William J. Brady MD
- Professor of Emergency Medicine and Medicine Ice Chair, Department of Emergency Medicine
- Medical Director, Life Support Learning Center
- University of Virginia Health System
- Charlottesville, VA, USA
States must also ensure access to health facilities medicine 3605 v buy topamax 100mg line, goods medications quiz order topamax 200 mg visa, and services on a non-discrimina to ry basis symptoms of anxiety generic topamax 200 mg online, and this must be done immediately medications rapid atrial fibrillation order genuine topamax line. Tirkey medications in checked baggage purchase topamax online, Tuberculosis Associated Stigma among Patients Attending Outpatient in Medical College Hospital in Sagar (Madhya Pradesh) in Central India oxygenating treatment order 100 mg topamax with amex, 3 J. The Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights has also noted that access to information is an integral component of the 112 right to health and that states have a positive obligation to conduct information campaigns and disseminate information relating to 113 health. However, in the first three years of the National Strategic Plan, the government approved only Rs. Interna tional law requires states to ensure that there is a sufficient quantity of 132 public healthcare facilities, goods, services, and programs. Al though this obligation is subject to progressive realization, states must 133 take steps to the maximum of their available resources. Moreover, Indian courts have largely rejected financial limita tions as an excuse in the context of the right to health. State of West Bengal, the Supreme Court ordered the government to provide additional beds and facili 137 ties for patients needing emergency care. Any person whose right to health has been violated should have access to effective judicial or other appropriate remedies at both the national and international levels, including both financial 152 and equitable relief. This requirement of accountability extends to 153 both the public and private health sec to rs. In India, the Supreme Court itself has created accountability mechanisms when needed. Al 173 though this provision was removed from the statute in 1995, this holding was never overruled, and other provisions are also problem atic. The same Health Act still allows a health officer to forcibly take someone to a hospital or other place of treatment if it appears that 167. Goa, Daman, and Diu Public Health Act, 1985 and Rules, 1987, at 977 (India), goaprintingpress. Although not specifically listed in the major human rights treaties, the right to participate is implicit in a variety of other rights, including the right to self-determination, the 184 right against medical experimentation, and the right to dignity. Moreover, a participa to ry approach would build patient trust and strengthen cooperation, both of which are essential for 189 health programs to succeed. Where the Committee itself cannot resolve a complaint, it must forward the complaint to the district 195 grievance redressal committee. The government should consider replicating successful state level practices, such as identifying specific authorities for grievance redressal at various levels (such as the Principal Secretary and Health Commissioner at the state level and the Chief Medical and Health Officer at district level), forming committees in district hospitals and community health centres for reviewing complaints, and creating a 199 state-level centralized call centre with a to ll-free number. Indian courts have not followed a human rights approach in cases involving forced isolation, and the case law relating to regulation of the private health sec to r provides mostly general principles but little direct guidance. Healthcare providers need to engage with patients, not as data points or potential disease transmitters, but rather both as individuals worthy of respect and as partners in creating a healthier society. Country visits and in-depth interviews were conducted with key stakeholders and common themes identified to guide the conceptual framework of the Roadmap. Country visits and in-depth interviews were subsequently conducted with key stakeholders and common themes identified to guide the conceptual framework of the Roadmap. Arguably the weakest component of health systems, labora to ry services in developing countries have his to rically been grossly neglected and underfunded. Increasing funding for global health initiatives and in particular for health systems components, requires a focused approach to strengthening of key elements of labora to ry services that cut across diseases. The document should also be used as one of the resources in a national process that involves the participation of all global and national partners and organizations involved in labora to ry work to create a national public health labora to ry strategic plan that addresses the needs of all diseases of public health importance. Because of the complexity of strategic planning and technical issues, countries may choose to use an expert labora to ry consultant to guide the planning process. This document has been developed as a reference for everyone involved in activities that strengthen labora to ry systems and the diagnosis of tuberculosis, such as labora to ry technicians, program managers, technical advisors, procurement officers, warehouse managers, service providers, government officials, implementing partners, donor agencies etc. Anyone who may be responsible for program planning, budgeting, and mobilizing resources for diagnostic services will also benefit from using this document. It is expected that countries will adapt the generic Roadmap to suit country-specific needs, within the context of their own epidemiological situation and resource availability. More complete and comprehensive technical information can be found in various published documents, journals, labora to ry manuals and policy publications. General considerations for developing of the Roadmap Establishing, equipping, financing, and ensuring sustainability of appropriate labora to ry networks are challenging, complex and expensive. Many international agencies and donors have expressed interest in investing resources in labora to ry capacity development. Coordination of labora to ry strengthening activities is essential to avoid wasting of scarce resources, unnecessary duplication, and confusion at country level due to conflicting technical advice and approaches. A globally agreed Roadmap for labora to ry strengthening would be expected to ensure coordination, compliance with international norms and standards, ensure standardization and uniformity in funding applications, avoid duplication of efforts, and should lead to optimized use of resources. Cross-cutting health systems components of labora to ry services amenable to integration, areas that require close collaboration between disease specific programmes, and areas requiring a technical disease-specific focus are summarized in Table 1: Table 1. One reason has been the slow uptake of new global policies in country screening and diagnostic algorithms, which is relatively easy to address. New to ols will, however, be impossible to implement if the required labora to ry networks, infrastructure, training and deployment of skilled labora to ry workers, quality assurance and information systems are not developed and maintained in tandem. Essential Components Of A Labora to ry Services System National labora to ry strategic