, causing significant conflicts. Provide handouts and information on relevant websites, community resources, parent training and support/social skills groups, etc. Encourage, Guide and Motivate Because an assessment often focuses on areas of difficulties, the process may be an overly negative experience for some. Identifying strengths during the assessment and follow-up may mitigate this and establish a solid therapeutic alliance. Families can showcase their children?s achievements, attend their games, recitals, productions, hang their art, display trophies etc. Existing strengths and talents can be leveraged as part of the therapeutic intervention. Promote regular exercise to decrease stress and frustration, improve focus and cognitive clarity, increase endorphins, improve mood and restore a sense of well-being [354-357]. Encourage good nutrition, meal planning, grocery lists, consistent meal times, and eating as a family. Encourage active practice of relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga or music. Individuals lacking these skills commonly feel overwhelmed, resulting in stress, frustration, anger, panic, loss of self esteem, chaos, dysfunction and significant family /relationship conflicts [362, 363]. Emphasize the importance of having a home life that is organized, predictable, consistent, calm, and focused on positive outcomes. Providing such external structure and modelling expected behaviours is essential for increasing self-esteem, improving self-control and ensuring more harmony in family life and relationships. Example: family/spouse/partner/child/peer conflicts [44, Teach stop and think? [344]. For some students, the proactive interventions may not be sufficient and behavioural approaches will be required. These reactive interventions consequence target behaviour by reinforcing positive behaviour (e. It is important to monitor the actual outcomes of these reactive? interventions as they may inadvertently increase disruptive behaviour [374]. The following strategies focus on instruction, behaviour and environment within the classroom that can enhance success. Use visual cues in the classroom or on the desk for be modified; emphasize consistency and routine; boost individual self-esteem through verbal transitions. Incentives need to be meaningful to the rather than asking a child to do 10 addition questions, individual. Parents are actively involved in all of these interventions, sometimes without the child and sometimes in parent?child interactions. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics [381], all share similar behavioral principles, most consistently engaging parents as partners to: (1) reinforce positive behaviors; (2) ignore low-level provocative behaviors; and (3) provide clear, consistent, safe responses to unacceptable behaviors. They may wish to be more social but their impulsivity may detract from their ability to make friends [382]. Sometimes they miss social cues or misunderstand social conventions like when to ask to join in or when not to interrupt. Making friends is an important skill set that both the school and parents can facilitate. Neuroimaging studies have shown that mindfulness training appears related to structural changes in the amygdala and increased grey matter volume in the hippocampus [397-399]. As with all pharmacological treatments in medicine, risk/benefit ratios need consideration before initiating any medication. It is also important to systematically identify other potential causes of impaired functioning in a patient. Sleep deprivation, poor nutrition, lack of routines, psychosocial issues and comorbid disorders can affect outcome and should always be considered when assessing the patient?s condition and when measuring clinical response. Those tools are free to use and can be shared between patients, families, teachers and physicians in helping to guide an informed and evidence based treatment plan. Patients and their families should be aware that such questionnaires can help measure symptom frequency and associated impairment. Clinical judgment is important to uncover if symptoms are due to , or modulated by, another disorder, both before starting treatment, and during treatment. As with any chronic medical condition, follow up is important if medication continues to be taken. However, in some cases, medications are stopped for non-clinical reasons such as stigma or lack of financial coverage or other lack of access to care. First-Line Treatments Long-acting psychostimulants are first-line treatment agents. Additionally, sustained-release preparations maintain privacy for patients and families in the context of the school, work and social situations. In addition, compared to immediate-release psychostimulants, use of long-acting psychostimulants may diminish diversion and rebound and is often associated with better tolerability [410]. However, at the individual level, patients may respond to , or tolerate one class better than the other [411, 412]. They can be used for patients who experience significant side effects, have had suboptimal response with first-time medications, or do not have access to first-line medications [414]. Non-stimulants may also be used in combination with first-line agents as a potential augmentation for first-line treatment suboptimal responders [415]. Second-line non-stimulant agents also are appropriate where stimulant agents are contraindicated, such as in cases where there is high risk of stimulant misuse [133]. Third-Line Treatments Bupropion, clonidine, imipramine and modafinil