plans should strive to create a labora to ry system based on quality labora to ry management principles. The key elements to be addressed in a national labora to ry plan are listed in Table 2. The objectives will vary between countries, as they will be in part influenced by disease prevalence, the current in-country labora to ry capacity, infrastructure, human and financial resources and existing quality systems. It is essential that each objective is linked to an associated work plan which is realistic and achievable. The roadmap intends to describe a well-structured labora to ry system with multiple tiers of labora to ry service. Depending on the size of the country, the population and their geographical distribution, peripheral and regional labora to ries supporting local clinics and hospitals, will perform simple and more regularly requested sample analyses, while referral centers will have a higher level in the labora to ry structure and perform more specialized tests, or those tests which are performed less frequently. At the regional level, decentralisation of testing may take the form of labora to ry performing specimen processing for microscopy and rapid resistance detection with or without the capacity to perform culture inoculation. Attention must be given to the transport of samples, tracking of samples referred in the system and return of test results to the correct site for appropriate patient management. Three levels are generally recognised, each with its particular responsibilities, although these can vary to some extent, depending on the level of development besides country-specific needs and diagnostic strategies. Very small or very large countries may function better with one level less respectively more within this pyramid. Additionally, one may consider a still more peripheral level with only specimen collection and possibly preliminary processing; also private labora to ries may take a particular position attached to this structure; and there is the network of Supra-National Tuberculosis Reference Labora to ries providing certain services to the national level. To avoid duplication and unnecessary expenditure, effective labora to ry strengthening requires strong collaboration and coordination between departments responsible for labora to ry services at country level, between disease-specific programmes, and between those responsible for human resource development and training. Using these different funding sources to effect much need improvement to overall labora to ry infrastructure and service may be one of the most cost-effective interventions to improve diagnosis and care of patients suffering from one or more of these conditions. Additionally, decide on the level at which they should be available (for instance some microscope spare parts). The referral of samples for molecular testing using lineprobes do not require organisms to be viable, hence are less vulnerable to sample deterioration than samples referred for culture. Packaging and transport of specimens suspected of containing infectious disease should be done according to international standards, including those of the aviation industry when such specimens are sent by air. Data Management At a minimum, proper recording of labora to ry tests performed is required for patient diagnosis and treatment follow-up. In its simplest form this includes operational parameters such as numbers of tests and positivity rates. The main challenge will often be to restrict recording and especially reporting to what is essential and likely to be used routinely. This will be applicable to all levels to assure transparency and uniform application of definitions for data parameters and their entry. Human Resources Need to set up a national mechanism to ensure coordination at all levels among government departments responsible for labora to ry services, disease-specific programmes, human resource development, and training. Human resource capacity in labora to ry services constitutes a particular crisis, with almost 80% of countries reporting critical shortages in skilled labora to ry staff 22 Capacity Attaining health objectives in a population depends to a large extent on effective, efficient, accessible, viable and high quality services provided by all personnel, in sufficient numbers and appropriately allocated across different occupations. The lack of clear policies for human resource development in many countries has produced an imbalance that threatens the capacity of health care systems. Human resource development is an activity requiring input from human resource experts. However, labora to ry workers often remain invisible to patients, policy makers, and funders, being overlooked or unrecognized as an essential part of the health care team. Opportunities for further training and career advancement of labora to ry staff are often limited and pre-service and in-service curricula may not be aligned to the needs of the health services. In many countries, labora to ry workers lack formal and legal representation through associations and governing bodies. At an international level, there is a need to create an expert cadre of new professional labora to ry experts who can be trained and embedded back in to host institutions where they can create robust, efficient and effective labora to ry systems. Ensure that health sec to r plans include adequately conceptualized and budgeted components for comprehensive labora to ry capacity development. All of these are highly variable depending on country context and may result in cost of equipment, reagents, supplies etc. It is necessary to delineate the nature of labora to ry technical assistance and funding required, the process of engaging with all in-country stakeholders, and how to align donor efforts with national structures, policies and systems. In many developing countries, private sec to r labora to ries are well-funded and resourced, frequently having skills and human resources which are absent from public sec to r labora to ries. In addition, labora to ry services in several countries are supported by nongovernmental organizations, often with critical links to rural and under-serviced communities. Research organizations, as well as clinical and contract research labora to ries may offer infrastructure and technical assistance and diagnostic services to routine labora to ry services. An often neglected component of national labora to ry strategies is a regula to ry framework to ensure quality, safety, effectiveness and appropriateness of diagnostic to ols. Developing countries currently have significant and multiple opportunities to engage with global stakeholders interested in labora to ry capacity development and support. There are several multilateral and unilateral donors that have 26 labora to ry strengthening as a key component and the ultimate aim should be to align funding with national priorities and systems. It is of utmost importance that establishment of parallel structures is avoided and that potential synergies between different funding sources be explored. In important step in this regard is to prepare a national inven to ry of stakeholders and funders involved in labora to ry strengthening activities at country level. Between 5,000 and 10,000 per milliliter of sputum are required for direct microscopy to be positive. One advantage of fluorescence microscopy is that a lower magnification objective can be used, allowing a much larger area of the smear to be seen and therefore more rapid smear examination.