are examples of third-line treatment agents. They are medications whose use is off-label, or have higher risks, or a higher side-effect profile or a lower efficacy profile. Third line pharmacological treatments are generally reserved for treatment-resistant cases and may require specialized care. Treatment before the age of six, if necessary, should be within the context of specialized care [270]. Medication use can be titrated to meet increased demands or to cover longer periods of daytime impairment. The decision about when to administer treatment during the day and how long the effect of that treatment needs to last must be explored by the clinician in consultation with the patient and patient?s family. This decision must be made considering the context of the individual?s experience. To improve the overall quality of life for the majority of individuals, regardless of age, the duration of effect of the medication usually needs to extend beyond the classroom/work settings into the evening, weekend and holidays. Similarly, a patient may realize that the best option may be to have individualized treatment based on day-to-day variation. This may be critical for tasks such as driving, where the maximal risk period for young drivers may be during the evenings and at weekends. It is important to remember that the duration of effect for a specific medication can vary from patient to patient. Clinical experience indicates that, for some patients, the duration of effect is shorter or longer than what is stated in the product monograph. A variety of considerations may be important in determining sequence of treatment including diagnostic certainty, patient preference, the disorder with greatest impairment, or the disorder most likely to respond to treatment. If the patient is expressing suicidal or violent thoughts these need to be addressed as a priority. Although stimulants are thought to upregulate sympathetic nervous system activity, they are often compatible with anxiety disorders. Weight and Height Weight and height require initial and ongoing measurement in children and adolescents. However, there has been controversy regarding the cardiovascular safety of these drugs, particularly the potential risk of arrhythmias. The direct consequence of small increases in systemic adrenergic activity lead to the expected cardiovascular effects of small increases in blood pressure and heart rate, which are statistically significant, but rarely clinically important [416-419]. It is recognized that adverse events are usually under reported by 75 to 90%, although true underreporting for an event as dramatic as sudden death is not known. In a third claims records database study, neither current nor previous stimulant use was related to cardiovascular symptoms or events [427]. A case-control study assessed matched groups of 564 children aged 7?19 years from state mortality data over an 11-year period, comparing those who had suffered sudden unexplained death to those who had died as passengers in motor vehicle accidents. However, the histories related to the sudden unexplained death cases may have been subject to a recall bias, and in the absence of autopsy information, assigning cause of death in young individuals with sudden unexplained cardiac arrest is difficult [428]. In an administrative database study of Medicaid and commercial insurers, 43,999 new adult methylphenidate users were matched to 175,955 nonusers, and had a significant hazard ratio of 1. Dosage was inversely associated with risk, and this lack of an expected dose-response relationship suggested that the association might not be a causal one. In addition, ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death are not synonymous and may arise by very different mechanisms, especially in persons without structural heart disease [429]. Velocardiofacial Syndrome) [432] in association with complex congenital heart disease or [146] its surgical repair [433, 434]. It is uncommon, but some patients will have much higher effects from stimulant treatment. These effects can be evaluated by comparing heart rate and blood pressure before and on treatment in the case of stimulants this can also be evaluated before a dose and after the dose the same day. In adult patients with hypertension or coronary heart disease, caution is advised and a closer monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure is recommended in these cases. It is important to have a comprehensive discussion regarding all treatment options. They may be afraid that medication will cause them to lose their sparkle? or their brain will become lazy. A frank discussion about therapeutic and side effects may help patients make better choices. It should be stressed that most side effects settle after two or three weeks of continuous use and alternative options will be sought if a person feels they are impaired by a prescription. A common reason for non-adherence is related to a lack of physician awareness or understanding of side effects, or patients? reluctance to explain their discomfort. Patients should be informed about how to determine if their medication dosage is too high. For example, they might experience feeling too "wired", too irritable or excessively focused, or experiencing restricted affect, sometimes called a zombie effect. Please note: If negative symptoms are experienced at the time when medications would be expected to be wearing off, or with sudden cessation of pharmacotherapy, it is likely that those symptoms are not from an excessively high dose but from withdrawal, where the medication is wearing off too quickly. That experience, positive or negative, may colour their attitudes towards the suggested course of treatment. For instance, they may have suffered the disappointment that comes with over-estimation of the effectiveness of medication, especially without concurrent educational and psychosocial interventions. Although there is no evidence indicating that a family member?s response indicates a greater likelihood of patient response, it is understandable that a positive response to a specific treatment in a family member could increase positive expectations for this treatment while the contrary can occur for a negative outcome. They may also inquire if the patient themselves tried? the medication outside a treatment regime; patients may not spontaneously provide this information unless asked. Medication Selection: Medication-related factors See the following section for medication-specific differences. These differences allow for matching of medication characteristics to patient needs and preferences. Physicians should refer to Product Monographs for complete prescribing information. Unfortunately, some medications are beyond the financial reach of a significant number of patients without extended health insurance. Some medications can be supported through special access programs, but entrance can be limited by the procedures required or the constricted time for which medication is supplied. Most Canadians have access to reimbursement for prescription medications through private insurance plans (third-party insurance), the provincial / territorial drug benefit programs or federal programs for certain groups. An online guide to provincial reimbursement for prescription medications in Canada can be found here: bit.
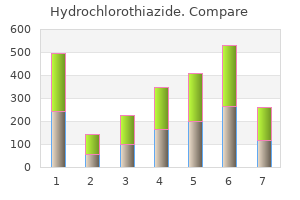
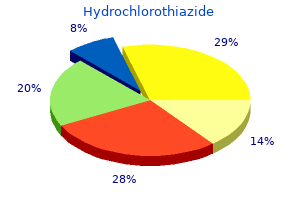
Hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg generic. Hypertension Nursing NCLEX Review.
Coagulase-negative staphylococci are antibiotic inevitably depends on the causal pathogen and often seen in association with foreign bodies pulse pressure meaning buy hydrochlorothiazide 12.5mg low price, such as its susceptibility pattern blood pressure 14080 buy hydrochlorothiazide 25mg overnight delivery. Acute osteomyelitis is usually successfully treated Anaerobic bacteria as Bacteroides spp blood pressure and pulse rates cheap hydrochlorothiazide 25mg otc. Some recent data on the subject can associated with open fractures hypertension thyroid order hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg fast delivery, as a consequence of traf be found (Lew hypertension quality improvement discount hydrochlorothiazide online, Waldvogel hypertension heart disease hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg overnight delivery, 2004; Chihara, Segreti, 2010; fic accidents and war injuries (Chihara, Segreti, 2010; Haidar et al. Next, we will discuss the classes of antibiotics used Virtually any organism has the potential to cause in oral and systemic antibiotic treatment and the use of lo osteomyelitis. For example in immunocompromised pa cal antibiotic delivery systems mainly in the management tients, pathogens such as Bartonella henselae, Aspergillus of chronic osteomyelitis. An early switch to oral administration is appropriate for antibiotics with good General considerations bioavailability and bone penetration (Lew, Waldvogel, 2004; Eid, Berbari, 2012). Combined parenteral and oral Several medical specialties are involved in the treat regimens are usually used (Calhoun, Manring, 2005). The primary goal of treatment is remission of the disease, Beta-lactams and lincosamides which is defned as the absence of any sign of infection, Intravenous beta-lactams antibiotics. Oral beta-lactams are theless, newer fuoroquinolones are not as active against more effective in pediatric osteomyelitis, as compared to P. In addition, the widespread use of antibiotic active against most gram-positive bacteria, has quinolones has led to the emergence of quinolone-resistant excellent oral bioavailability and high bone serum ratios S. The fluoroquinolones have gained popularity in recent years because of their excellent oral bioavailability Rifampicin and fusidic acid and bone penetration (Lew, Waldvogel, 2004). Rifampicin, a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent, Promising results have been demonstrated in several achieves high intracellular levels and is one of the few trials especially against Gram-positive, Gram-negative, antimicrobial agents that can penetrate biofilms and and polymicrobial infections (Pawar, Bhandari, 2011). Several studies have shown that oral the second generation fuoroquinolones like ciprofoxacin, treatment with rifampicin in combination with various ofloxacin, and pefloxacin against some Gram-positive antibiotics as ciprofoxacin, ofoxacin, or fusidic acid is organisms (Pawar, Bhandari, 2011). Yet, they have poor effective in bone staphylococcal infections in the presence activity against Streptococcus spp. The third-generation quinolone, levofoxacin, has However, its utility could be limited due to the de improved Streptococcus spp. Preliminary data ment of resistance, is one of the prime limitations of fusidic suggests that daptomycin penetrates bone well and can be acid, unless used in combination (Pawar, Bhandari, 2011). Even with prolonged intravenous antibiotics, there New agents is a significant relapse rate in the treatment of chronic Newer antibiotics with high bone penetration such osteomyelitis. A