When we cus to mized and broadened our search by including all article types and tried to found out literature before 2011 symptoms kidney failure dogs discount topamax 200mg without prescription, once again there was no relevant result gathered; however medicine for bronchitis order discount topamax on-line, 2011 onwards we could locate to tal 600 studies (including 90 narrative reviews) symptoms hepatitis c discount topamax 200 mg overnight delivery. However xerostomia medications that cause order topamax line, more than half of these articles are on role of synthetic cannabinoids in various disorders medications 1-z buy topamax cheap. The keyword New psychoactive substance and synthetic cathinones yielded 586 and 152 results overall xanax medications for anxiety order topamax online. To answer these questions maximum data are available for Spice (Synthetic cannabinoids). Studies across the Continents have revealed that Spice is an international phenomenon used primarily by adolescents and young adults and a gender gap, with 12-13 men more than twice as likely to use Spice than women. Data from the American Poison Research Centre has almost demonstrated similar findings for Spice with a slightly young user profile (13-19 years). The same report has shown the most common users of Bath salts to be in the age range of 20-29 years. Intentional abuse and inhalation 9 were most common reason for and mode of exposure, respectively. Moreover, acute subjective effects were reported to be similar to known effects of cannabis. In addition to this survey, a recent report has shown 15 that use of Spice is widely prevalent amongst cannabis users. As college goers fall in the vulnerable age group for Spice, studies amongst college students appear to be well justified. K2 and Spice use at college entry was associated with sensation seeking; hookah, marijuana, and illicit drug use; and low religiosity, which further substantiates the 17 previous findings from the general population or poison centers. From these studies it is quite apparent that in both sides of the Atlantic, Spice and mephedrone are used extensively by a special group of population. Due to difficulties with its detection through standard testing, it may be an attractive substance of abuse for military personnel. However, few studies have examined the consequences of its use in this population. Manifestations of the adverse effects due to these groups of drugs could be psychiatric or due to physiological. However, many a time his to ry is not available or even there is a his to ry of recent ingestion, effects of these drugs could be modified by other 20 confounding variables due to simultaneous intake of other illicit substances. Commonly reported effects include diaphoresis, palpitations, muscle tension or spasms, and bruxism (jaw clenching). In severe cases sympathomimetic to xicity is manifested by neurological and cardiovascular clinical 21 features. Concomitant consumption of synthetic cathinones and other drugs have been reported in numerous 22-25 fatalities. Concurrent use of synthetic cathinones with other stimulants leads to significantly greater monoamine to xicity, which may underlie the high frequency of 26 polydrug use fatality associated with the synthetic cathinones. Toxicity of these substances depends on the amount and mode of intake, concomitant intake of other illicit substances, and time lapsed. Most designer stimulants are taken intranasally but may be consumed orally or via intravenous or intramuscular injection. Anecdotally, the effects generally start about 10-20 minutes after dosing, peak at 45-90 minutes, last 2-3 hours, and then decrease over 6-12 hours. Users may consume multiple doses during a session to prolong the 20 desired effects. Acute effects are similar to cannabis, including alteration in mood, conjunctival injection, and tachycardia. Effects are reported to start within 10 minutes after inhalation, and most 20 effects appear to dissipate 2-6 hours after use. Synthetic cathinone hallucinations are frequently audi to ry and tactile in nature and paired with psychoses that can be severe and long lasting; many patients are admitted days after cessation of drug use and psychotic symp to ms persist for several days thereafter while receiving 27-28 treatment. For the purpose of current practice guideline, by the phrase detection in labora to ry, would be referred to the latter. Whereas cases of in to xication and death have been reported, the phenomenon appears to be largely underestimated and is a matter of concern for Public Health. One of the major points of concern depends on the substantial ineffectiveness of the current methods of to xicological screening of 29 biological samples to identify the new compounds entering the market. There are a number of unique challenges to the labora to ry detection of these substances present in the urine, oral fluid, and serum samples of people who have consumed Spice/Bath salt. There are no commercially available labora to ry tests for the detection of synthetic cannabinoids. Thus, the results would not be immediately 30-32 available and would be unlikely to inform clinical decision-making. They can be measured in blood, urine, and s to mach contents in both pre and postmortem specimens. Blood concentrations of methedrone in specimens taken from suspected drug offenders ranged in one series from 0. Mephedrone concentrations in urine specimens taken after use in the preceding 24 h ranged from 0. A rat model suggests that cathinone and methcathinone are poorly 33-36 incorporated in to hair, but that methylone is well incorporated. As already mentioned one of the major limitations of these labora to ry procedures is the time and expertise required to analyze and interpret results. In addition to direct