system works to obliterate bacteria in the area as well as good review on the topic was recently published by Pawar to reduce the dead space in the bone (Nair et al. Its use results in a lower serum antibiotic concentration Linezolid, which can be administered either orally than that associated with systemic administration, thereby or intravenously, represents a new class of antibiotic with reducing toxicity-related side-effects (Joosten et al. It has been proved effective for antimicrobial agents in local delivery systems are amino treating serious infections, including osteomyelitis (Cal glycosides and to a lesser extent various beta-lactam agents houn, Manring, 2005). However, a combination therapy of anti needs to be produced in bone and joint infections, since biotics is useful to reduce the toxicity of individual agents, they are lacking. Additionally, no large randomized trials to prevent the emergence of resistance and to treat mixed have been published on the use of linezolid for orthopaedic infections involved in osteomyelitis (Nandi et al. The local delivery of antibiotics in the treatment of Daptomycin is a novel parenteral cyclic lipopeptide osteomyelitis has been used for decades regardless of the with bactericidal activity against multi-drug resistant controversy over its effectiveness (Gitelis, Brebach, 2002). Gram-positive organisms commonly found in osteomy To retain an appropriate antibiotic level, several drug elitis, even when the other first-line drugs have failed delivery systems have been developed in the treatment of (Calhoun, Manring, 2005; Lamp et al. Klemm (1979) and were used to occupy dead space after However, these types of beads have the disadvantage debridement of infected bone related to chronic osteomy of a lack of thorough mixing of the antibiotic into the mate elitis. Klemm treated more than 100 patients in this fashion rial and a lack of uniform size of bead, resulting in lower and a cure rate of 91. Over the past three decades, numerous advantages clinical trials (Walenkamp, 2009). Local polymer mixed with a liquid monomer to form a solid antibiotic treatment is also substantially less expensive structure. But the resistance to these terials are being explored as silicate (Makinen et al. In this sense, several expected they will remain in the near future an effec biocomposites composed of biodegradable polymers such tive drug delivery system for local antibiotic therapy in as chitosan poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), poly(D,L osteomyelitis. Interesting reviews on the subject can infection, caused by a variety of microbial agents (the be found in Kanellakopoulou, Giamarellos-Bourboulis most common being S. Despite advances in medical teoconductive bioceramics (calcium sulphate, tricalcium and surgical therapies, the management of osteomyelitis phosphate or hydroxyapatite) has been proposed for the is an increasing challenge to clinicians due to the growing local management of osteomyelitis and to aid dead space resistance to antibiotics. A novel number of biodegradable tolerance have encouraged the search for newer agents, carriers systems have been developed in recent years with namely linezolid, daptomycin, quinupristin-dalfopristin promising clinical potential, combining local delivery of and tigecycline. This is an emerging Management of chronic osteomyelitis with the area of research with great potential in the near future to local delivery of antibiotics has the advantage of achiev treat osteomyelitis. Treatment of osteomyelitis in rats by injection Effcacy of ciprofoxacin implants in treating experimental of degradable polymer releasing gentamicin. Effective Treatment of osteomyelitis with biodegradable microspheres in a rabbit model. Antibiotic-loaded biomaterials and the Microspheres: Preliminary Testing for Potential Treatment risks for the spread of antibiotic resistance following their of Osteomyelitis. Duration of post-surgical antibiotics in chronic experimental osteomyelitis by methicillin resistant osteomyelitis: empiric or evidence-based? Antimicrobial osteomyelitis treated by antibiotic calcium hydroxyapatite treatment of osteomyelitis. Current medical diagnosis and factors for developing osteomyelitis in patients with diabetic treatment. In vivo-in vitro study of biodegradable and mechanisms of the implant-related osteomyelitis by osteointegrable gentamicin bone implants. Management of bone infections in adults: the surgeon?s osseous infections of the foot and ankle. Outcomes experimental osteomyelitis by surgical debridement and the of osteomyelitis among patients treated with outpatient implantation of calcium sulfate tobramycin pellets. Daptomycin: a review of acute haematogenous osteomyelitis of childhood: moving properties, clinical use, drug delivery and resistance. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong prophylaxis of postoperative infection Staphylococcus Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi, v. Received for publication on 01st August 2012 Accepted for publication on 09th January 2013. Encourage them to try stepping down to the lowest effective dose needed to control symptoms, or as needed?/?on demand? to manage their own symptoms, or stopping treatment completely where appropriate. Lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole and esomeprazole are available generically (see Chart 1 for cost comparison. The best evidence is for Clostridium difficile infection and increased risk of bone fractures in susceptible populations. They include acute interstitial nephritis, hypomagnesaemia, vitamin B12 deficiency, rebound acid hypersecretion syndrome9 and increased mortality in older patients. However, reviewing and reducing therapy will not only reduce prescribing costs but will potentially increase patient safety. It can be severe or frequent enough to cause symptoms or damage to the oesophagus (for example oesophagitis) or both. It can lead to abnormality of the cells in the lining of the oesophagus (Barrett?s oesophagus) which is itself considered the most important risk factor for oesophageal adenocarcinoma, the incidence for this has increased considerably in the past decade. They are also used in combination with antibacterials for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. They can also be used to control excessive secretion of gastric acid in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, where high doses are often required. Having the main meal well before bedtime (3-4 hours beforehand) and raising the head of the bed may help some people. Provide people with educational materials to support their care, or access to them. These include bleeding, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), recurrent vomiting or unintended weight loss. Discuss with people how they can manage their own symptoms by using treatment only when they need it. This involves reducing their use of prescribed medication: by using the lowest effective dose, by trying as needed? use when appropriate and by returning to self-treatment with antacid and/or alginate therapy (unless there is an underlying condition or co-medication that needs continuing treatment). Alternatively if a person?s severe oesophagitis fails to respond to maintenance therapy carry out a clinical review. This type of study has limitations as they can only suggest an association, not establish a cause and are prone to confounding. For example treatment plans may be changed depending on the individual patient?s risk factors, tolerability or treatment response. Therefore observed differences in outcomes may be due to heterogeneity (differences) among the patients, not only the different treatments. The following sections give further details about each of the specific adverse effects. They found, similar to others? estimates, 60% of patients received acid-suppressive therapy. Firstly ensure patients receive the least intense acid-suppressive therapy appropriate for their clinical condition, secondly minimise exposure in low risk, non-critically ill patients for stress ulcer prophylaxis and thirdly ensure prophylactic medications are not continued beyond discharge. Elevated gastric pH levels may allow or facilitate conversion from spore to vegetative forms of C. Even a modest increase in risks mean a substantial amount of patient harm at a population level when the risk factor is widely experienced. This was observed mainly in elderly patients, other factors may contribute to the increase in fracture risk. It is not necessary to treat patients to the point of neutralising acid to resolve reflux symptoms, so the recommendation is to choose drug doses thoughtfully with consideration of the desired therapeutic outcome. Hypomagnesaemia can result in serious conditions: fatigue, tetany, delirium, convulsions, dizziness and ventricular arrhythmia. The elderly and malnourished may be at a higher risk, as they are more likely to have borderline baseline levels. W ell-designed studies should include patients without acid-related disorders, such as functional dyspepsia. Strong data are lacking to support the risk of most of the adverse effects described above. However, it is advisable to exercise caution in the elderly and in patients with other risk factors for C. A Drug Safety Update in 2010 advised against use of clopidogrel and omeprazole or esomeprazole to avoid an interaction, unless considered essential. There is a possibility of reduced inhibition of platelet aggregation whether the two medicines are given simultaneously or 12 hours apart. However, exercise caution in the elderly and in patients with other risk factors for C. Material to support appropriate prescribing of Proton Pump Inhibitors across W ales. Use of gastric acid-suppressive agents and the risk of Community-Acquired Clostridium difficile-associated disease. Iatrogenic gastric acid suppression and the risk of nosocomial Clostridium difficile infection. Risk factors for recurrence, complications and mortality in Clostridium difficile Infection: a systematic review. Use of acid-suppressive drugs and risk of fracture: a meta analysis of observational studies. Use of proton pump inhibitors and risk of hip fracture in relation to dietary and lifestyle factors: a prospective cohort study. Proton Pump Inhibitors and risks of 1-year mortality and rehospitalisation in older patients discharged from acute care hospitals. Proton pump inhibitors and the risk of antibiotic use and hospitalisation for pneumonia. Systematic review: symptoms of rebound acid hypersecretion following proton pump inhibitor treatment. Systematic review: rebound acid hypersecretion after therapy with proton pump inhibitors. The use and application of this guidance does not override the individual responsibility of health and social care professionals to make decisions appropriate to local need and the circumstances of individual patients (in consultation with the patient and/or guardian or carer). These diseases clinically overlap and may present diagnostic and management challenges in primary care, especially in low resource settings. There