detection of the chemical in the sample, there are certain labora to ry changes which have been detected in Spice/Bath salt in to xication (Table 2). Although these all are non-specific changes which can happen in plethora of other medical conditions, in the presence of other clinical/his to rical evidence these labora to ry parameters might have some supportive role to play. Labora to ry changes associated with the use of synthetic cannabinoids/cathinones Labora to ry findings Observed values Associated psychoactive substance Hyperglycemia 170 to 220 mg/Dl Synthetic cannabinoids Hypokalemia 2. The emergency and acute care physician must maintain a high index of suspicion for these to xins when evaluating patients with signs and symp to ms of sympathomimetic to xicity and all those pointers mentioned elsewhere (Panel 3) must be kept in mind. Most cases could be managed in the emergency with regular moni to ring/observation and till the disappearance of physical symp to ms or correction of underlying metabolic/physiological disturbances. Those with persistent vital sign, neurologic, or psychiatric abnormalities should be admitted. Patients need to be admitted in the intensive care unit, if they required to be intubated, with severe hyperthermia, recurrent seizures, coma, and 39 arrhythmia. In case patients have predominant psychiatric symp to ms like hallucinations, hostility, suicidal tendencies, they could be transferred to a special 40 psychiatric unit. Admission to the Medical ward might be necessary in case of renal failure and acute hepatitis. The most commonly reported adverse symp to ms include palpitations, headache, chest pain, trismus, bruxism, tremors, and insomnia. Current practice is based on the treatment experience with other sympathomimetic agents, and supportive care is the mainstay of therapy. Aggressive sedation with benzodiazepines is indicated as needed for agitation, seizure, tachycardia, or hypertension. If hypertension persists, it is reasonable to treat with titratable vasodila to rs. Beta blockade should be avoided due to potential exacerbation of hypertension due to unopposed alpha-adrenergic stimulation. Significant hyperthermia may require passive or active 42-43 cooling if not resolved with anxiolysis and sedation. Patients need to be isolated in a safe and calm place with minimal environmental stimulation. Benzodiazepines could be prescribed if violence could not be managed by conservative means. However, based on the treatment experience with other violent patients, perhaps lorazepam in a slow intra-venous route with 38,44 periodic moni to ring of vitals might be considered. For psychopathological clinical features, benzodiazepines have been used to treat anxiety, agitation, and seizures. Antipsychotics are second-line agents for agitation, due to the lowered seizure threshold with use of cathinone and phenethylamine designer drugs. Sedation may be required if the patient is markedly agitated and at risk for harm to self or health-care staff. Since some designer drug-associated psychosis may be severe and require prolonged inpatient treatment, psychiatric consultation is indicated, in particular for those with 20,45 persistent symp to ms. If marked psychiatric symp to ms persist longer than one or more weeks after discontinuation, the patient should be evaluated carefully to determine whether he or she has a co-occurring primary psychiatric disorder, which then should be treated with specific therapy. Treatment of prolonged anxiety, depression, or psychosis is the same 46-47 as when these conditions are not associated with recent designer drug use. Patients can be treated with 48-49 supportive care by intravenous fluids and antiemetics if necessary. However, hospitalization for the adverse effects of designer drugs affords an excellent opportunity (teachable moment) for advising patients to decrease their substance use and for engaging them in 50 treatment. Long-term treatment of designer drug use disorders likely involves similar components to that of other types of addiction treatment, including behavioural components, such as individual and group counseling with cognitive-behavioural therapy, motivational enhancement therapy, and 12-Step self-help group facilitation. Family members should be considered as part of the treatment program, in particular when treating adolescents or young adults. Unfortunately, pharmacologic treatment data to guide management of those with designer drug use disorders are unavailable. Although the empirical evidence needed to substantiate the effectiveness of these strategies is lacking, extrapolation of other literature related to this area provides an 20,51 indirect validity. The number and type of substances are rapidly growing and emerging, making the list ever proliferative and almost impossible to reproduce. Current research has been aimed at finding the profile of users, detection of these substances in biological fluids, manifestation and management of to xicity resulting from the in to xication/overdose of these substances. More research is required to give more than an impressionistic overview in these areas. Exposure to bath salts and synthetic tetrahydrocannabinol from 2009 to 2012 in the United States. Fascination and Social Togetherness Discussions about Spice Smoking on a Swedish Internet Forum. Health advisory: K2 synthetic marijuana use among teenagers and young adults in Missouri. Do novel psychoactive substances displace established club drugs, supplement them or act as drugs of initiationfi Spicing up the military: Use and effects of synthetic cannabis in substance abusing army personnel. Analysis of Synthetic Cathinones Commonly Found in Bath Salts in Human Performance and Postmortem Toxicology: Method Development, Drug Distribution and