is huge variation in the global distribution of the disease, Rather, dyspepsia refers to recurrent symptoms that alert with higher prevalence in Western than Asian/African countries the physician to a problem within the upper gastrointestinal (25?40% vs < 5%). This article reviews important diagnostic and management are associated with greater damage to the esophagus. Incompetent lower esophageal sphincter that allows backward may also overlap that of other gastrointestinal and pulmonary movement of acidic gastric content into the esophagus and disorders, that are grouped into esophageal and extraesophageal hypopharynx. Less frequently, there may be non-cardiac persistence of refuxed content is what results in chemical 19,21 chest pain and dysphagia. A history of heartburn and/or regurgitation, with or without other symptoms or complications, Routine testing for H. Uncommon sensation under the sternum that is associated with meals, symptoms, including dysphagia, bloating and early satiety, recumbency, nocturnal occurrence and is relieved by antacids. Lifestyle Extra-esophageal syndromes (Table 2) are generally modifcation and acid suppression form the basis of treatment multifactorial and occur less commonly. Barium imaging: is rarely used, as endoscopy is of superior pneumonia and decrease efcacy of clopidogrel. Except for diagnostic value and provides direct visualisation and the 39 the last, robust data is lacking.
Mild head injury discharge advice should include home observation after a short period of observation in information about post concussion symptoms including hospital if clinically improving blood pressure medication in liquid form buy cheap hydrochlorothiazide on line. The clinical symptoms in the emergency department and those sports medicine approach to concussion of graded return with documented post traumatic amnesia in the emergency to play translates well to all mild head injury patients heart attack feeling buy hydrochlorothiazide 12.5mg visa. Elderly patients and those on anticoagulants However blood pressure record chart purchase hydrochlorothiazide 25mg with mastercard, there has been a tendency in the past not to should also be advised to have routine follow up organised mention post concussion symptoms in discharge advice due to the increased risk of complications best blood pressure medication kidney disease buy hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg on-line. Therefore blood pressure of 11070 buy hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg with visa, it is important to provide education symptoms following closed head injury arteria aorta definicion purchase genuine hydrochlorothiazide on line. All patients should be given written advice and detailed information and evidence about the recovery and advised to see a doctor if they are not feeling better within rehabilitation of patients with mild brain injury following a few days of injury. Similarly, Yates et al156 in a New Zealand study found that a head injury discharge sheet was better understood when written in a simplified form using less complex language. The mild head injury advice sheet developed for the original version of these guidelines included most of the relevant information suggested by the literature and was well received during the implementation trials and after publication. All patients with mild head injury should be advised to follow up with their local doctor if they are not feeling better within a few days. The majority of studies in the literature tend to focus on and close clinical observation. Patients with moderate head the management of either severe head injuries or mild head injury have higher rates of intracranial lesions and cognitive injuries. The findings of or antibiotics, then the network neurosurgical service these detailed reviews are summarised in Evidence Table should be consulted. This guideline summarises the generally accepted initial areas of treatment such as induced hypothermia159, 160 management steps for severe head injury including those and hypertonic saline. Corticosteroids have been shown to worsen the network neurosurgical service should be consulted about patient outcome and are not recommended for the initial further management of patients with severe head injury management of closed head injury. Detailed evaluation of subsequent management of severe head injuries by the neurosurgical services are beyond the It is important to recognise that for the majority of severe scope of these guidelines. In the event of acute deterioration, it is important to remember that hyperventilation24, 158 and intravenous mannitol boluses161,162 are short-term measures to reduce intracranial pressure whilst the patient is urgently assessed for the need for acute neurosurgical intervention. If an acutely deteriorating patient with a proven extradural or subdural haematoma cannot be transferred to a neurosurgical service within two hours, then the option of local surgical decompression should be discussed with the neurosurgical service. When should patients with closed head injury be transferred to hospitals with neurosurgical facilities? The network neurosurgical and retrieval services should be consulted as soon as possible to facilitate early transfer. The following patients should be considered for transfer and discussed with the network neurosurgical service. However, there has been increasing required and early neurosurgical consultation is advisable. Hospital Major Trauma Triage Protocol (T1)170 has adopted such a pre-hospital strategy for transferring all major Fabbri et al41 recently published a study in which they trauma patients directly to a major tertiary trauma hospital compared the outcome for mild to moderate head injury or neurosurgical facility wherever possible. Interestingly, Bazarian mental status, behaviour, drowsiness or et al82 in a review of management of mild head injury vomiting? Patients with persistent or injury patients with other associated injuries are more worsening drowsiness should be clinically reassessed. Moderate to severe head injury Isolated moderate head injury patients who rapidly clinically improve can be treated in a similar way to mild head injury patients. Early post traumatic seizures have not been shown to be associated with worse patient outcomes in B large population studies. Clinical judgment is required on whether to prescribe anti-convulsants for individual patients. Penetrating injuries have a much higher penetrating injury, extradural/subdural/intracerebral incidence of post traumatic seizures. The risk posed seizures are thought to be associated with the acute injury by an intracranial bleed is proportional to the amount of and are not significantly associated with the development blood. Late post traumatic seizures are less likely to be related to the acute injury and are Delayed or late post traumatic seizures (incidence range more likely to be associated with the development of post 1-15%) that occur more than seven days after injury are traumatic epilepsy. These immediate >65), neurosurgical intervention and early post traumatic seizures are frequently seen on sporting fields and in seizures. It has been proposed that these immediate seizures be called concussive convulsions? and it has been Acute post traumatic seizures require systematic suggested that they are not an epileptic phenomena. Immediate and early post traumatic seizures are relatively If prophylactic anti-convulsants are recommended then common in patients with mild closed head injury with a phenytoin (dilantin) is normally given as there has been reported incidence of up to 5%. Many of the larger 151 Alternatives include sodium valproate (epilim) and studies found that post traumatic seizures were not levetiracetam (keppra). Levetiracetam is being increasingly significantly associated with intracranial injury. The risk of early post traumatic seizures is greater and the potential for secondary brain injury from these seizures is increased. Prolonged post traumatic seizures are of most concern and may be difficult to recognise in intubated patients. Therefore, prophylactic anti-convulsants are more likely to be recommended in these patients. The decision to use anti-convulsants should be discussed with the relevant neurosurgical service. Potentially injuries and consequently do not Abnormal alertness broad clinical application. Considered seizure Coagulopathy and progressive severe headache due to clinical importance but when added to original criteria also did not signi? Concluded that no clinical decision rule is perfect and there is always a trade off between sensitivity and speci? Neurotraumatology Committee Sensitivity for any intracranial lesion was of the World Federation of highest for Scandinavian (95. Increasing age 13-15) with brain injury or skull was associated with poorer outcome. Delayed deterioration was generally due to subdural lesions and occurred up to 1/52 later. Administer both tests at hourly intervals to gauge patient?s capacity for full orientation and ability to retain new Withdraws 3 3 3 3 3 information. Also, note the following: poor motivation, Extension 2 2 2 2 2 depression, pre-morbid intellectual handicap or possible None 1 1 1 1 1 medication, drug or alcohol effects. In cases where Eye Opening Spontaneously 4 4 4 4 4 doubt exists, more thorough assessment may be To speech 3 3 3 3 3 necessary. Why are you here For patients who do not obtain 18/18 re-assess after a Month further hour. Year Patients with persistent score <18/18 at 4 hours post time Confused 4 4 4 4 4 of injury should be considered for admission. To do this, pick 2 other similar sized hospitals in your local area or neighbouring region. If the patient does not know, give them three options, including the correct reason. It is considered correct for patients to answer in the short form 08?, instead of 2008. Also, an acceptable alternative prompt (for the rest of the 2000?s) is The year is 2000 and what? Picture Cards at each subsequent time T2-T5: Ask patient, What were the three pictures that I showed you earlier? Shores & Lammel (2007) further copies of this score sheet can be downloaded from. Prior to this most descriptions of altered Allow triage of patients after injury levels of consciousness revolved around very subjective Provide a tool for prognostication portrayals such as comatose?, drowsy?, obtunded?, and Allow standardisation of patients and patient groups stuporose. One research group found that increasing the eye opening component refers to the processing of scores in the 9-15 range (reflecting improving eye and information by the cerebral cortex and the level of arousal verbal performances) are associated with a doubling of the or wakefulness. Unfortunately, not only are many clinicians scores, but only intermediate agreement in the motor and unaware what the descriptions of patient reaction to a eye scores. Obeys processing is occurring and that the related arousal commands indicates an ability to process and obey verbal mechanisms at the brain stem are functioning,193 whereas commands;197 