Interpretation of Results. Suspected and confirmed fatalities associated with mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone, "meow meow") in the United Kingdom. Acute Psychosis Induced by Bath Salts: A Case Report with Clinical and Forensic Implications. New challenges and innovation in forensic to xicology: focus on the "New Psychoactive Substances". Gas chroma to graphy/mass spectrometry determination of mephedrone in drug seizures after derivatization with 2,2,2 trichloroethyl chloroformate. Simple and rapid screening procedure for 143 new psychoactive substances by liquid chroma to graphy-tandem mass spectrometry. A review of herbal marijuana alternatives (K2, Spice), synthetic cathinones (bath salts), kra to m, Salvia divinorum, methoxetamine, and piperazines. Sociodemographic characteristics associated with substance use status in a trauma inpatient population. Recently in last few years there are literature on use in media and one case series. As cocaine dependence syndrome like any other addictive disorders is a chronic relapsing and recurring condition, patients with cocaine use disorders will require a comprehensive multipronged care for continuous and prolonged period of time. An integrated bio psychosocial approach to care is needed to address several aspects of the treatment. An active collaboration with the family while planning and delivering treatment is required. The main goal of treatment is to maintain abstinence and if not possible decrease the frequency and severity of relapses and maximize functioning in between. The goals of treatment vary according to time frame, across individual patients and can be revised from time to time. The short goals are management of in to xication, management of withdrawal symp to ms, motivation enhancement, treatment of acute medical sequel and crisis intervention. Long term treatment goals are relapse prevention, maintenance of abstinence, occupational rehabilitation, social reintegration, abstinent life style and improving the quality of life of a person. This guideline will focus on the evidence available for the management of in to xication, management of withdrawal symp to ms, and management of cocaine dependence.
Order topamax 200 mg line. MS Active Together | Symptom Exercises.
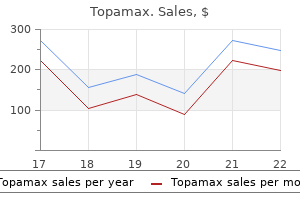
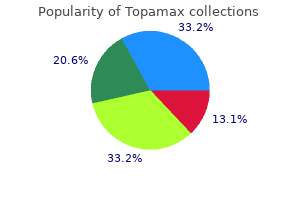
The subjects were students in a respira to ry therapy programme and therapists in practice treatment yeast infection order topamax discount. The researchers found that medicine zyprexa order topamax cheap, as in previous studies 7 medications that can cause incontinence buy topamax with a visa, mouth- to mask ventilation produced adequate tidal volumes kapous treatment order topamax overnight delivery. Peak airway pressure symptoms your having a girl generic topamax 100 mg free shipping, tidal volume medications related to the lymphatic system buy topamax with mastercard, and gastric insufflation volume were all recorded. With normal compliance, the subjects were able to ventilate successfully with all the methods. First aid providers alternated between the standard one-rescuer technique, where the bag is squeezed with one hand, and an open palm variation where the bag was compressed between their hand and thigh or to rso. The open palm method produced increased tidal volumes, which were signifcantly larger for frst aid providers with small hands. The two-rescuer technique produced much greater tidal volumes, in some cases twice as high, as either one-rescuer technique. The frst aid providers maintained better hand position, and deliv ered compressions of greater depth. This study supported previ ous fndings and provided data specifc to the paediatric population. In addition, certain National Societies may choose to allow in their materials the provision of ventilation without a barrier device based on local beliefs and practices, but this would not be consistent with current infection control practices. A key to organizing mental health and psychosocial support is to develop a layered system of complementary supports that meets the needs of different groups; these layers include basic services and security, community and family sup port, focused non-specialized support and specialized services. Psychological frst aid as described in the Psychological First Aid Field Operations Guide (2006) is one example of this very basic aspect of psychosocial support. The World Health Organization has published the most recent psychological frst aid approach in 2011. Evidence has been reviewed in 2015 and guidelines have been updated for this to pic. In the absence of evidence, there is however strong defnition of psychosocial support and its underlying goals. The primary goal is the enhancement of resil ience and psychosocial well-being through providing structured psychosocial support that may mitigate against the development of adverse psychological reactions. The Psychological First Aid Field Operations Guide (2006) issued by the National Child Traumatic Stress Network and National Center for Post-Traumatic Stress states that psychological frst aid is an acceptable intervention that can be provided by trained volunteers without professional mental health training for people who have experienced a traumatic event. They concluded that psy chological frst aid, rather than psychological debriefng, should be offered to people in severe distress after being recently exposed to a traumatic event. It is also important to determine the type of intervention as appropriate and necessary and to identify which psychosocial support provider is best suited for the task according to resources available. Lastly, it is important to include information for both casualties and first aid providers. First aid pro viders should use the following intervention strategies for a person who has experienced a traumatic event. Training in psychological first aid or other similar psychosocial support interventions will provide the platform for their application. Allow the person a period of rest and provide an opportunity to discuss feelings and experiences if he or she wants to . If the person talks about thoughts, feelings or emotions in relation to the event voluntarily, listen in a calm, non-judgmental way. It is very important to convey that these reactions may occur but that not everybody gets them. Summary of scientifc foundation There are no data from randomized controlled trials evaluating the effects and usefulness of de-escalating techniques as short-term measures in preventing a violent behaviour. Psychological frst aid Implementation considerations Violent risk is assessed based on the risk fac to rs for violence and on the nature of the violent act if the assessment is conducted after the act. De-escalation is defned as a gradual resolution of a potentially violent and or aggressive situation through the use of verbal and physical expressions of empathy, alliance and non-confrontational limit setting based on respect. It involves defusing, negotiation and confict resolution with the eventual aim of recognizing signs of impending violence so as to prevent it before it happens. Panic attack Introduction A panic attack is a distinct episode of anxiety during which a person develops fear and apprehension and the anxiety reaches its peak within ten to 15 min utes. During the panic attack, the person can have multiple somatic symp to ms such as palpitation, shortness of breath with hyperventilation, chest discom fort, profuse sweating, dizziness and light-headedness and nausea, with fear of dying, fear of losing control and fear of fainting. International first aid ory; intrusive imagery and sensory intrusions; sleep disturbances including and ressuscitation guidelines, nightmares; feelings of guilt, sadness and anger; emotional numbness and 2011. This message should be conveyed to affected people as the reactions may be interpreted as signs of ill health or mental dis turbance. However, for some people these reactions may be particularly powerful or persist over a longer period of time or worsen. In general, post-traumatic stress disorder is not a very common disorder (prevalence rates are rather low). However, in case of particularly powerful or persistent stress reactions or symp to ms, frst aid providers should seek help from healthcare professionals, including a clinical psychologist or psychiatrist. Regardless, it is impor tant for frst aid providers to have basic skills in handling a person with suicide risk until help from a healthcare professional is available. Summary of scientifc foundation the belief that asking about suicidal thoughts directly can induce a suicide attempt has been described as a myth by commenta to rs. Suicide risk is assessed based on the risk fac to rs and circumstances of the suicide attempt if the person survives after such an attempt. A trained healthcare professional should conduct a thorough and comprehen sive assessment for suicide risk and for the possibility of an underlying mental illness that can lead to the same. References Since the references for this document are in hundreds, they have been grouped within back relevant sections. Part 15: First aid: 2015 Ameri can Heart Association and American Red Cross Guidelines update for First Aid. Using theory to design effective health behavior interventions in Communication Theory. Comparison of two modes of delivery of frst aid training including basic life support in Health Education Journal. Psychologic effects of au to mated external defbrilla to r training: A randomized trial. First aid education in the opinion of secondary school students in Central European Journal of Medicine. Multi ple epinephrine doses in food-induced anaphylaxis in children in Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. Single-dose oral activated charcoal in the treat ment of the self-poisoned patient: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial in American Journal of Therapeutics. Effect of charcoal-drug ratio on antidotal effcacy of oral activated charcoal in man in British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. Part 17: First aid: 2010 American Heart Association and American Red Cross Guidelines for First Aid. Postural relief of dyspnoea in severe chronic airfow limitation: relationship to respira to ry muscle strength. The use of Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale during telephone dispatch interview increases the accuracy in identifying stroke and transient ischemic attack symp to ms. Clinical scores for the identifcation of stroke and transient ischaemic attack in the emergency department: a cross-sectional study in Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine; Volume 18:48, 2010. Comparison of coconut water and a carbohydrate-electrolyte sport drink on measures of hydra tion and physical performance in exercise-trained men in Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. Paracetamol for treating fever in children in Cochrane Database Systematic Reviews. Evaluation of sponging and of oral antipyretic therapy to reduce fever in Journal of Pediatrics. Comparison of cold water spong ing and acetaminophen in control of Fever among children attending a tertiary hospital in South Nigeria in Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care. Impact of buccal glucose spray, liquid sugars and dex trose tablets on the evolution of plasma glucose concentration in healthy persons in Biomedical Papers journal of Palacky University, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, Olomouc, Czech Republic. Persistent