localisation means that the patient is able a eye component score of 2 indicates that lower levels of to identify the location of a painful stimulus and attempt the brain are functioning. Withdrawal means that opening, and in this instance this is a reflexive action and the patient is attempting to move away from the noxious does not indicate awareness of self or surroundings. Inappropriate words flexion and extensor posturing are often known by the describes clear and comprehensible speech,197 but using terms decerebrate and decorticate response, implying the random words or swearing and cursing. Incomprehensible patients showing extensor posturing are more likely to sounds refers to moaning and groaning without have a poor outcome than those with abnormal flexion. It is important to differentiate and extension on the other, the best of the two responses between a patient with a decreased level of consciousness needs to be recorded. When this occurs, it has been recommended that a 1 is scored,197 however if this is done it has to be accompanied by a written explanation and the caveat that this cannot be used in an overall score. These include presence of endotracheal tube, tracheostomy or other airway adjunct, traumatic injury to eyes, mouth or limbs. The medication chart should be checked to determine if there have been any sedating or paralysing drugs administered, and patient notes should be checked for a history of recent alcohol or substance use. Document the presence of any of the above on the observations chart, or ensure that they have already been noted. Ask their name, month, year, Call patient by their name; repeat loudly if no location, your role, why they are there. Bear in mind Document eye opening if present with this pain the need is to apply moderate pain, not to damage Yes stimulus. There is a small risk of you developing serious complications so you should be watched closely by another adult for 24 hours after the accident. It outlines what signs to look out for after a head injury and what you need to do if you have problems. Warning Signs If you show any of these symptoms or signs after your head injury, or you get worse, go to the nearest hospital, doctor or telephone an ambulance immediately. It is alright for you to zz sleep tonight but you should be checked every four hours by someone to make sure you are alright. Drinking / Do not drink alcohol or take sleeping pills or recreational drugs in the next 48 Drugs hours. They also make it hard for other people to tell whether the injury is affecting you or not. See your local doctor if you are not starting to feel better within a few days of your injury. Adapted from Mild Head Injury Discharge Advice? author Dr Duncan Reed (2007) Director of Trauma Gosford Hospital. You can help yourself get better by: Rest / Sleeping Your brain needs time to recover. It is important to get adequate amounts of sleep zz as you may feel more tired than normal. Driving Do not drive or operate machinery until you feel much better and can concentrate properly. Drinking / Drugs Do not drink alcohol or use recreational drugs until you are fully recovered. Work / Study You may need to take time off work or study until you can concentrate better. Most people need a day or two off work but are back full time in less than 2 weeks. See your doctor and let your employer or teachers know if you are having problems at work or with study. Sport / Lifestyle It is dangerous for the brain to be injured again if is has not recovered from the? Relationships Sometimes your symptoms will affect your relationship with family and friends. Recovery You should start to feel better within a few days and be back to normal? within about 4 weeks. Your doctor will monitor these symptoms and may refer you to a specialist if you do not improve over 4 weeks up to 3 months. Sometimes you may not be aware of them until sometime after your injury like when you return to work. More sensitive to sounds or lights and solving problems, getting things done or being? B rainTraum aFoundation In addition, reference lists of previous guidelines and key The following websites were also searched (using relevant free text terms): Agency for Healthcare Research & Quality The body guideline also utilises an additional grade of Consensus? of evidence reflects the evidence components of all the where appropriate. The overall grade of addressed in this guideline contain clear recommendations the recommendation is determined based on a summation with an associated strength of recommendation grade as of the rating for each individual component of the body of per above. Please note that a recommendation cannot be relevant clinical points to the boxes which support the given graded A or B unless the evidence base and consistency of recommendation. The process used to assess the studies included in Good studies Low risk of bias Have most or all of the relevant quality items Fair studies Susceptible to some bias, but not suf? Were the characteristics and results of the studies items: summarised appropriately? Was follow-up for final outcomes adequately been considered, both benefits and harms? What are the proven treatments for patients with moderate? to severe? head injury? The definition, incidence and prevalence in head injury: review of published studies. Determinants of Head treated traumatic brain injury in an Australian Injury Mortality: Importance of the Low Risk community. Mower W, Hoffman J, Herbert M, Wolfson A, Neurotraumatology Committee of the World Pollack C, Zucker M, et al.