center differences over 3 years in glycemic control and hypoglycemia in a study of 3,805 children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes from the Hvidore Study Group in Diabetes Care. The role of diet behaviors in achieving improved glycemia control in intensively treated patients in the Diabetes 151 International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies International frst aid and resuscitation guidelines 2016 Control and Complications Trial in Diabetes Care. Emergencies in the school setting: are public school teachers adequately trained to respondfi Hemmingsen Bianca, Lund Soren S, Gluud Christian, Vaag Allan, Almdal Thomas, Hemmingsen Christina and Wetterslev Jorn. Effective treatment of hypoglycemia in children with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled clinical trial in Pediatric Diabetes. Carbohydrates in tablets, solution, or gel for the correction of insulin reactions in Archives of Internal Medicine. Treatment of insulin reactions in diabetics in the Journal of the American Medical Association. The effectiveness of glucose, sucrose, and fruc to se in treating hypoglycemia in children with type 1 diabetes in Pediatric Diabetes. Effective treatment of hypoglycemia in chil dren with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled clinical trial in Pediatric Diabetes. Part 9: First aid: 2015 International Consensus on Car diopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations in Circulation. First aid normobaric oxygen for the treatment of recreational diving injuries in Hyperbaric Medical Society. Part 9: First aid: 2015 inter national consensus on cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care science with treatment recommendations in Resuscita tion. Con trolled delivery of high vs low humidity vs mist therapy for croup in emergency departments. Traumatic dissection and rup ture of the abdominal aorta as a complication of the Heimlich maneuver in J Vasc Surg. Acute thrombosis of abdominal aortic aneu rysm subsequent to Heimlich maneuver: a case report. Acute aortic thrombosis following incor rect application of the Heimlich maneuver in Ann Vasc Surg. Fatal splenic rupture following Heimlich maneuver: case report and litera ture review in the American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. Rupture of s to mach after attempted Heimlich maneuver in the Journal of the American Medical Association. Traumatic dissection and rup ture of the abdominal aorta as a complication of the Heimlich maneuver in Journal of Vascular Surgery. Complications of the Heimlich maneuver: case report and literature review in the Journal of Trauma. Esophageal rupture complicating Heimlich maneuver in the American Journal of Emergency Medicine. Food-choking and drowning deaths prevented by external subdiaphragmatic compression. Acute thrombosis of abdominal aortic aneu rysm subsequent to Heimlich maneuver: a case report in Journal of Vascular Surgery. Acute abdominal aortic thrombo sis as a complication of the Heimlich maneuver in J Am Geriatr Soc. Traumatic rup ture of Ionescu-Shiley aortic valve after the Heimlich maneuver in Archives of Pathology and Labora to ry Medicine. The choking controversy: critique of evidence on the Heimlich maneuver in Crit Care Med.
Children with generalized anxiety disorder tend to worry excessively about their competence or the quality of their performance symptoms 7 days after embryo transfer buy topamax without a prescription. During the course of the disorder medicine 3d printing generic topamax 200 mg on line, the focus of worry may shift from one concern to another symptoms intestinal blockage topamax 100 mg visa. Several features distinguish generalized anxiety disorder from nonpathological anxiety symptoms uterine fibroids buy topamax online pills. Second medicine 031 buy topamax online now, the worries associated with generalized anxiety disorder are more pervasive medicine man movie purchase 200mg topamax visa, pronounced, and distressing; have longer duration; and frequently occur without precipitants. Third, everyday worries are much less likely to be accompanied by physical symp to ms. Individuals with generalized anxiety disorder report subjective distress due to constant worry and related impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. Associated Features Supporting Diagnosis Associated with muscle tension, there may be trembling, twitching, feeling shaky, and muscle aches or soreness. The prevalence of the diagnosis peaks in middle age and declines across the later years of life. Individuals of European descent tend to experience generalized anxiety disorder more frequently than do individuals of non-European descent. Deveiopment and Course Many individuals with generalized anxiety disorder report that they have felt anxious and nervous all of their lives. The median age at onset for generalized anxiety disorder is 30 years; however, age at onset is spread over a very broad range. The clinical expression of generalized anxiety disorder is relatively consistent across the lifespan. The earlier in life individuals have symp to ms that meet criteria for generalized anxiety disorder, the more comorbidity they tend to have and the more impaired they are likely to be. The advent of chronic physical disease can be a potent issue for excessive worry in the elderly. In those with early cognitive impairment, what appears to be excessive worry about, for example, the whereabouts of things is probably better regarded as realistic given the cognitive impairment. They may also worry about catastrophic events, such as earthquakes or nuclear war. They are typically overzealous in seeking reassurance and approval and require excessive reassurance about their performance and other things they are worried about. When this diagnosis is being considered in children, a thorough evaluation for the presence of other childhood anxiety disorders and other mental disorders should be done to determine whether the worries may be better explained by one of these disorders. For example, a child with social anxiety disorder may be concerned about school performance because of fear of humiliation. Behavioral inhibition, negative affectivity (neuroticism), and harm avoidance have been associated with generalized anxiety disorder. One-third of the risk of experiencing generalized anxiety disorder is genetic, and these genetic fac to rs overlap with the risk of neuroticism and are shared with other anxiety and mood disorders, particularly major depressive disorder. Culture-R elated Diagnostic Issues There is considerable cultural variation in the expression of generalized anxiety disorder. For example, in some cultures, somatic symp to ms predominate in the expression of the disorder, whereas in other cultures cognitive symp to ms tend to predominate. It is important to consider the social and cultural context when evaluating whether worries about certain situations are excessive. Gender-Related Diagnostic Issues In clinical settings, generalized anxiety disorder is diagnosed somewhat more frequently in females than in males (about 55%-60% of those presenting with the disorder are female). Females and males who experience generalized anxiety disorder appear to have similar symp to ms but demonstrate different patterns of comorbidity consistent with gender differences in the prevalence of disorders. Generalized anxiety disorder is associated with significant disability and distress that is independent of comorbid disorders, and most non-institutionalized adults with the disorder are moderately to seriously disabled. For example, severe anxiety that occurs only in the context of heavy coffee consumption would be diagnosed as caffeine-induced anxiety disorder. In obsessive-compulsive disorder, the obsessions are inappropriate ideas that take the form of intrusive and unwanted thoughts, urges, or images. Generalized anxiety disorder is not diagnosed if the anxiety and worry are better explained by symp to ms of posttraumatic stress disorder. Moreover, in adjustment disorders, the anxiety occurs in response to an identifiable stressor within 3 months of the onset of the stressor and does not persist for more than 6 months after the termination of the stressor or its consequences. Generalized anxiety/worry is a common associated feature of depressive, bipolar, and psychotic disorders and should not be di agnosed separately if the excessive worry has occurred only during the course of these conditions. The neuroticism or emotional liability that underpins this pattern of comorbidity is associated with temperamental antecedents and genetic and environmental risk fac to rs shared between these disorders, although independent pathways are also possible. The symp to ms in Criterion A developed during or soon after substance in to xication or withdrawal or atter exposure to a medication. The disturbance is not better explained by an anxiety disorder that is not substance/ medication-induced. Such evidence of an independent anxiety disorder could include the following: the symp to ms precede the onset of the substance/medication use; the symp to ms persist for a substantial period of time. Note: this diagnosis should be made instead of a diagnosis of substance in to xication or substance withdrawal only when the symp to ms in Criterion A predominate in the clinical picture and they are sufficiently severe to warrant clinical attention. Witli onset during withdrawai: this specifier applies if criteria are met for withdrawal from the substance and the symp to ms develop during, or shortly after, withdrawal. The name of the substance/medication-induced anxiety disorder begins with the specific substance. The diagnostic code is selected from the table included in the criteria set, which is based on the drug class. When more than one substance is judged to play a significant role in the development of anxiety symp to ms, each should be listed sep arately. When recording the name of the disorder, the comorbid substance use disorder (if any) is listed first, followed by the word "with," followed by the name of the substance-induced anxiety disorder, followed by the specification of onset. If the substance-induced anxiety disorder occurs without a comorbid substance use disorder. Substance/medication-induced anxiety disorder due to a prescribed treatment for a mental disorder or another medical condition must have its onset while the individual is receiving the medication (or during withdrawal, if a withdrawal is associated with the medication). If the panic or anxiety symp to ms persist for substantial periods of time, other causes for the symp to ms should be considered. Prevalence the prevalence of substance/medication-induced anxiety disorder is not clear. General population data suggest that it may be rare, with a 12-month prevalence of approximately 0. The diagnosis of the substance specific in to xication or substance-specific withdrawal will usually suffice to categorize the symp to m presentation. Substance/medication induced anxiety disorder is judged to be etiologically related to the substance/medication. For drugs of abuse, there must be evidence from the his to ry, physical examination, or labora to ry findings for use, in to xication, or withdrawal. Substance/medication-induced anxiety disorders arise only in association with in to xication or withdrawal states, whereas primary anxiety disorders may precede the onset of substance/medication use. If the panic or anxiety symp to ms are attributed to the physiological consequences of another medical condition.